
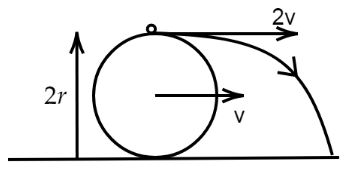
A wheel of radius \[r\]rolls without slipping on the ground, with speed \[v\]. When it is at a point $P$, a piece of mud flies off tangentially from its highest point, lands on the ground at point $Q$. Find the distance P Q ?
Answer
523.2k+ views
Hint: The path of the piece of mud follows a path of projectile motion. Find the horizontal velocity of the piece of mud and calculate the time of flight to calculate the distance of PQ.
Formula used:
The displacement of a particle in one dimensional motion is given by,
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
where, \[s\] is the displacement of the particle \[u\] is the initial velocity of the particle \[t\] is the time and \[a\] is the acceleration of the particle.
The velocity of a body, moving with a velocity while rolling is,
\[{V_{rot}} = {V_{cm}} + \omega \times r\]
where, \[{V_{rot}}\] is the velocity with respect to the origin, \[{V_{cm}}\] is the velocity with respect to the centre of mass and \[r\] is the radius of the body and \[\omega \] is angular velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
Since the body is moving while rolling so the speed of the piece of mud will be,
\[{V_{rot}} = {V_{cm}} + \omega \times r\]
Here, we have given, \[{V_{cm}} = v\]and since the radius of the wheel is \[r\] so, \[\omega \times r\]must be equal to \[v\]. So,
\[{V_{rot}} = v + v = 2v\].
Now, the piece of mud drops from a height of \[r + r = 2r\]. So, the time of flight is equal to time taken to drop from the height \[2r\].
Hence, we can write for the vertical motion of piece of mud,
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 2r = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Up on simplifying we have, \[t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4r}}{g}} \]
Now, the distance covered horizontally must be equal to the product of velocity and time of flight since the horizontal velocity does not change with time. Hence, the distance $PQ$ will be equal to,
\[d = (2v)t\]
Putting the value of time \[t\] we have,
\[d = 2v\sqrt {\dfrac{{4r}}{g}} \]
\[\therefore d = 4v\sqrt {\dfrac{r}{g}} \]
Hence, distance between the points P and Q is \[4v\sqrt {\dfrac{r}{g}} \].
Note: The piece of mud only travels the path of a half projectile. The path of the piece of mud is similar to when a stone or something is thrown horizontally from a height.For, a projectile motion time of flight is equal to, \[\dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\] where \[u\sin \theta \] is vertical component of the velocity of the particle.
Formula used:
The displacement of a particle in one dimensional motion is given by,
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
where, \[s\] is the displacement of the particle \[u\] is the initial velocity of the particle \[t\] is the time and \[a\] is the acceleration of the particle.
The velocity of a body, moving with a velocity while rolling is,
\[{V_{rot}} = {V_{cm}} + \omega \times r\]
where, \[{V_{rot}}\] is the velocity with respect to the origin, \[{V_{cm}}\] is the velocity with respect to the centre of mass and \[r\] is the radius of the body and \[\omega \] is angular velocity.
Complete step by step answer:
Since the body is moving while rolling so the speed of the piece of mud will be,
\[{V_{rot}} = {V_{cm}} + \omega \times r\]
Here, we have given, \[{V_{cm}} = v\]and since the radius of the wheel is \[r\] so, \[\omega \times r\]must be equal to \[v\]. So,
\[{V_{rot}} = v + v = 2v\].
Now, the piece of mud drops from a height of \[r + r = 2r\]. So, the time of flight is equal to time taken to drop from the height \[2r\].

Hence, we can write for the vertical motion of piece of mud,
\[s = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}\]
\[\Rightarrow 2r = 0 + \dfrac{1}{2}g{t^2}\]
Up on simplifying we have, \[t = \sqrt {\dfrac{{4r}}{g}} \]
Now, the distance covered horizontally must be equal to the product of velocity and time of flight since the horizontal velocity does not change with time. Hence, the distance $PQ$ will be equal to,
\[d = (2v)t\]
Putting the value of time \[t\] we have,
\[d = 2v\sqrt {\dfrac{{4r}}{g}} \]
\[\therefore d = 4v\sqrt {\dfrac{r}{g}} \]
Hence, distance between the points P and Q is \[4v\sqrt {\dfrac{r}{g}} \].
Note: The piece of mud only travels the path of a half projectile. The path of the piece of mud is similar to when a stone or something is thrown horizontally from a height.For, a projectile motion time of flight is equal to, \[\dfrac{{2u\sin \theta }}{g}\] where \[u\sin \theta \] is vertical component of the velocity of the particle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




