
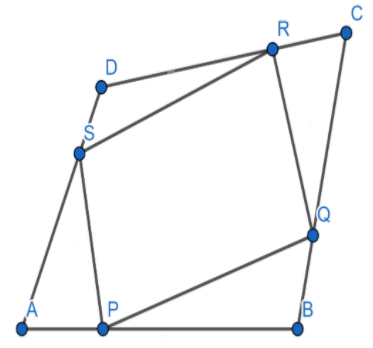
ABCD is a quadrilateral. If P, Q, R, S are the points of trisection of the sides AB, BC, CD, and DA respectively and are adjacent to A and C, then prove that PQRS is a parallelogram.

Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint: Trisection points are the points, which exactly divide the line segment into three equal parts.

In the above line segment A, B, C, D are the points of trisection as they divide the above line segment into three equal parts,
AB: BC: CD = 1:1:1 => AB: BD = 1:2, AC: CD = 2:1
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the question it is given that the points P, Q, R, S are the points of trisection of AB, BC, CD, DA which implies that
AP : PB = 1 : 2, CQ : QB = 1 : 2, CR : RD = 1 : 2, AS : SD = 1 : 2
Now, let us consider the triangle ABC,
From the data derived we have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{CQ}{QB}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow &\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB}\], considering the line segment to be SR, from the above theorem we can now say that PQ || AC.
Similarly now let us consider the triangle ADC
From the derived data we now have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{AS}{SD}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow & \dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{AS}{SD} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{AS}{SD}\], considering the line segment to be PQ, from the above theorem we can now say that SR|| AC.
Now here we have SR||AC and PQ||AC which implies SR||PQ.
Firstly let us imagine a line segment BD between points B and D.
Now, let us consider the triangle DCB,
From the data derived we have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{CQ}{QB}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow\dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB}\], considering the line segment to be RQ, from the above theorem we can now say that RQ || DB.
Similarly now let us consider the triangle ADB
From the derived data we now have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{AS}{SD}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow &\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{AS}{SD} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{AS}{SD}\], considering the line segment to be DB, from the above theorem we can now say that PS|| DB.
Now here we have PS||DB and RQ||DB which implies PS||RQ.
PS||RQ and SR || PQ can be said from the above conclusions
Hence, it is proved that the PQRS is a parallelogram
Note: Basic proportionality theorem should be known first to know its converse. Basic proportionality states that "If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio". From this, our converse can be derived.

In the above line segment A, B, C, D are the points of trisection as they divide the above line segment into three equal parts,
AB: BC: CD = 1:1:1 => AB: BD = 1:2, AC: CD = 2:1
Complete step-by-step solution:
From the question it is given that the points P, Q, R, S are the points of trisection of AB, BC, CD, DA which implies that
AP : PB = 1 : 2, CQ : QB = 1 : 2, CR : RD = 1 : 2, AS : SD = 1 : 2
Now, let us consider the triangle ABC,
From the data derived we have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{CQ}{QB}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow &\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB}\], considering the line segment to be SR, from the above theorem we can now say that PQ || AC.
Similarly now let us consider the triangle ADC
From the derived data we now have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{AS}{SD}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow & \dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{AS}{SD} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{AS}{SD}\], considering the line segment to be PQ, from the above theorem we can now say that SR|| AC.
Now here we have SR||AC and PQ||AC which implies SR||PQ.
Firstly let us imagine a line segment BD between points B and D.
Now, let us consider the triangle DCB,
From the data derived we have
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{CQ}{QB}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow\dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{CR}{RD}=\dfrac{CQ}{QB}\], considering the line segment to be RQ, from the above theorem we can now say that RQ || DB.
Similarly now let us consider the triangle ADB
From the derived data we now have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{AS}{SD}=\dfrac{1}{2} \\
\Rightarrow &\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{AS}{SD} \\
\end{align}\]
From the converse of Basic proportionality theorem which states that, "In a triangle, if a line segment intersects two sides and divides them in the same ratio, then it will be parallel to the third side".
Since, \[\dfrac{AP}{PB}=\dfrac{AS}{SD}\], considering the line segment to be DB, from the above theorem we can now say that PS|| DB.
Now here we have PS||DB and RQ||DB which implies PS||RQ.
PS||RQ and SR || PQ can be said from the above conclusions
Hence, it is proved that the PQRS is a parallelogram
Note: Basic proportionality theorem should be known first to know its converse. Basic proportionality states that "If a line is drawn parallel to one side of a triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio". From this, our converse can be derived.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





