
(a) What product is released after the first step of glucose breakdown? Where does it take place?
(b) How is the small intestine designed to perform absorption of food?
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: The mechanism by which one glucose molecule is converted into two pyruvate molecules, two hydrogen ions and two water molecules are called glycolysis. The 'high-energy' intermediate molecules are synthesised via this process. The small intestine is a major part of the absorption of food in the gastrointestinal tract.
Complete answer:
(a) In the first stage of glucose oxidation, glucose, which is a 6-carbon molecule, is broken down into two pyruvate molecules (glycolysis). Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cells. At the end of glycolysis, the pyruvate produced is then transferred to mitochondria where the pyruvate is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide.
(b)There is a small intestine present between the large intestine and the stomach. It is one of the most important parts of the food canal for both food digestion and absorption. There are three regions of the small intestine:
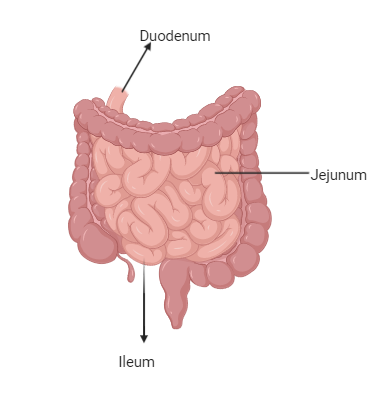
a) Duodenum, which is U-shaped.
b) Jejunum is the middle part and is coiled.
c) Ileum is the last region and is strongly coiled.
Absorbent cells or enterocytes are used to help absorb dietary nutrients and minerals in the small intestine. Tiny finger-like projections that normally present the lumen of the small intestine are villi. The length of each villa is 0.5 to 1.6 mm approximately. These finger-like projections help increase the surface area for food absorption. Villi, along with a large lymph vessel known as the lactate, consists of a network of capillaries. It helps in transporting lipid molecules. The intestinal wall is also surrounded by blood vessels that help transport food molecules to various parts of the body.
Note: The function of the small intestine is as follows; it helps to digest food, it also helps to extract minerals and nutrients from the digested food. The undigested food is transported from the small intestine to the big intestine.
Complete answer:
(a) In the first stage of glucose oxidation, glucose, which is a 6-carbon molecule, is broken down into two pyruvate molecules (glycolysis). Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of the cells. At the end of glycolysis, the pyruvate produced is then transferred to mitochondria where the pyruvate is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide.
(b)There is a small intestine present between the large intestine and the stomach. It is one of the most important parts of the food canal for both food digestion and absorption. There are three regions of the small intestine:

a) Duodenum, which is U-shaped.
b) Jejunum is the middle part and is coiled.
c) Ileum is the last region and is strongly coiled.
Absorbent cells or enterocytes are used to help absorb dietary nutrients and minerals in the small intestine. Tiny finger-like projections that normally present the lumen of the small intestine are villi. The length of each villa is 0.5 to 1.6 mm approximately. These finger-like projections help increase the surface area for food absorption. Villi, along with a large lymph vessel known as the lactate, consists of a network of capillaries. It helps in transporting lipid molecules. The intestinal wall is also surrounded by blood vessels that help transport food molecules to various parts of the body.
Note: The function of the small intestine is as follows; it helps to digest food, it also helps to extract minerals and nutrients from the digested food. The undigested food is transported from the small intestine to the big intestine.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




