
According to the Boyle’s law $PV$ is equal to:
A.Temperature
B.Constant
C.$nRT$
D.$\dfrac{w}{MRT}$
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint:In Boyle’s law, the number of moles and temperature is constant and fixed. This is a gas law in which these variables like $P,V,T$ are related to one another. Boyle's law gives a relationship between pressure and volume.
Complete step by step answer:
-Before talking about the question, you should know about Boyle's law. It states that for a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature, the volume occupied by the gas is inversely proportional to the pressure applied to it.
$V\propto \dfrac{1}{P}$
$P\times V=K$
Where, $K$ is constant
$P$ denotes the pressure of the system
$V$ denotes the volume of the gas
-As long as the temperature is constant , the amount of energy that is given to the system persists throughout its operation.
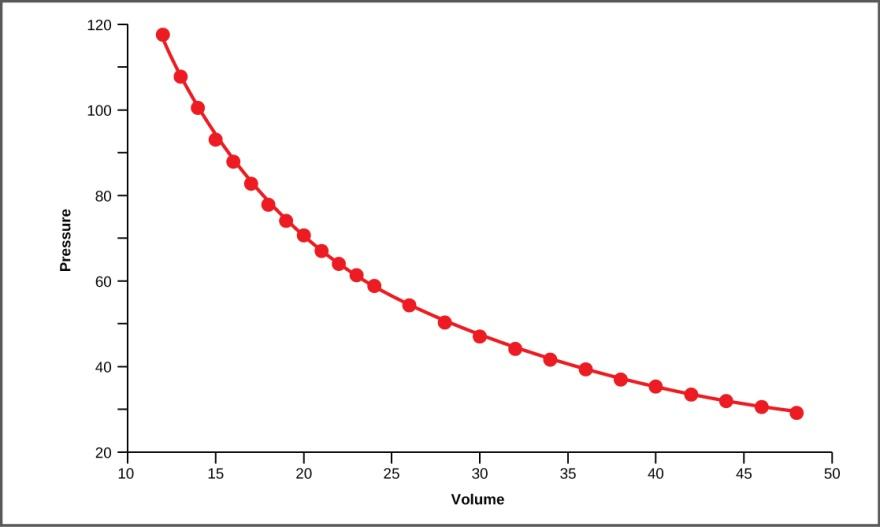
Graph between $P$ and $V$ at constant $T$
Comparing the substances under same set two different conditions , this law can also be expressed as:
${{P}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}$
This equation states that as the amount of volume increases there will be a decrease in the pressure of gas.
Therefore, the correct option is $\left( B \right)$.
Additional Information:
Gas is defined as the collection of free particles which collide with each other and moves randomly in motion. There are two types of gases that exist :
Ideal gas is defined as the gas that obeys all law under all conditions of temperature and pressure. The volume of the gas is equal to the volume of the container. There is no intermolecular attraction force.
Real gas is defined as the gas that obeys laws under low pressure and high temperature. The volume of the gas is not equal to the volume of the container. There is an intermolecular force of attraction.
Pressure is defined as the force that is exerted by the gaseous molecules due to the collision of particles on the walls of the container or collision with each other. Pressure can be calculated in $bar,atm,N/{{m}^{2}}$
Note:
The graph plotted between $P$ v/s $V$ is known as isotherm because the temperature is constant.
The graph formed is hyperbola.
If for example the volume of the gas gets doubled when the pressure is halved.
Complete step by step answer:
-Before talking about the question, you should know about Boyle's law. It states that for a fixed amount of gas at constant temperature, the volume occupied by the gas is inversely proportional to the pressure applied to it.
$V\propto \dfrac{1}{P}$
$P\times V=K$
Where, $K$ is constant
$P$ denotes the pressure of the system
$V$ denotes the volume of the gas
-As long as the temperature is constant , the amount of energy that is given to the system persists throughout its operation.

Graph between $P$ and $V$ at constant $T$
Comparing the substances under same set two different conditions , this law can also be expressed as:
${{P}_{1}}{{V}_{1}}={{P}_{2}}{{V}_{2}}$
This equation states that as the amount of volume increases there will be a decrease in the pressure of gas.
Therefore, the correct option is $\left( B \right)$.
Additional Information:
Gas is defined as the collection of free particles which collide with each other and moves randomly in motion. There are two types of gases that exist :
Ideal gas is defined as the gas that obeys all law under all conditions of temperature and pressure. The volume of the gas is equal to the volume of the container. There is no intermolecular attraction force.
Real gas is defined as the gas that obeys laws under low pressure and high temperature. The volume of the gas is not equal to the volume of the container. There is an intermolecular force of attraction.
Pressure is defined as the force that is exerted by the gaseous molecules due to the collision of particles on the walls of the container or collision with each other. Pressure can be calculated in $bar,atm,N/{{m}^{2}}$
Note:
The graph plotted between $P$ v/s $V$ is known as isotherm because the temperature is constant.
The graph formed is hyperbola.
If for example the volume of the gas gets doubled when the pressure is halved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




