
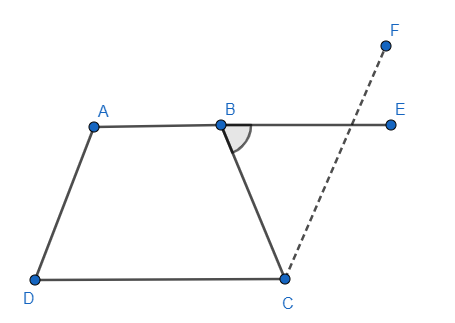
ABCD is a trapezium in which $AB||CD$ and $AD=BC$. Show that
A. $\angle A=\angle B$
B. $\angle C=\angle D$
C. $\Delta ABC=\Delta BAD$
D. diagonal AC equal to diagonal BD

Answer
511.8k+ views
Hint: We use the concept of exterior angles and parallel sides to find relations between the angles. We draw the parallel to the line DA which cuts the extended AB at G. we show that $AGCD$ is a parallelogram. We also use that the sum of the consecutive angles of a parallelogram is equal to $\pi $.
Complete answer:
We draw a line from point C parallel to the line DA which cuts the extended AB at G. We also join points A with C and B with D.
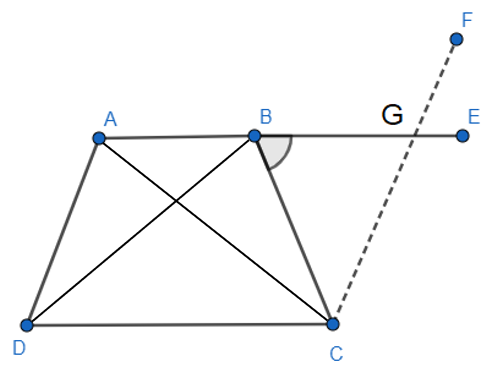
Now for $AGCD$, we have $AG||DC$ as $AB||CD$ and $AD||GC$. So, $AGCD$ is a parallelogram. We get $AD=GC$ and $\angle DAB=\angle EGC$.
For $\Delta BGC$, $BC=GC$ as $BC=AD=GC$. This gives $\angle GBC=\angle BGC$.
We find the exterior angles of $\angle GBC$ and $\angle BGC$. They are $\angle ABC$ and $\angle EGC$ respectively.
As $\angle GBC=\angle BGC$, we get $\angle ABC=\angle EGC$.
We have $\angle DAB=\angle EGC$ which gives \[\angle DAB=\angle EGC=\angle ABC\]. So, $\angle A=\angle B$.
We have that \[\angle DAB=\angle ABC\]. This gives \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle GBC\].
As $AB||CD$ and BC are transverse lines, we get \[\angle BCD=\angle GBC\]. So, \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle BCD\].
As $AGCD$ is a parallelogram, we can say \[\angle DAB+\angle CDA=\pi \] which gives \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle CDA\].
Therefore, \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle BCD=\pi -\angle CDA\]. This gives \[\angle BCD=\angle CDA\]. So, $\angle C=\angle D$.
Now we take the $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta BAD$. We get
(i) $BC=AD$
(ii) \[\angle ABC=\angle DAB\]
(iii) AB is the common side
Therefore, \[\Delta ABC\cong \Delta BAD\]. We use the SAS congruence theorem.
The congruency of the triangles gives $AC=BD$ as they are corresponding sides of triangles.
Note:
For SAS congruence we need to be careful about the angle being exactly in between two sides. Any angle other than cannot be taken for SAS congruence. Also, the consecutive sides and angles theorem can only be applied for parallelograms. It is not applicable for trapezium.
Complete answer:
We draw a line from point C parallel to the line DA which cuts the extended AB at G. We also join points A with C and B with D.

Now for $AGCD$, we have $AG||DC$ as $AB||CD$ and $AD||GC$. So, $AGCD$ is a parallelogram. We get $AD=GC$ and $\angle DAB=\angle EGC$.
For $\Delta BGC$, $BC=GC$ as $BC=AD=GC$. This gives $\angle GBC=\angle BGC$.
We find the exterior angles of $\angle GBC$ and $\angle BGC$. They are $\angle ABC$ and $\angle EGC$ respectively.
As $\angle GBC=\angle BGC$, we get $\angle ABC=\angle EGC$.
We have $\angle DAB=\angle EGC$ which gives \[\angle DAB=\angle EGC=\angle ABC\]. So, $\angle A=\angle B$.
We have that \[\angle DAB=\angle ABC\]. This gives \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle GBC\].
As $AB||CD$ and BC are transverse lines, we get \[\angle BCD=\angle GBC\]. So, \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle BCD\].
As $AGCD$ is a parallelogram, we can say \[\angle DAB+\angle CDA=\pi \] which gives \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle CDA\].
Therefore, \[\angle DAB=\pi -\angle BCD=\pi -\angle CDA\]. This gives \[\angle BCD=\angle CDA\]. So, $\angle C=\angle D$.
Now we take the $\Delta ABC$ and $\Delta BAD$. We get
(i) $BC=AD$
(ii) \[\angle ABC=\angle DAB\]
(iii) AB is the common side
Therefore, \[\Delta ABC\cong \Delta BAD\]. We use the SAS congruence theorem.
The congruency of the triangles gives $AC=BD$ as they are corresponding sides of triangles.
Note:
For SAS congruence we need to be careful about the angle being exactly in between two sides. Any angle other than cannot be taken for SAS congruence. Also, the consecutive sides and angles theorem can only be applied for parallelograms. It is not applicable for trapezium.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




