
ABCD is a square with side ‘a’. With centres A, B, C and D four circles are drawn such that each circle touches externally two of the remaining three circles and all have the same radius. Find the area of the region in the interior of the square and exterior of the circles:
(A). ${{a}^{2}}\left( 1-\pi \right)$
(B). ${{a}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{4-\pi }{4} \right)$
(C). ${{a}^{2}}\left( \pi -1 \right)$
(D). $\dfrac{\pi {{a}^{2}}}{4}$
Answer
613.5k+ views
Hint: First we will draw the diagram and with that we will find the radius of the circle in terms of ‘a’ and then we will subtract the area of intersection of all four circles with the square and that will be our final answer.
Complete step-by-step solution -
First let’s look at the figure,
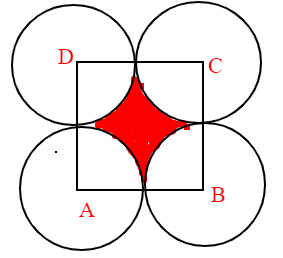
R = radius of circle.
Now as per the question the radius of all four circles are the same and they touch each other so the sum of the radius of two circles must be equal to the side of square ‘a’.
Hence 2R = a
$R=\dfrac{a}{2}$
So, now we have find the radius of circle in terms of ‘a’,
Now the area of intersection between square and circle is:
4 times area of each circle intersected by square.
And the area intersected by square and one circle will be $\dfrac{1}{4}\times $ area of cirle
Area of circle is $\pi {{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
$\begin{align}
& 4\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& =\dfrac{\pi {{a}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Area of square = ${{a}^{2}}$
Now the area interior of the square and exterior of the circles is:
Area of square – area of circles intersected with square
$\begin{align}
& ={{a}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi {{a}^{2}}}{4} \\
& ={{a}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{4-\pi }{4} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Hence option (b) is correct.
Note: The diagram for this question is very important and with that one can get the clear picture of what is happening in the question and what we have to find. And the formulas should be used carefully while calculating the values.
Complete step-by-step solution -
First let’s look at the figure,

R = radius of circle.
Now as per the question the radius of all four circles are the same and they touch each other so the sum of the radius of two circles must be equal to the side of square ‘a’.
Hence 2R = a
$R=\dfrac{a}{2}$
So, now we have find the radius of circle in terms of ‘a’,
Now the area of intersection between square and circle is:
4 times area of each circle intersected by square.
And the area intersected by square and one circle will be $\dfrac{1}{4}\times $ area of cirle
Area of circle is $\pi {{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}}$
$\begin{align}
& 4\times \dfrac{\pi }{4}{{\left( \dfrac{a}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& =\dfrac{\pi {{a}^{2}}}{4} \\
\end{align}$
Area of square = ${{a}^{2}}$
Now the area interior of the square and exterior of the circles is:
Area of square – area of circles intersected with square
$\begin{align}
& ={{a}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi {{a}^{2}}}{4} \\
& ={{a}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{4-\pi }{4} \right) \\
\end{align}$
Hence option (b) is correct.
Note: The diagram for this question is very important and with that one can get the clear picture of what is happening in the question and what we have to find. And the formulas should be used carefully while calculating the values.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




