
A weight W is tied to two strings passing over the frictionless pulleys A and B as shown in the figure. If weights P and Q move downwards with speed V, the weight W at any instant rises with the speed:
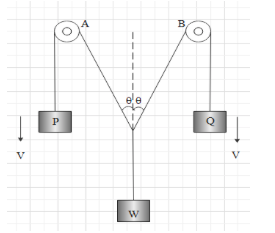
A. $V\cos \theta $
B. $2V\cos \theta $
C. $\dfrac{V}{{\cos \theta }}$
D. $\dfrac{{2V}}{{\cos \theta }}$

Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint-In the given figure we can consider a right triangle connecting one of the pulleys, the midpoint of line joining the two pulleys and point of suspension of weight W. Using Pythagoras theorem, we will get an equation relating length of the string and height to which weight can be raised. By differentiating this equation with respect to time we can find the velocity with which the weight moves upward.
Step by step solution:
It is given that a weight is tied to two strings passing over two frictionless pulleys. If weights P and Q move downwards with a speed V, the weight W Rises upward. We need to find the speed with which weight W rises upward.
Consider the triangle BOS shown in the figure below.
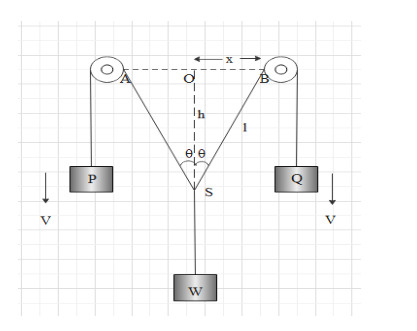
Since it is a right-angled triangle, we can use the Pythagoras theorem.
let the length of the string be l. Then we can write
${l^2} = {h^2} + {x^2}$
Let us differentiate this equation with respect to t.
$ \Rightarrow 2l\dfrac{{dl}}{{dt}} = 2h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} + 0$..............(1)
We know that the rate of change of distance is velocity. Hence, we can write
$\dfrac{{dl}}{{dt}} = V$
Substituting this in equation 1 we get
$ \Rightarrow 2l \times V = 2h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} + 0$.................(2)
The rate of change of the height h will give us the velocity of the block upwards. Let this velocity be denoted as u.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = u$
Thus equation 2 becomes
$ \Rightarrow 2lV = 2hu$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{lV}}{h}$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{V}{{\dfrac{h}{l}}}$
From the triangle BOS, we can find that the value of $\cos \theta $ is given as
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{adjacent}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{h}{l}$
Thus, we can substitute $\cos \theta $ instead of $\dfrac{h}{l}$
Using this we get the value of velocity u as
$\therefore u = \dfrac{V}{{\cos \theta }}$
So, the correct option is option C.
Note:Remember that while taking the derivative of equation ${l^2} = {h^2} + {x^2}$ , the derivative of x with respect to time will be zero. This is because the value of x is a constant. Its value does not change with time. So, its derivative with respect to time will be zero.
Step by step solution:
It is given that a weight is tied to two strings passing over two frictionless pulleys. If weights P and Q move downwards with a speed V, the weight W Rises upward. We need to find the speed with which weight W rises upward.
Consider the triangle BOS shown in the figure below.

Since it is a right-angled triangle, we can use the Pythagoras theorem.
let the length of the string be l. Then we can write
${l^2} = {h^2} + {x^2}$
Let us differentiate this equation with respect to t.
$ \Rightarrow 2l\dfrac{{dl}}{{dt}} = 2h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} + 0$..............(1)
We know that the rate of change of distance is velocity. Hence, we can write
$\dfrac{{dl}}{{dt}} = V$
Substituting this in equation 1 we get
$ \Rightarrow 2l \times V = 2h\dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} + 0$.................(2)
The rate of change of the height h will give us the velocity of the block upwards. Let this velocity be denoted as u.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{dh}}{{dt}} = u$
Thus equation 2 becomes
$ \Rightarrow 2lV = 2hu$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{{lV}}{h}$
$ \Rightarrow u = \dfrac{V}{{\dfrac{h}{l}}}$
From the triangle BOS, we can find that the value of $\cos \theta $ is given as
$\cos \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{adjacent}}\,{\text{side}}}}{{{\text{hypotenuse}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \cos \theta = \dfrac{h}{l}$
Thus, we can substitute $\cos \theta $ instead of $\dfrac{h}{l}$
Using this we get the value of velocity u as
$\therefore u = \dfrac{V}{{\cos \theta }}$
So, the correct option is option C.
Note:Remember that while taking the derivative of equation ${l^2} = {h^2} + {x^2}$ , the derivative of x with respect to time will be zero. This is because the value of x is a constant. Its value does not change with time. So, its derivative with respect to time will be zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




