
ABCD is a rhombus whose diagonals intersect at O. If AB = 10 cm, diagonal BD = 16 cm, then find the length of the other diagonal AC.
Answer
528.2k+ views
Hint – In this particular question use the concept that in a rhombus all sides are equal and the diagonals of the rhombus bisect each other later on in the solution apply the Pythagoras’ theorem so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
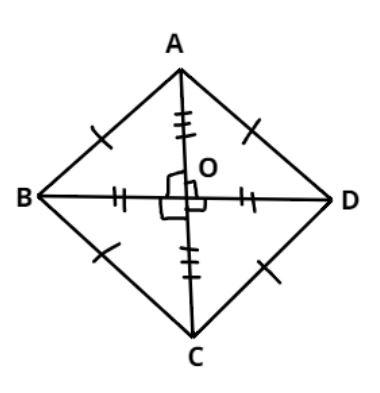
Consider the rhombus ABCD as shown in the figure and the diagonals of the rhombus intersect at point O.
As we know that in a rhombus all sides are equal as shown in the figure.
Therefore, AB = BC = CD = CA
And it is given that AB = 10cm.
So, AB = BC = CD = CA = 10cm
Now as we all know the diagonals of the rhombus bisect each other as shown in the figure.
Therefore, OA = OC = $\dfrac{{AC}}{2}$, and OB = OD = $\dfrac{{BD}}{2}$.
Now it is given that BD = 16 cm.
So, OB = OD = $\dfrac{{16}}{2} = 8$ cm.
Now apply Pythagoras theorem in triangle AOB we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2}$
Now again substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{10}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{8}} \right)^2}$
Now simplify this equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow 100 = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} + 64$
$ \Rightarrow 100 - 64 = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 36 = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} = {6^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\text{OA}}} \right) = 6$ cm
So the value of the other diagonal AC is,
$ \Rightarrow $6 = OC = $\dfrac{{AC}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow AC = 2\left( 6 \right) = 12$ cm.
So the value of the other diagonal of the rhombus is 12 cm.
So this is the required answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall the conditions of rhombus which is all stated above and always recall the formula of Pythagoras theorem which is also stated above then simply substitute the values in the Pythagoras theorem equation as above and simplify we will get the required value of the other diagonal.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Consider the rhombus ABCD as shown in the figure and the diagonals of the rhombus intersect at point O.
As we know that in a rhombus all sides are equal as shown in the figure.
Therefore, AB = BC = CD = CA
And it is given that AB = 10cm.
So, AB = BC = CD = CA = 10cm
Now as we all know the diagonals of the rhombus bisect each other as shown in the figure.
Therefore, OA = OC = $\dfrac{{AC}}{2}$, and OB = OD = $\dfrac{{BD}}{2}$.
Now it is given that BD = 16 cm.
So, OB = OD = $\dfrac{{16}}{2} = 8$ cm.
Now apply Pythagoras theorem in triangle AOB we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{AB}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{OB}}} \right)^2}$
Now again substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{10}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\text{8}} \right)^2}$
Now simplify this equation we have,
$ \Rightarrow 100 = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} + 64$
$ \Rightarrow 100 - 64 = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 36 = {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{OA}}} \right)^2} = {6^2}$
$ \Rightarrow \left( {{\text{OA}}} \right) = 6$ cm
So the value of the other diagonal AC is,
$ \Rightarrow $6 = OC = $\dfrac{{AC}}{2}$
$ \Rightarrow AC = 2\left( 6 \right) = 12$ cm.
So the value of the other diagonal of the rhombus is 12 cm.
So this is the required answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of questions the key concept we have to remember is that always recall the conditions of rhombus which is all stated above and always recall the formula of Pythagoras theorem which is also stated above then simply substitute the values in the Pythagoras theorem equation as above and simplify we will get the required value of the other diagonal.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




