
A YO-YO is a toy in which a string is wound round a central shaft as shown in the figure. The string unwinds and rewinds itself alternatively making the YO-YO rise and fall. The ratio of the tension in the string during descent and ascent is:
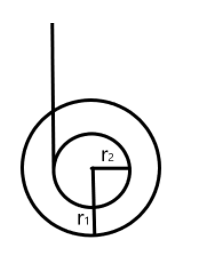
\[\begin{align}
& \text{A) 1:1} \\
& \text{B) }{{r}_{2}}:{{r}_{1}} \\
& \text{C) }{{r}_{1}}:{{r}_{2}} \\
& \text{D) }{{r}_{1}}:1 \\
\end{align}\]

Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: We know that the YO-YO toys are a direct application of the mass-tension relation. We need to understand its working and need to consider any chance of relation with the radii of the shafts used in the toy as per the figure in the problem.
Complete answer:
The YO-YO toy uses a wire wound around its inner circle to descent and ascent. It descends due to the gravitational force due to the mass of the shaft and ascents back to the initial situation due to the tension caused on the wire during its descent.
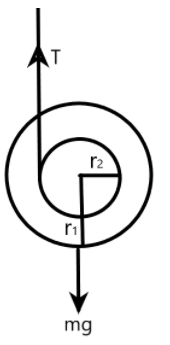
We can understand that the toy doesn’t require any external force of momentum as the gravitational force by virtue of its mass and height has enough potential energy which converts to kinetic energy during descent and again converts back to potential energy on ascent.
The tension on the string attached to the shaft is offered by the gravitational force which is given as the weight of the shaft. The tension on the string can be given as –
\[T=mg\]
From the relation, we understand that the radii of the two shafts of the toy are not related to the tension on the string at any instant.
The ratio between the tension during ascent and descent is therefore, \[\text{1:1}\].
The correct answer is option A.
Note:
The YO-YO toy’s functioning is greatly dependent on the mass of the shaft used in the toy. The force due to gravitational force increases with mass and the body descents faster, also this increases the tension on the string making a faster ascent.
Complete answer:
The YO-YO toy uses a wire wound around its inner circle to descent and ascent. It descends due to the gravitational force due to the mass of the shaft and ascents back to the initial situation due to the tension caused on the wire during its descent.

We can understand that the toy doesn’t require any external force of momentum as the gravitational force by virtue of its mass and height has enough potential energy which converts to kinetic energy during descent and again converts back to potential energy on ascent.
The tension on the string attached to the shaft is offered by the gravitational force which is given as the weight of the shaft. The tension on the string can be given as –
\[T=mg\]
From the relation, we understand that the radii of the two shafts of the toy are not related to the tension on the string at any instant.
The ratio between the tension during ascent and descent is therefore, \[\text{1:1}\].
The correct answer is option A.
Note:
The YO-YO toy’s functioning is greatly dependent on the mass of the shaft used in the toy. The force due to gravitational force increases with mass and the body descents faster, also this increases the tension on the string making a faster ascent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




