
A wheel is rolling straight on the ground without slipping. If the centre of mass of the wheel has speed $v$ , the instantaneous velocity of a point $P$ on the rim, defined by angle $\theta $ , relative to the ground will be:
A. $v\cos \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$
B. $2v\cos \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$
C. $v\sin \left( {\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)$
D. $v\sin \theta $
Answer
495k+ views
Hint: This question comes under pure rolling because it is mentioned in the question that the wheel is rolling without slipping. And in this question linear velocity and angular velocity become the same. After pointing all the velocity components, we will vector sum to get the required answer.
Formula used:
$V = r\omega $
Where,
$V$ is the linear speed,
$r$ is the radius and
$\omega $ is the angular velocity.
Complete answer:
As according to the question, it is said that wheel is rolling straight on ground without slipping So we can write that,
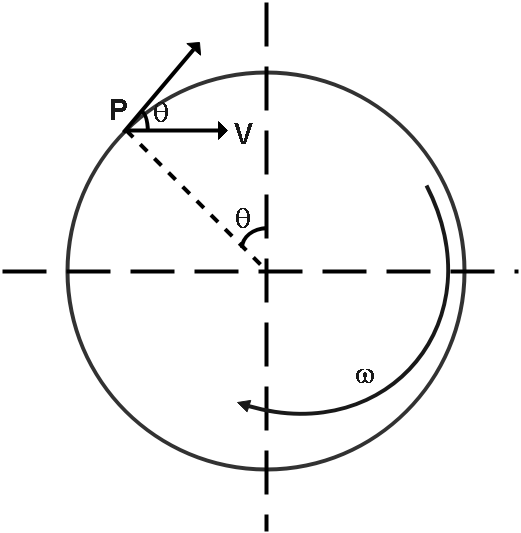
$v = r\omega $
Here, $v$ is the linear velocity of the wheel.
So now we have to find the instantaneous velocity at the point $P$ with respect to ground.
Now, vector sum of both the velocity it becomes,
${V_{net}} = \sqrt {v_1^2 + v_2^2 + 2{v_1}{v_2}\cos \theta } $
As, ${v_1}$ and ${v_2}$ are same so,
$
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = \sqrt {v_1^2 + v_2^2 + 2{v_1}{v_2}\cos \theta } \\
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = \sqrt {2{v^2} + 2{v^2}\cos \theta } \\
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = v\sqrt {2(1 + \cos \theta )} \\
$
Now, we will apply trigonometry, and we know that,
$1 + \cos 2\theta = 2{\cos ^2}\theta $
And if we replace $2\theta $ by \[\dfrac{\theta }{2}\] it becomes,
$
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = v\sqrt {2\left( {2{{\cos }^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)} \\
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = 2v\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
$
So, the instantaneous velocity of a point $P$ on the rim, defined by angle $\theta $ , relative to the ground is $2v\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}$ .
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:
In pure rolling slipping doesn’t take place whereas in rolling slipping takes place. A pure rolling body acts like it is at rest at the point where it touches the ground whereas rolling at every point of contact sliding takes place.
Do not assume that the friction is $0$ in pure rolling, that is not true. This is because there is no external force to stop this motion.
Formula used:
$V = r\omega $
Where,
$V$ is the linear speed,
$r$ is the radius and
$\omega $ is the angular velocity.
Complete answer:
As according to the question, it is said that wheel is rolling straight on ground without slipping So we can write that,

$v = r\omega $
Here, $v$ is the linear velocity of the wheel.
So now we have to find the instantaneous velocity at the point $P$ with respect to ground.
Now, vector sum of both the velocity it becomes,
${V_{net}} = \sqrt {v_1^2 + v_2^2 + 2{v_1}{v_2}\cos \theta } $
As, ${v_1}$ and ${v_2}$ are same so,
$
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = \sqrt {v_1^2 + v_2^2 + 2{v_1}{v_2}\cos \theta } \\
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = \sqrt {2{v^2} + 2{v^2}\cos \theta } \\
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = v\sqrt {2(1 + \cos \theta )} \\
$
Now, we will apply trigonometry, and we know that,
$1 + \cos 2\theta = 2{\cos ^2}\theta $
And if we replace $2\theta $ by \[\dfrac{\theta }{2}\] it becomes,
$
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = v\sqrt {2\left( {2{{\cos }^2}\dfrac{\theta }{2}} \right)} \\
\Rightarrow {V_{net}} = 2v\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2} \\
$
So, the instantaneous velocity of a point $P$ on the rim, defined by angle $\theta $ , relative to the ground is $2v\cos \dfrac{\theta }{2}$ .
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:
In pure rolling slipping doesn’t take place whereas in rolling slipping takes place. A pure rolling body acts like it is at rest at the point where it touches the ground whereas rolling at every point of contact sliding takes place.
Do not assume that the friction is $0$ in pure rolling, that is not true. This is because there is no external force to stop this motion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




