
A window is in the form of a rectangle surmounted by a semicircular opening. The total perimeter of the window is 10 m. Find the dimensions of the window to admit maximum light through the whole opening.\[\]
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: The maximum light may only come through maximum area. We take the length of the rectangle as $x$ and breadth as $y$. We use the value of the given semi-perimeter to express $y=f\left( x \right)$. We put $y$ in the expression for the total area of the window and maximize it to find $x$ as a critical point using the second derivative test. We then find $y.$\[\]
Complete step-by-step solution
We know from the second derivative test that the function $f\left( x \right)$ will have a local maxima at critical point $x=c$ if ${{f}^{''}}\left( c \right)<0$. The critical points are the solutions of ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=0$.\[\]
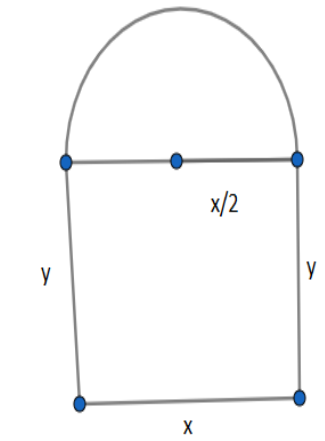
We are given that a window is in the form of a rectangle surmounted by a semicircular opening. If we want maximum light to pass through the opening we want the light passed through the entire area made by a rectangular window and the semi-circular opening. \[\]
Let us assume that the length of the rectangle is $x$ and breadth is $y$. So the radius of the semi-circular opening is $\dfrac{x}{2}.$ It is given in the question that the perimeter of the entire window is 10m. We have
\[\begin{align}
& 2\left( x+y \right)+\pi \left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)-x=10 \\
& \Rightarrow x+2y+\dfrac{\pi x}{2}=10 \\
& \Rightarrow y=5-x\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)...(1) \\
\end{align}\]
The total area of the window is the sum of the areas of rectangle and semi-circle. We have,
\[A=xy+\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {{\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)}^{2}}\]
We put the obtained values of $y$ in the above equation to get,
\[\begin{align}
& A=x\left( 5-x\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {{\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=5x-\dfrac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi }{4}{{x}^{2}}+\dfrac{\pi }{8}{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=5x-\dfrac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi }{8}{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We have to maximize the area. Let us differentiate $A$ once with respect to $x$ and the equate to 0 so that we can find critical points where $A$ can have a maxima. We have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dA}{dx}=5-x-\dfrac{\pi x}{4}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{1+\dfrac{\pi }{4}}=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4} \\
\end{align}\]
We have obtained only one critical point $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$. We find the value of the second derivative of $A$ at $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}A}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{dA}{dx} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}A}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 5-x-\dfrac{\pi x}{4} \right)=-1-\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
\end{align}\]
We see that $\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}A}{dx}<0$ for all $x\in R$ including $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$. So $A$ will have a maxima at $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$. We put $x$ in equation (1) and get,
\[\begin{align}
& y=5-\left( \dfrac{20}{\pi +4} \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=5-\left( \dfrac{20}{\pi +4} \right)\left( \dfrac{2+\pi }{4} \right) \\
& =5-5\dfrac{\pi +2}{\pi +4}=5\left( \dfrac{\pi +2-\pi -4}{\pi +4} \right)=5\dfrac{2}{\pi +4}=\dfrac{10}{\pi +4} \\
\end{align}\]
So the dimension of the window to admit maximum light through the whole opening is length $\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$m and breadth $\dfrac{10}{\pi +4}$m.\[\]
Note: We need to be careful that the perimeter of the window does not include the diameter of the semicircle. We note that if the second derivative would have ${{f}^{''}}\left( c \right)=0$ we would have done a third derivative test and so on. The function $f\left( x \right)$ has a maxima at $x=c$ if ${{f}^{n+1}}\left( c \right) < 0$ and ${{f}^{'}}\left( c \right)={{f}^{''}}\left( c \right)=...={{f}^{n}}\left( c \right)=0$
Complete step-by-step solution
We know from the second derivative test that the function $f\left( x \right)$ will have a local maxima at critical point $x=c$ if ${{f}^{''}}\left( c \right)<0$. The critical points are the solutions of ${{f}^{'}}\left( x \right)=0$.\[\]

We are given that a window is in the form of a rectangle surmounted by a semicircular opening. If we want maximum light to pass through the opening we want the light passed through the entire area made by a rectangular window and the semi-circular opening. \[\]
Let us assume that the length of the rectangle is $x$ and breadth is $y$. So the radius of the semi-circular opening is $\dfrac{x}{2}.$ It is given in the question that the perimeter of the entire window is 10m. We have
\[\begin{align}
& 2\left( x+y \right)+\pi \left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)-x=10 \\
& \Rightarrow x+2y+\dfrac{\pi x}{2}=10 \\
& \Rightarrow y=5-x\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)...(1) \\
\end{align}\]
The total area of the window is the sum of the areas of rectangle and semi-circle. We have,
\[A=xy+\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {{\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)}^{2}}\]
We put the obtained values of $y$ in the above equation to get,
\[\begin{align}
& A=x\left( 5-x\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right) \right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\pi {{\left( \dfrac{x}{2} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=5x-\dfrac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi }{4}{{x}^{2}}+\dfrac{\pi }{8}{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow A=5x-\dfrac{1}{2}{{x}^{2}}-\dfrac{\pi }{8}{{x}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
We have to maximize the area. Let us differentiate $A$ once with respect to $x$ and the equate to 0 so that we can find critical points where $A$ can have a maxima. We have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{dA}{dx}=5-x-\dfrac{\pi x}{4}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{1+\dfrac{\pi }{4}}=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4} \\
\end{align}\]
We have obtained only one critical point $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$. We find the value of the second derivative of $A$ at $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$.
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}A}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( \dfrac{dA}{dx} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{d}^{2}}A}{dx}=\dfrac{d}{dx}\left( 5-x-\dfrac{\pi x}{4} \right)=-1-\dfrac{\pi }{4} \\
\end{align}\]
We see that $\dfrac{{{d}^{2}}A}{dx}<0$ for all $x\in R$ including $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$. So $A$ will have a maxima at $x=\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$. We put $x$ in equation (1) and get,
\[\begin{align}
& y=5-\left( \dfrac{20}{\pi +4} \right)\left( \dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)=5-\left( \dfrac{20}{\pi +4} \right)\left( \dfrac{2+\pi }{4} \right) \\
& =5-5\dfrac{\pi +2}{\pi +4}=5\left( \dfrac{\pi +2-\pi -4}{\pi +4} \right)=5\dfrac{2}{\pi +4}=\dfrac{10}{\pi +4} \\
\end{align}\]
So the dimension of the window to admit maximum light through the whole opening is length $\dfrac{20}{\pi +4}$m and breadth $\dfrac{10}{\pi +4}$m.\[\]
Note: We need to be careful that the perimeter of the window does not include the diameter of the semicircle. We note that if the second derivative would have ${{f}^{''}}\left( c \right)=0$ we would have done a third derivative test and so on. The function $f\left( x \right)$ has a maxima at $x=c$ if ${{f}^{n+1}}\left( c \right) < 0$ and ${{f}^{'}}\left( c \right)={{f}^{''}}\left( c \right)=...={{f}^{n}}\left( c \right)=0$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




