
According to the laws of Boolean algebra, the expression (A+AB) is equal to,
$\left( a \right)A$
$\left( b \right)AB$
$\left( c \right)B$
$\left( d \right)\bar A$
Answer
520.5k+ views
Hint – In this question consider the basics of the truth table of OR, AND and NOT gate for basic inputs of, 1. In general 4 basic cases will arise that is 0 operation 1, 0 operation 0, 1 operation 0 and 1 operation 1. Then try and create the same truth table considering the cases for the given Boolean expression that is $\left( {A + AB} \right)$. Compare the results obtained with the basic gates, this will help getting the right answer.
Complete answer:
As we know in Boolean algebra if we don’t know the inputs then we cannot calculate the output of any equation when it is a simple sum or subtraction equation.
For example: If A and B are the two inputs of a logic function in Boolean algebra then without knowing the value of the inputs we cannot calculate the output of the logic function.
If output is in simple form say A + B.
I.e. it is an OR output in OR the two variables are simply added.
Output can be anything depending upon the logic circuit, it may be simple, simple complex or very complex.
But if we know the input we will know how the output will behave as follows:.
If A = B = 1, then A + B = 1 + 1 = 1
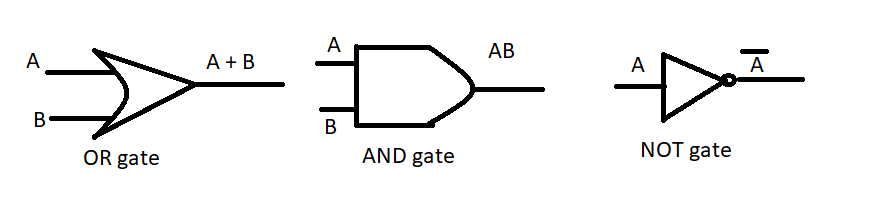
In Boolean algebra the rules are as follows,
OR rule
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 0 =1
1 + 1 =1
AND rule
0.0 = 0
0.1 = 0
1.0 = 0
1.1 = 1
NOT rule
$\bar 0 = 1$
$\bar 1 = 0$
Now if we add one (1) in any variable it will behave as 1.
I.e. 1 + x = 1.
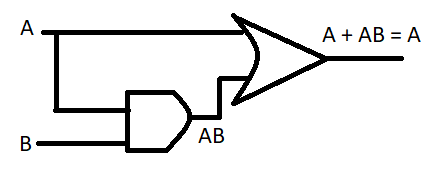
Now the given expression is
(A + AB)
Now take A common we have,
$ \Rightarrow A\left( {1 + B} \right)$
Now from above rule discussed (1 + B) = 1 so we have,
$ \Rightarrow A\left( 1 \right)$
Now in the multiplication rule if we multiply any variable with 1 it will give us the same variable and if we multiply any variable with 0 it will give us simply 0.
$ \Rightarrow A\left( 1 \right) = A$
So this is the required simplified expression of the given expression.
Hence option (a) is the correct answer.
Note – The gates are very important in terms of electronic circuits or even in power systems as they can be used to control the circuit as they take very less time in comparison to odd switches to turn off and on. NAND gate is a basic gate formed by the combination of the NOT gate and the AND gate.
Complete answer:


As we know in Boolean algebra if we don’t know the inputs then we cannot calculate the output of any equation when it is a simple sum or subtraction equation.
For example: If A and B are the two inputs of a logic function in Boolean algebra then without knowing the value of the inputs we cannot calculate the output of the logic function.
If output is in simple form say A + B.
I.e. it is an OR output in OR the two variables are simply added.
Output can be anything depending upon the logic circuit, it may be simple, simple complex or very complex.
But if we know the input we will know how the output will behave as follows:.
If A = B = 1, then A + B = 1 + 1 = 1
In Boolean algebra the rules are as follows,
OR rule
0 + 0 = 0
0 + 1 = 1
1 + 0 =1
1 + 1 =1
AND rule
0.0 = 0
0.1 = 0
1.0 = 0
1.1 = 1
NOT rule
$\bar 0 = 1$
$\bar 1 = 0$
Now if we add one (1) in any variable it will behave as 1.
I.e. 1 + x = 1.
Now the given expression is
(A + AB)
Now take A common we have,
$ \Rightarrow A\left( {1 + B} \right)$
Now from above rule discussed (1 + B) = 1 so we have,
$ \Rightarrow A\left( 1 \right)$
Now in the multiplication rule if we multiply any variable with 1 it will give us the same variable and if we multiply any variable with 0 it will give us simply 0.
$ \Rightarrow A\left( 1 \right) = A$
So this is the required simplified expression of the given expression.
Hence option (a) is the correct answer.
Note – The gates are very important in terms of electronic circuits or even in power systems as they can be used to control the circuit as they take very less time in comparison to odd switches to turn off and on. NAND gate is a basic gate formed by the combination of the NOT gate and the AND gate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




