
ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral where BC is the diameter and angle ADC = 130 degree. Find the value of angle ACB.
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: First of all, draw the diagram according to the information in the question to clearly visualize it. Then find \[\angle ABC\] by using the sum of the opposite angles as \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle BAC\] would be \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] as it is subtended by the diameter BC. Now, find \[\angle ACB\] by using the sum of the interior angles of the triangles as \[{{180}^{\circ }}.\]
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given that ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral where BC is the diameter and angle ADC = 130 degrees. We have to find the value of angle ACB. Before proceeding with the question, let us see what a cyclic quadrilateral is.
A cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral (polygon of 4 sides) whose all vertices lie on a single circle. This circle is called circumcircle and vertices of a cyclic quadrilateral are said to be concyclic. The sum of the opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral is \[{{180}^{\circ }}.\]
In the above figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Also,
\[\angle A+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }}\]
\[\angle B+\angle D={{180}^{\circ }}\]
Now, let us consider our question. We are given a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD where BC is the diameter and \[\angle ADC={{130}^{\circ }}\] as follows
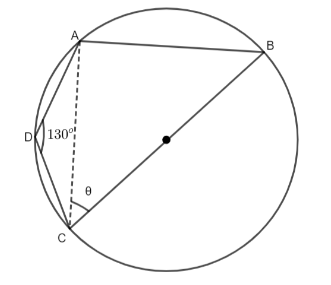
In the above figure, we have to find \[\angle ACB\] that is the angle \[\theta .\]
We know that the opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary, so we get,
\[\angle ADC+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
By substituting the value of \[\angle ADC={{130}^{\circ }},\] we get,
\[{{130}^{\circ }}+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}-{{130}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ABC={{50}^{\circ }}......\left( i \right)\]
We know that the diameter always subtends an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] on the circumference of the circle. As we know that BC is the diameter, so it will also subtend an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] on the circumference. So, we get,
\[\angle BAC={{90}^{\circ }}......\left( ii \right)\]
Now, in any triangle we know that the sum of its interior angles is \[{{180}^{\circ }}.\] So, let us consider triangle ABC, so we get,
\[\angle ACB+\angle BAC+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
By substituting the value of \[\angle ABC={{50}^{o}}\] from equation (i) and \[\angle BAC={{90}^{o}}\] from equation (ii), we get,
\[\angle ACB+{{90}^{o}}+{{50}^{o}}={{180}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}-{{50}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{140}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ACB={{40}^{\circ }}\]
Hence, we get the value of \[\angle ACB={{40}^{\circ }}.\]
Note: In these types of questions, where cyclic quadrilateral is concerned, instead of remembering that \[\angle A+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle B+\angle D={{180}^{\circ }},\] students must remember that the sum of the opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] because the naming of the vertices of a quadrilateral can change which can lead to mistakes. Also, remember that for every quadrilateral sum of all the interior angles is \[{{360}^{\circ }}\] but for only cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles are supplementary.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In this question, we are given that ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral where BC is the diameter and angle ADC = 130 degrees. We have to find the value of angle ACB. Before proceeding with the question, let us see what a cyclic quadrilateral is.
A cyclic quadrilateral or inscribed quadrilateral is a quadrilateral (polygon of 4 sides) whose all vertices lie on a single circle. This circle is called circumcircle and vertices of a cyclic quadrilateral are said to be concyclic. The sum of the opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral is \[{{180}^{\circ }}.\]

In the above figure, ABCD is a cyclic quadrilateral. Also,
\[\angle A+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }}\]
\[\angle B+\angle D={{180}^{\circ }}\]
Now, let us consider our question. We are given a cyclic quadrilateral ABCD where BC is the diameter and \[\angle ADC={{130}^{\circ }}\] as follows

In the above figure, we have to find \[\angle ACB\] that is the angle \[\theta .\]
We know that the opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral are supplementary, so we get,
\[\angle ADC+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
By substituting the value of \[\angle ADC={{130}^{\circ }},\] we get,
\[{{130}^{\circ }}+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}-{{130}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ABC={{50}^{\circ }}......\left( i \right)\]
We know that the diameter always subtends an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] on the circumference of the circle. As we know that BC is the diameter, so it will also subtend an angle of \[{{90}^{\circ }}\] on the circumference. So, we get,
\[\angle BAC={{90}^{\circ }}......\left( ii \right)\]
Now, in any triangle we know that the sum of its interior angles is \[{{180}^{\circ }}.\] So, let us consider triangle ABC, so we get,
\[\angle ACB+\angle BAC+\angle ABC={{180}^{\circ }}\]
By substituting the value of \[\angle ABC={{50}^{o}}\] from equation (i) and \[\angle BAC={{90}^{o}}\] from equation (ii), we get,
\[\angle ACB+{{90}^{o}}+{{50}^{o}}={{180}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{90}^{\circ }}-{{50}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ACB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{140}^{\circ }}\]
\[\Rightarrow \angle ACB={{40}^{\circ }}\]
Hence, we get the value of \[\angle ACB={{40}^{\circ }}.\]
Note: In these types of questions, where cyclic quadrilateral is concerned, instead of remembering that \[\angle A+\angle C={{180}^{\circ }}\] and \[\angle B+\angle D={{180}^{\circ }},\] students must remember that the sum of the opposite angles of the cyclic quadrilateral is \[{{180}^{\circ }}\] because the naming of the vertices of a quadrilateral can change which can lead to mistakes. Also, remember that for every quadrilateral sum of all the interior angles is \[{{360}^{\circ }}\] but for only cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles are supplementary.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




