
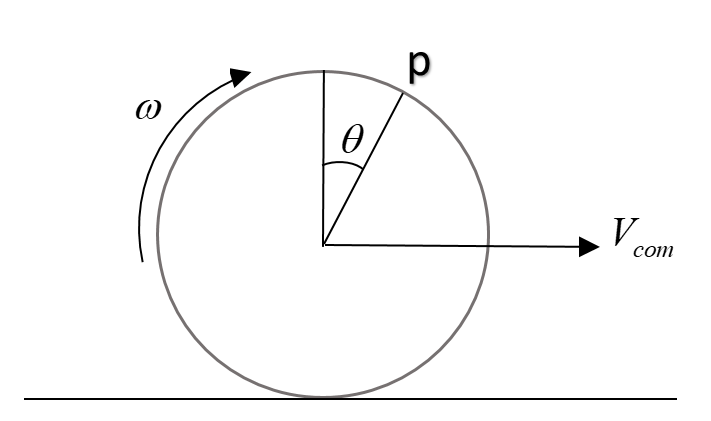
A wheel rolls purely on the ground. If the speed of point ‘P’ as shown on the periphery of the body is equal to the velocity of the centre of mass of the body. Find $\theta$

Answer
591k+ views
Hint: Speed is a scalar quantity. Speed means the magnitude of net velocity. Velocity is a vector quantity. Hence for a body or point, the net velocity is the vector sum of all the velocities in different directions. Coming to rotational + translational motion. If a body undergoes both rotational and translational motion, then every point of the body will have two kinds of velocities, one due to translational motion and other due to rotational motion.
Formula used:
$v=r\omega , \ \vec{v_{net}}=\vec v_{transitional}+\vec v_{rotational}$
Complete answer:
As the speed of point is the result of two speeds, transitional and rotational.
Now in case of rolling, every point on the wheel will have the same transitional speed i.e. speed of centre of mass. So, $v_{transitional} = |v_{com}|$
Now, as we know, $v_{rotational} = r\omega$, hence, rotational speed of the point will be;
$v_{rotational} = r\omega$
And for pure rolling, $\omega = \dfrac {v_{com}}r$
Hence $v_{rotational} = |v_{com}|$
Now, using $\ \vec{v_{net}}=\vec v_{transitional}+\vec v_{rotational}$;
Putting $v_{rotational} = |v_{com}|$ and $v_{transitional} = |v_{com}|$, we get;
$v_{com}^2 = v_{com}^2+ v_{com}^2+ 2\times v_{com} v_{com} cos \theta$
$cos\theta = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
$\theta = 120^\circ$
Note:
In these types of questions, students should give emphasis on slipping conditions. If there is not a pure rolling condition, then even the contact point does not have velocity zero. But in general, if there’s a pure rolling, then one must remember that the velocity of the contact point is zero whereas the velocity of the uppermost point is 2 times the velocity of the centre of mass. In case of slipping of the wheel, the transitional velocity of all the points will be the transitional velocity of centre of mass, but in that scenario, $v \neq r\omega$ and we have to proceed using angular momentum equations.
Formula used:
$v=r\omega , \ \vec{v_{net}}=\vec v_{transitional}+\vec v_{rotational}$
Complete answer:
As the speed of point is the result of two speeds, transitional and rotational.
Now in case of rolling, every point on the wheel will have the same transitional speed i.e. speed of centre of mass. So, $v_{transitional} = |v_{com}|$
Now, as we know, $v_{rotational} = r\omega$, hence, rotational speed of the point will be;
$v_{rotational} = r\omega$
And for pure rolling, $\omega = \dfrac {v_{com}}r$
Hence $v_{rotational} = |v_{com}|$
Now, using $\ \vec{v_{net}}=\vec v_{transitional}+\vec v_{rotational}$;
Putting $v_{rotational} = |v_{com}|$ and $v_{transitional} = |v_{com}|$, we get;
$v_{com}^2 = v_{com}^2+ v_{com}^2+ 2\times v_{com} v_{com} cos \theta$
$cos\theta = - \dfrac{1}{2}$
$\theta = 120^\circ$
Note:
In these types of questions, students should give emphasis on slipping conditions. If there is not a pure rolling condition, then even the contact point does not have velocity zero. But in general, if there’s a pure rolling, then one must remember that the velocity of the contact point is zero whereas the velocity of the uppermost point is 2 times the velocity of the centre of mass. In case of slipping of the wheel, the transitional velocity of all the points will be the transitional velocity of centre of mass, but in that scenario, $v \neq r\omega$ and we have to proceed using angular momentum equations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




