
A wedge of masses m2 is kept on a spring balance. A small block of mass m1 can move along the frictionless incline of the wedge. What is the reading of the balance while the block slides? Ignore the recoil of the wedge.
Answer
593.4k+ views
Hint: Wedges are used to lift heavy objects, separating them from the surface upon which they rest. Consider a block that is to be lifted by a wedge. As the wedge slides under the block, the block slides up the sloped side of a wedge. This lifts the weight FB of the block.
Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Complete step by step solution:
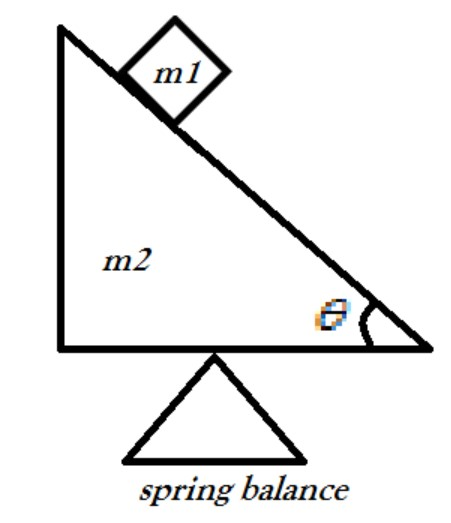
The above diagram is constructed as per the question.
Now,
Drawing a free body diagram of mass m1 and resolving the force into its components.
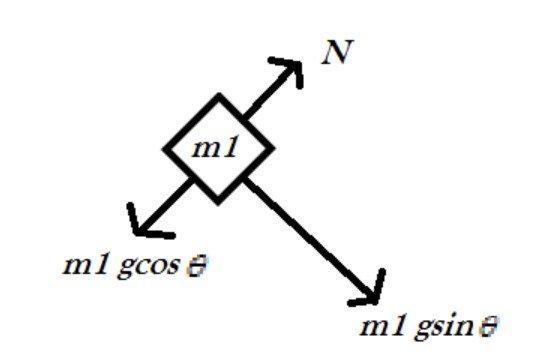
Here, N represents the Normal component, g represents the acceleration due to gravity.
Since the mass m1 remains in contact therefore $N = m_1 \times g\cos \theta $
Now,
Drawing the free body diagram of the wedge,
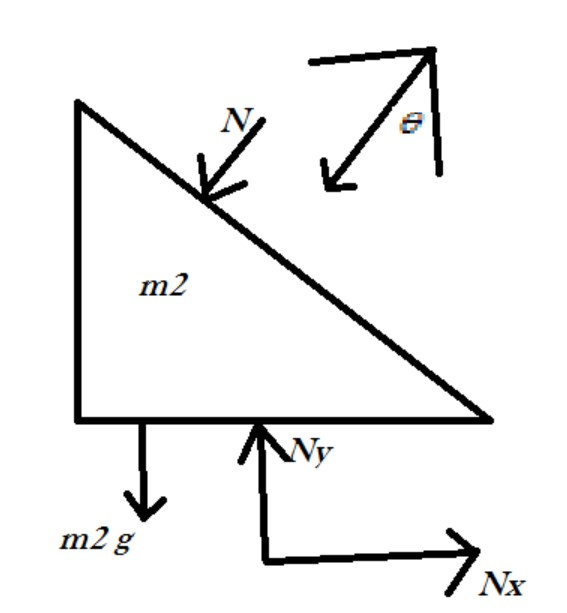
So, clearly from the above and by balancing all the forces, we can write,
\[
Ny = (m_2 \times g) + (N\cos \theta ) \\
Ny = (m_2 \times g) + (m_1g\cos \theta \times \cos \theta ) \\
Ny = (m_2 \times g) + (m_1g{\cos ^2}\theta ) \\
\]
And, by balancing forces in X direction we can write,
$
Nx = N\sin \theta \\
Nx = m_1g\cos \theta \sin \theta \\
$
Now, since we know that weight balance only reads upward normal force, therefore it will only read Ny.
Thus,
$
Ny = m_2g + m_1g(1 - {\sin ^2}\theta ) \\
Ny = g(m_2 + m_1) - m_1g{\sin ^2}\theta \\
$
Hence the reading of the spring balance will be $ = g(m_2 + m_1) - m_1g{\sin ^2}\theta $
Note: In problems of wedge and block always try to draw the free body diagram and try to resolve the components and then proceed. This will always help you in solving problems easily and avoiding any confusions.
Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
Complete step by step solution:

The above diagram is constructed as per the question.
Now,
Drawing a free body diagram of mass m1 and resolving the force into its components.

Here, N represents the Normal component, g represents the acceleration due to gravity.
Since the mass m1 remains in contact therefore $N = m_1 \times g\cos \theta $
Now,
Drawing the free body diagram of the wedge,

So, clearly from the above and by balancing all the forces, we can write,
\[
Ny = (m_2 \times g) + (N\cos \theta ) \\
Ny = (m_2 \times g) + (m_1g\cos \theta \times \cos \theta ) \\
Ny = (m_2 \times g) + (m_1g{\cos ^2}\theta ) \\
\]
And, by balancing forces in X direction we can write,
$
Nx = N\sin \theta \\
Nx = m_1g\cos \theta \sin \theta \\
$
Now, since we know that weight balance only reads upward normal force, therefore it will only read Ny.
Thus,
$
Ny = m_2g + m_1g(1 - {\sin ^2}\theta ) \\
Ny = g(m_2 + m_1) - m_1g{\sin ^2}\theta \\
$
Hence the reading of the spring balance will be $ = g(m_2 + m_1) - m_1g{\sin ^2}\theta $
Note: In problems of wedge and block always try to draw the free body diagram and try to resolve the components and then proceed. This will always help you in solving problems easily and avoiding any confusions.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




