
Accomplish the following conversions:
Aniline to benzyl alcohol
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the various reactions and reagents in organic chemistry. An Aniline group can be substituted easily to prepare a large variety of compounds by preparing its diazonium salt.
Complete step by step solution:
Diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds that contain the functional group
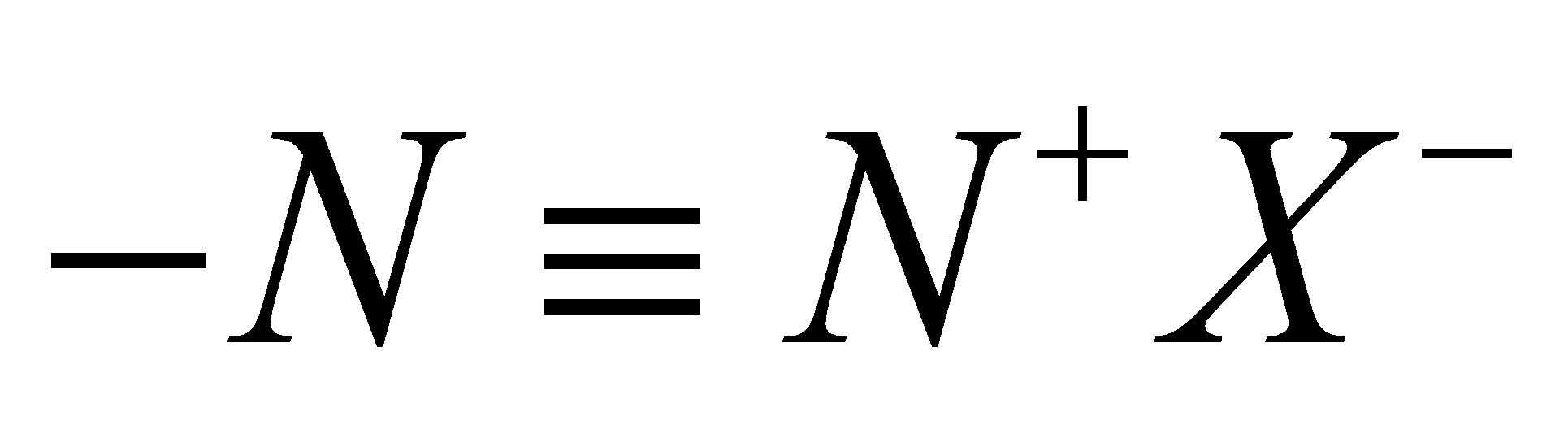 . The nitrogen group is covalently bonded to an organic compound, may be either an alkyl or aryl group and the X denotes an organic or inorganic anion, commonly halide ions are used. It is not a very stable group and thus is very reactive. It can be easily substituted by a number of nucleophiles producing nitrogen gas as a side- product.
. The nitrogen group is covalently bonded to an organic compound, may be either an alkyl or aryl group and the X denotes an organic or inorganic anion, commonly halide ions are used. It is not a very stable group and thus is very reactive. It can be easily substituted by a number of nucleophiles producing nitrogen gas as a side- product.
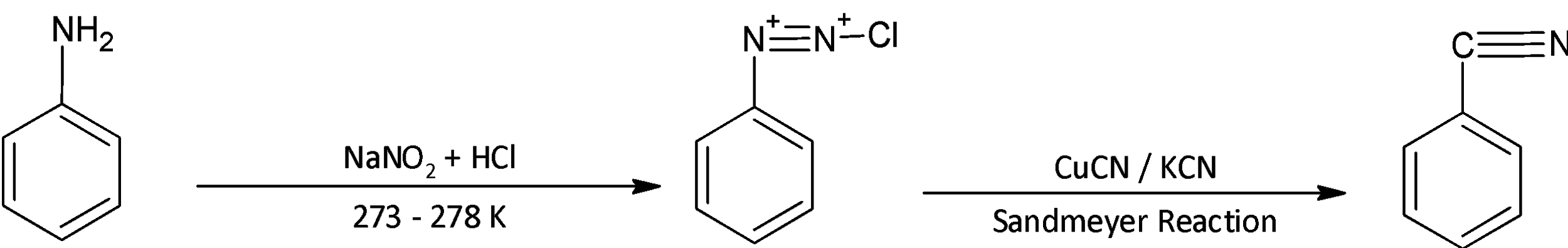
Here, we convert aniline to benzene diazonium chloride. It is a salt of the diazonium cation and chloride anion. It is formed from aniline by treating it with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures of around 273- 278 Kelvin. The attacking species is $ {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} $ and it is formed in- situ due to its high reactivity.
After the benzene diazonium chloride is formed, we substitute the diazo group with a cyanide group in order to increase the number of carbon atoms. For this we use the Sandmeyer reaction treating the diazonium salt with potassium chloride in presence of copper cyanide. We obtain benzonitrile.
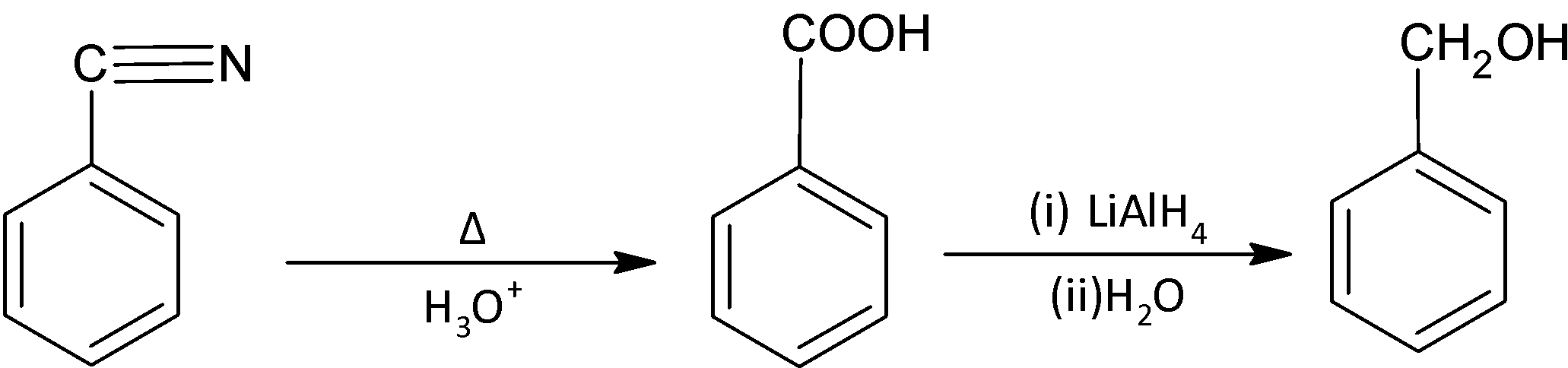
Now we have to remove the nitrogen atom and for that we hydrolyze benzonitrile to produce benzoic acid. Benzoic acid can then be reduced easily to obtain benzyl alcohol.
Note:
It should be noted that the reactions involving diazonium salt must be carried out at a temperature less than $ 278{\text{ K}} $ above which it becomes unstable and dissociates.
Complete step by step solution:
Diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds that contain the functional group
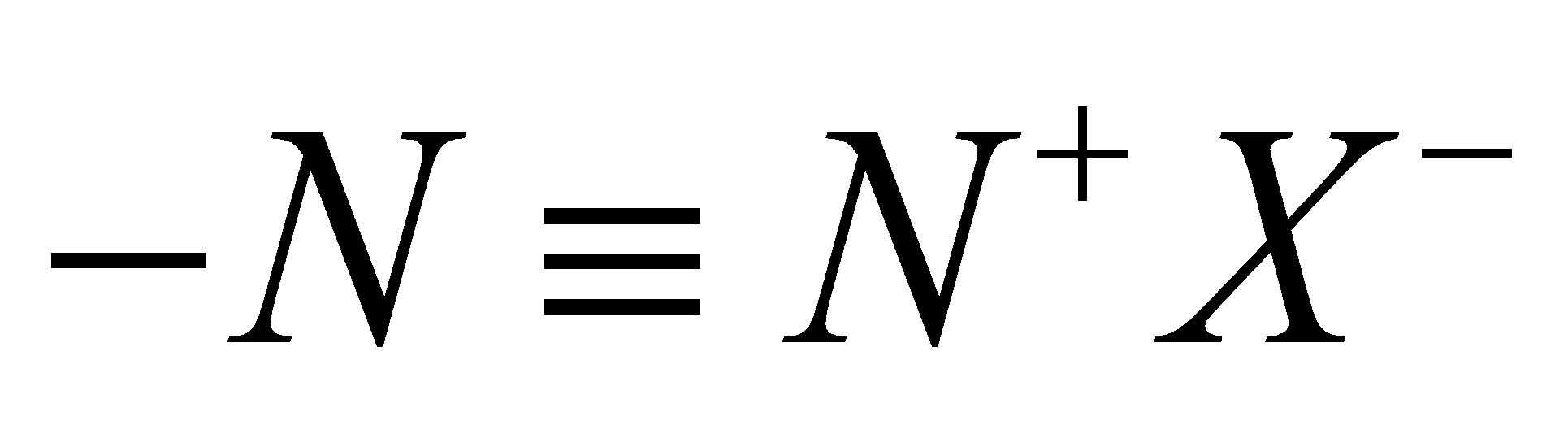
Here, we convert aniline to benzene diazonium chloride. It is a salt of the diazonium cation and chloride anion. It is formed from aniline by treating it with sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid at low temperatures of around 273- 278 Kelvin. The attacking species is $ {\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}} $ and it is formed in- situ due to its high reactivity.
After the benzene diazonium chloride is formed, we substitute the diazo group with a cyanide group in order to increase the number of carbon atoms. For this we use the Sandmeyer reaction treating the diazonium salt with potassium chloride in presence of copper cyanide. We obtain benzonitrile.
Now we have to remove the nitrogen atom and for that we hydrolyze benzonitrile to produce benzoic acid. Benzoic acid can then be reduced easily to obtain benzyl alcohol.


Note:
It should be noted that the reactions involving diazonium salt must be carried out at a temperature less than $ 278{\text{ K}} $ above which it becomes unstable and dissociates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




