
A wood ceiling with thermal resistance \[{R_1}\] , is covered with a layer of insulation with resistance \[{R_2}\] . Prove that the effective thermal resistance of the combination is \[R = {R_1} + {R_2}\].
Answer
480.6k+ views
Hint: First let us understand the concept of thermal resistance and heat flux through a plane. So one can say that thermal resistance is a heat property which is a measurement of a temperature difference by which an object resists a heat flow while heat flux, a vector quantity is a flow of energy per unit of area per unit of time. Now use this concept to solve the question.
Complete step by step answer:
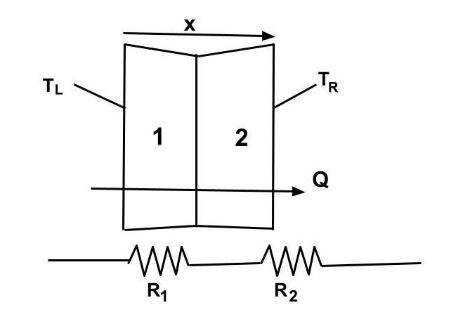
Let rate of flow of heat = $Q$
Then $Q{R_1} = {T_1} - T$............(1)
Where $R_1$ is the thermal resistance of the wooden ceiling and $T$ denotes the temperature of the interface between two layers.
Similarly $Q{R_2} = T - {T_2}$........(2)
Add (1) and (2), we get
$Q({R_1} + {R_2}) = {T_1} - {T_2}$
$\therefore ({R_1} + {R_2}) = \dfrac{{{T_1} - {T_2}}}{Q}$
So the effective thermal resistance of the combination is $R = ({R_1} + {R_2})$.
Note: Thermal resistance is inversely proportional to thermal Conductance. Thermal resistance is a measure of opposition to the flow of heat. More the thermal resistance it becomes difficult for the heat energy to flow from one place to another place. When the rods are connected in series the same rate of flow happens through both. But the temperature difference at the two ending junctions is going to be different because of the receiving of different heat energy. The temperature difference between the first and the last end is equal to the sum of temperature difference between the junctions as shown above.
Complete step by step answer:

Let rate of flow of heat = $Q$
Then $Q{R_1} = {T_1} - T$............(1)
Where $R_1$ is the thermal resistance of the wooden ceiling and $T$ denotes the temperature of the interface between two layers.
Similarly $Q{R_2} = T - {T_2}$........(2)
Add (1) and (2), we get
$Q({R_1} + {R_2}) = {T_1} - {T_2}$
$\therefore ({R_1} + {R_2}) = \dfrac{{{T_1} - {T_2}}}{Q}$
So the effective thermal resistance of the combination is $R = ({R_1} + {R_2})$.
Note: Thermal resistance is inversely proportional to thermal Conductance. Thermal resistance is a measure of opposition to the flow of heat. More the thermal resistance it becomes difficult for the heat energy to flow from one place to another place. When the rods are connected in series the same rate of flow happens through both. But the temperature difference at the two ending junctions is going to be different because of the receiving of different heat energy. The temperature difference between the first and the last end is equal to the sum of temperature difference between the junctions as shown above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




