
(a) Write the mechanism of Friedel-craft alkylation of benzene.
(b) Complete the following reaction
i)${\text{HC}} \equiv {\text{CH}}\,{\text{ + }}\,\,{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\mathop {\, \to
}\limits^{{{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}/{\text{H}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}} $
ii)${{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{Cl}}\,{\text{ +
}}\,{\text{KO}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{alc}}}}\, \to \,?\, + \,{\text{KCl}}\,{\text{ +
}}\,{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}$
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: Friedel craft alkylation an aromatic alkene reacts with base to form a cation. Aromatic alkene gives a substitution reaction with this cation. The product has two joined rings. The reagent ${{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{/}}\,{\text{H}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}$ cause mercuration and demercuration.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) To attach substituents on aromatic rings the Friedel craft alkylation reactions are used. Friedel craft alkylation reactions are the reaction of aromatic rings with alkyl groups in presence of Lewis acid.
Firstly, the cyclohexene reacts with acid hydrogen fluoride, so cyclohexene abstract protons from the hydrogen fluoride form a cation of cyclohexane.
The reaction is shown as follows:
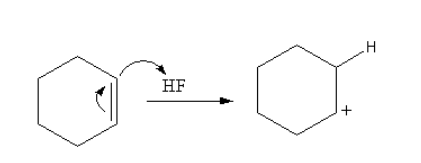
The benzene attacks on the cyclohexane cation to form the cation again. The attack of benzene attacks on the cyclohexane joins the two rings or we can say alkylate the benzene ring.
The reaction is shown as follows:
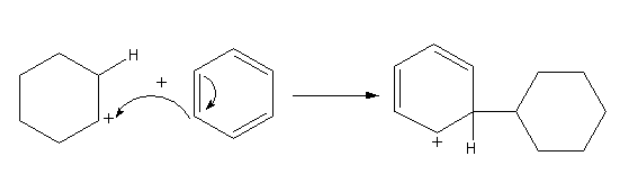
The positive charge is stabilized by the delocalization in the benzene ring. The abstraction of hydrogen from the benzene ring gives the final product.
The product is shown as follows:
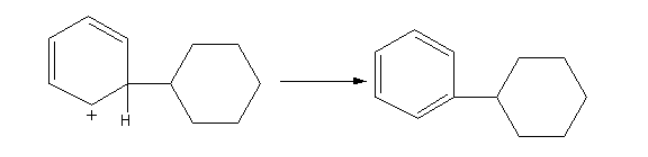
So, the product P of the reaction of benzene with cyclohexene in presence of Lewis acid hydrogen fluoride is $1 - $cyclohexylbenzene.
(b)
i)
First the mercury attacks on the reactant and forms a cyclic structure. Then water attacks on this cyclic structure forming a mercury cation. Then by the removal of hydride alcohol forms. The enol can be converted into keto form by keto-enol tautomerism. The oxygen atom of the ketone attacks on the acid and gets protonated and the diacation of mercury removes. The enol form again converts into keto form by keto-enol tautomerism.
So, the product of reaction-I) is an acetaldehyde.
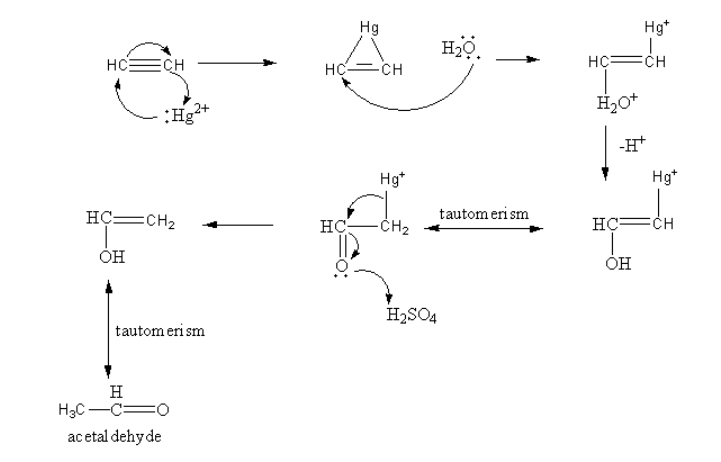
ii)
$\beta - $elimination reactions take place in presence of a base such as alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
When an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide reacts with an alkyl halide, the alkyl halide undergoes elimination reaction. The hydrogen halide eliminates and alkene forms.
The compound which gives more substituted alkene will be most reactive for $\beta - $elimination reaction because more substituted alkene is more stable alkene.
The product of $\beta - $elimination reaction is shown as follows:
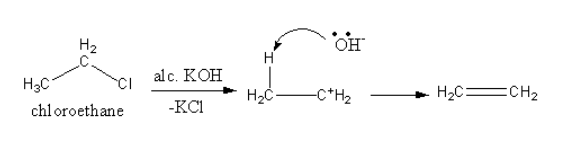
So, the product of the reaction is ethene.
Note: In reaction-II mercury attaches with the reactant in between the reaction mechanism and then removes. The reaction-II is known as oxymercuration demercuration. Alcoholic potassium hydroxide works as bas. Aqueous potassium hydroxide works as acid. The aqueous potassium hydroxide from alcohol form alkyl halide whereas alcoholic potassium hydroxide forms alkene.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) To attach substituents on aromatic rings the Friedel craft alkylation reactions are used. Friedel craft alkylation reactions are the reaction of aromatic rings with alkyl groups in presence of Lewis acid.
Firstly, the cyclohexene reacts with acid hydrogen fluoride, so cyclohexene abstract protons from the hydrogen fluoride form a cation of cyclohexane.
The reaction is shown as follows:

The benzene attacks on the cyclohexane cation to form the cation again. The attack of benzene attacks on the cyclohexane joins the two rings or we can say alkylate the benzene ring.
The reaction is shown as follows:

The positive charge is stabilized by the delocalization in the benzene ring. The abstraction of hydrogen from the benzene ring gives the final product.
The product is shown as follows:

So, the product P of the reaction of benzene with cyclohexene in presence of Lewis acid hydrogen fluoride is $1 - $cyclohexylbenzene.
(b)
i)
First the mercury attacks on the reactant and forms a cyclic structure. Then water attacks on this cyclic structure forming a mercury cation. Then by the removal of hydride alcohol forms. The enol can be converted into keto form by keto-enol tautomerism. The oxygen atom of the ketone attacks on the acid and gets protonated and the diacation of mercury removes. The enol form again converts into keto form by keto-enol tautomerism.
So, the product of reaction-I) is an acetaldehyde.

ii)
$\beta - $elimination reactions take place in presence of a base such as alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
When an alcoholic solution of potassium hydroxide reacts with an alkyl halide, the alkyl halide undergoes elimination reaction. The hydrogen halide eliminates and alkene forms.
The compound which gives more substituted alkene will be most reactive for $\beta - $elimination reaction because more substituted alkene is more stable alkene.
The product of $\beta - $elimination reaction is shown as follows:

So, the product of the reaction is ethene.
Note: In reaction-II mercury attaches with the reactant in between the reaction mechanism and then removes. The reaction-II is known as oxymercuration demercuration. Alcoholic potassium hydroxide works as bas. Aqueous potassium hydroxide works as acid. The aqueous potassium hydroxide from alcohol form alkyl halide whereas alcoholic potassium hydroxide forms alkene.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




