
ABCD is a kite in which \[AB = AD\] and \[BC = DC\] and. M, N and O are mid-points of sides AB, BC and CD. Prove that
(i) $\angle MNO = {90^ \circ }$
(ii) The line MP drawn parallel to NO bisects AD.
Answer
590.4k+ views
Hint: Here we will use the mid-point theorem. Mid-point theorem says that If there is a line that joins the midpoints of two sides of a triangle then it will be parallel to the remaining third side of the triangle.
Complete step by step solution:
The following is the schematic diagram of the kite in which Join AC and BD.
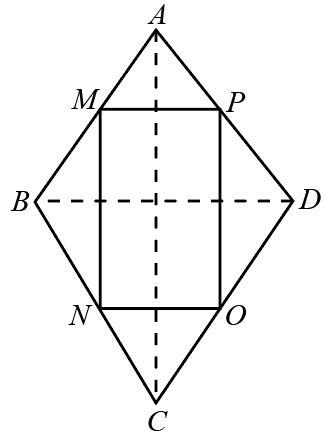
(i) In the triangle BCD, N and O are midpoint of BC and CD that implies ON is equal to half of BD.
In the triangle ABC, M and N are midpoints of AB and BC that implies MN is equal to half of AC.
In a kite, the diagonals intersect at right angles.
So, Angle MNO will be at the right angle.
$\angle MNO = 90^\circ $
Therefore, it is proved that angle MNO will be right angle.
(ii) Since, M is midpoint and MP is parallel to NO which is further parallel to BD.
That means MP is equal to half of BD.
So, P is the midpoint of AD.
Therefore, it is proved that MP bisects AD.
Note: It happens only in rhombus, square and kite that the diagonals intersect each other at right angles. We could not have used the above process in case ABCD was a parallelogram or rectangle. The important point in this solution is the mid-point theorem which helps in proving the answer clearly.
Complete step by step solution:
The following is the schematic diagram of the kite in which Join AC and BD.

(i) In the triangle BCD, N and O are midpoint of BC and CD that implies ON is equal to half of BD.
In the triangle ABC, M and N are midpoints of AB and BC that implies MN is equal to half of AC.
In a kite, the diagonals intersect at right angles.
So, Angle MNO will be at the right angle.
$\angle MNO = 90^\circ $
Therefore, it is proved that angle MNO will be right angle.
(ii) Since, M is midpoint and MP is parallel to NO which is further parallel to BD.
That means MP is equal to half of BD.
So, P is the midpoint of AD.
Therefore, it is proved that MP bisects AD.
Note: It happens only in rhombus, square and kite that the diagonals intersect each other at right angles. We could not have used the above process in case ABCD was a parallelogram or rectangle. The important point in this solution is the mid-point theorem which helps in proving the answer clearly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




