
(a) Which phenomenon can we study by the following diagram?
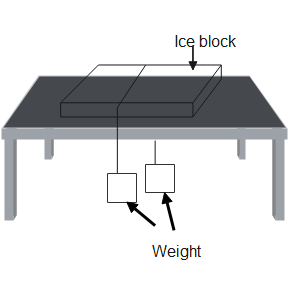
(b) Define that phenomenon which is related to the above experiment
(c) If crushed ice is pressed and then pressure is released, a lump of ice is formed. Justify it.

Answer
501.6k+ views
Hint: From the given diagram we can see that pressure is being applied on a lump of ice, placed on a table top, by using two weights which are tied by a wire. Thus we can now tell by the diagram that the phenomenon which is taking place here is the phenomenon of regelation.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) Regelation is the phenomenon due to which there is a decrease in the melting point of the ice due to the increase in pressure on it, and it falls below ${0^\circ }C$ .
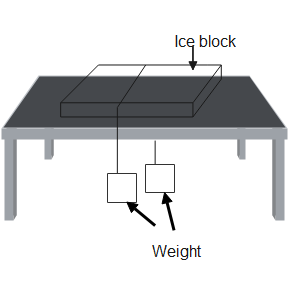
(b) Now when the pressure is released, the water which has liquified will again solidify and form ice. We see in the above diagram a block of ice is placed on a table and pressure is being applied on it by using weights, tied to a wire. Now due to this application of pressure, the melting point of ice falls and the ice liquifies at the point of contact with the wire. Thus, the wire moves down the ice surface. Now as soon as the pressure becomes normal, the liquified water again gets freezed. Thus at the end we see that the ice block remains as it was and the wire has come in the middle of the ice surface.
(c) Now, if crushed ice is pressed, by application of pressure its melting point decreases and it forms water. Now when pressure is released, the water molecules by coalition join each other and refreeze into ice, thus forming a lump of ice from crushed ice.
Note: It is important to note when ice has its melting point decreases, by increase or decrease of pressure. This application of regulation is found in the glaciers, and that’s why we see glaciers melting even though the pole’s remain at less than ${0^\circ }C$.
Complete step by step solution:
(a) Regelation is the phenomenon due to which there is a decrease in the melting point of the ice due to the increase in pressure on it, and it falls below ${0^\circ }C$ .

(b) Now when the pressure is released, the water which has liquified will again solidify and form ice. We see in the above diagram a block of ice is placed on a table and pressure is being applied on it by using weights, tied to a wire. Now due to this application of pressure, the melting point of ice falls and the ice liquifies at the point of contact with the wire. Thus, the wire moves down the ice surface. Now as soon as the pressure becomes normal, the liquified water again gets freezed. Thus at the end we see that the ice block remains as it was and the wire has come in the middle of the ice surface.
(c) Now, if crushed ice is pressed, by application of pressure its melting point decreases and it forms water. Now when pressure is released, the water molecules by coalition join each other and refreeze into ice, thus forming a lump of ice from crushed ice.
Note: It is important to note when ice has its melting point decreases, by increase or decrease of pressure. This application of regulation is found in the glaciers, and that’s why we see glaciers melting even though the pole’s remain at less than ${0^\circ }C$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




