
A weightless rod of length \[2l\] carries two equal masses $m$ one second at lower end $A$ and the other at the middle of the rod at $B$ . The rod can rotate in a vertical plane about a fixed horizontal axis passing through $C$ . What horizontal velocity must be imparted to the mass at $A$ so that it just completes the vertical circle.
A. $\sqrt {\dfrac{{48}}{5}gl} $
B. $\sqrt {\dfrac{{45}}{5}gl} $
C. $\sqrt {\dfrac{{40}}{5}gl} $
D. $\sqrt {\dfrac{{35}}{5}gl} $
Answer
495.3k+ views
Hint: In this question first we will find the potential energy and then kinetic energy and then we will apply law of conservation of energy and then compare to get the horizontal velocity that must be imparted to the mass at $A$ so that it just completes the vertical circle.
Formula used:
$K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Where,
$m$ is the mass and
$v$ is the velocity.
$P.E = mgh$
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and
$h$ is the height.
Complete step by step solution:
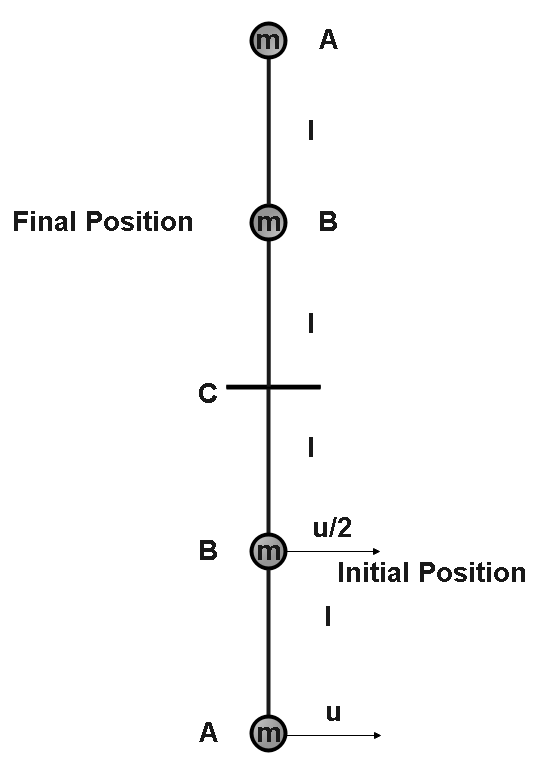
Given,
Length of the rod is $2l$
And mass is given $m$
Let the initial velocity given to the mass at A be $u$
Then, the velocity of mass at B is $\dfrac{u}{2}$
As the system moves from initial position to final position.
Then, there is an increase in potential energy
And that is
$P.{E_{total}} = {(mgh)_A} + {(mgh)_B}$
Now substituting the value, we get,
$
P.{E_{total}} = mg4l + mg2l \\
P.{E_{total}} = 6mgl \\
$
We know that from law of conservation of energy potential energy is equal to kinetic energy
So, \[
6mgl = \dfrac{{mv_B^2}}{2} + \dfrac{{mv_A^2}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow 6mgl = \dfrac{1}{2}m{\left( {\dfrac{u}{2}} \right)^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} \\
\]
Where, velocity of mass at B is $\dfrac{u}{2}$ substituting and further solving the equation,
\[
\Rightarrow 6mgl = \dfrac{1}{8}m{u^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} \\
\Rightarrow 6mgl = \dfrac{5}{8}m{u^2} \\
\]
Now, cross multiplying to find $u$
\[
\Rightarrow {u^2} = \dfrac{{48}}{5}lg \\
\Rightarrow u = \sqrt {\dfrac{{48}}{5}gl} \\
\]
So, the horizontal velocity must be imparted to the mass at $A$ so that it just completes the vertical circle \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{48}}{5}gl} \]
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
The potential energy of point A is ${(mgh)_A} = 4mgl$ because if we see in the diagram that the distance between final and initial position is $4l$ so we have put $h$ as $4l$ .You must remember the conservation of energy to solve this question.
Formula used:
$K.E. = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$
Where,
$m$ is the mass and
$v$ is the velocity.
$P.E = mgh$
$g$ is the acceleration due to gravity and
$h$ is the height.
Complete step by step solution:

Given,
Length of the rod is $2l$
And mass is given $m$
Let the initial velocity given to the mass at A be $u$
Then, the velocity of mass at B is $\dfrac{u}{2}$
As the system moves from initial position to final position.
Then, there is an increase in potential energy
And that is
$P.{E_{total}} = {(mgh)_A} + {(mgh)_B}$
Now substituting the value, we get,
$
P.{E_{total}} = mg4l + mg2l \\
P.{E_{total}} = 6mgl \\
$
We know that from law of conservation of energy potential energy is equal to kinetic energy
So, \[
6mgl = \dfrac{{mv_B^2}}{2} + \dfrac{{mv_A^2}}{2} \\
\Rightarrow 6mgl = \dfrac{1}{2}m{\left( {\dfrac{u}{2}} \right)^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} \\
\]
Where, velocity of mass at B is $\dfrac{u}{2}$ substituting and further solving the equation,
\[
\Rightarrow 6mgl = \dfrac{1}{8}m{u^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2} \\
\Rightarrow 6mgl = \dfrac{5}{8}m{u^2} \\
\]
Now, cross multiplying to find $u$
\[
\Rightarrow {u^2} = \dfrac{{48}}{5}lg \\
\Rightarrow u = \sqrt {\dfrac{{48}}{5}gl} \\
\]
So, the horizontal velocity must be imparted to the mass at $A$ so that it just completes the vertical circle \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{48}}{5}gl} \]
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:
The potential energy of point A is ${(mgh)_A} = 4mgl$ because if we see in the diagram that the distance between final and initial position is $4l$ so we have put $h$ as $4l$ .You must remember the conservation of energy to solve this question.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




