
ABCD is a trapezium having $AB||DC$ . Prove that O, the point of intersection of diagonals, divides the two diagonals in the same ratio. Also prove that
$\dfrac{ar\left( \Delta OCD \right)}{ar\left( \Delta OAB \right)}=\dfrac{1}{9}$ , if AB = 3 CD.
Answer
583.8k+ views
Hint: First prove that the triangles formed by diagonals of a trapezium are congruent, by this we can say that corresponding sides are in proportion. If you write an equation of proportion then you get the required condition on the ratio. Now substitute the formula of areas of triangle in the ratio. Then you get the value in terms of product of 2 ratios. Now use the congruence properties and turn this product of 2 ratios into square of one ratio, by using the given condition find the ratio of areas directly you get it as square of ratio. This will be our required result, area of triangle is given by area of triangle
$\dfrac{1}{2}bh$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now take a trapezium ABCD, AB||DC and O as point of intersection of 2 diagonals AC, BD. Now take the triangle AOB, COD as opposite angles are equal, we can say
$\angle AOB=\angle COD$
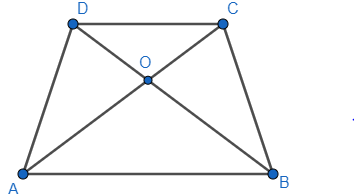
As the lines AB, CD are parallel and AC is transversal we know transversal makes equal angles are parallel lines
$\angle OAB=\angle OCD$
By using AA similarity, we can say that the triangle:
$\Delta AOB\sim \Delta COD$
So, the ratio of corresponding sides is equal in ABCD. By using the above condition, we can say the equation as:
$\dfrac{AO}{OC}=\dfrac{BO}{OD}$
Taking in view of the geometry, we can say the above equation as, the point O divides the diagonal in equal ratio hence proved.
Now we need ratio of their areas, as they are similar their ratio of heights will be equal to ratio of sides by taking ratio of area and substituting the formula:
$\text{Area}=\dfrac{1}{2}bh$
We get the ratio as
$\dfrac{\left( \text{Area of }\Delta OCD \right)}{\left( \text{Area of }\Delta OAB \right)}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}\times CD\times {{b}_{OCD}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}\times AB\times {{h}_{OAB}}}$
By substituting the heights ratio, we get it as:
$\dfrac{\left( \Delta OCD \right)}{\left( \Delta DAB \right)}=\dfrac{CD}{AB}\times \dfrac{CD}{AB}$
Given in the question AB = BCD, by substituting this
$\dfrac{\left( \Delta OCD \right)}{\left( \Delta OAB \right)}=\dfrac{CD}{3CD}\times \dfrac{CD}{3CD}$
By simplifying above equation, we get the ratio of area as
$\dfrac{\Delta OCD}{\Delta OAB}=\dfrac{1}{9}$
By this we can say the ratio of triangles OAB, OCD in this case is 1 : 9.
Hence proved both the equations asked.
Note: While proving the similarity use the AA axiom properly, you can also take the other diagonal as transversal between other 2 parallel sides. Anyways you get the same result, you can use the direct point that the ratio of areas is square to the ratio of sides in similar triangles.
$\dfrac{1}{2}bh$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now take a trapezium ABCD, AB||DC and O as point of intersection of 2 diagonals AC, BD. Now take the triangle AOB, COD as opposite angles are equal, we can say
$\angle AOB=\angle COD$

As the lines AB, CD are parallel and AC is transversal we know transversal makes equal angles are parallel lines
$\angle OAB=\angle OCD$
By using AA similarity, we can say that the triangle:
$\Delta AOB\sim \Delta COD$
So, the ratio of corresponding sides is equal in ABCD. By using the above condition, we can say the equation as:
$\dfrac{AO}{OC}=\dfrac{BO}{OD}$
Taking in view of the geometry, we can say the above equation as, the point O divides the diagonal in equal ratio hence proved.
Now we need ratio of their areas, as they are similar their ratio of heights will be equal to ratio of sides by taking ratio of area and substituting the formula:
$\text{Area}=\dfrac{1}{2}bh$
We get the ratio as
$\dfrac{\left( \text{Area of }\Delta OCD \right)}{\left( \text{Area of }\Delta OAB \right)}=\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2}\times CD\times {{b}_{OCD}}}{\dfrac{1}{2}\times AB\times {{h}_{OAB}}}$
By substituting the heights ratio, we get it as:
$\dfrac{\left( \Delta OCD \right)}{\left( \Delta DAB \right)}=\dfrac{CD}{AB}\times \dfrac{CD}{AB}$
Given in the question AB = BCD, by substituting this
$\dfrac{\left( \Delta OCD \right)}{\left( \Delta OAB \right)}=\dfrac{CD}{3CD}\times \dfrac{CD}{3CD}$
By simplifying above equation, we get the ratio of area as
$\dfrac{\Delta OCD}{\Delta OAB}=\dfrac{1}{9}$
By this we can say the ratio of triangles OAB, OCD in this case is 1 : 9.
Hence proved both the equations asked.
Note: While proving the similarity use the AA axiom properly, you can also take the other diagonal as transversal between other 2 parallel sides. Anyways you get the same result, you can use the direct point that the ratio of areas is square to the ratio of sides in similar triangles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




