
A wedge of mass \[M\] with a spring of stiffness $k$ is kept on a smooth horizontal surface. A rod of mass m is kept on the wedge as shown in the figure. The system is in equilibrium. Assuming that all surfaces are smooth, the potential energy stored in the spring is:
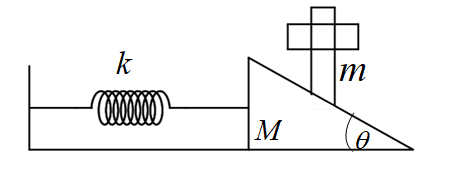
A. $\dfrac{{m{g^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$
B. $\dfrac{{{m^2}g{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$
C. $\dfrac{{{m^2}{g^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$
D. $\dfrac{{{m^2}{g^{^2}}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{k}$

Answer
487.2k+ views
Hint: In Physics, spring is a device used to store potential energy in the form of elastic energy. When we extend the spring by applying an external force on it, this force is stored inside it as mechanical energy, as soon as we withdraw the applied force spring regains its original position using the stored energy.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first draw a free body diagram to show all the forces acting on the rod as shown in the figure.
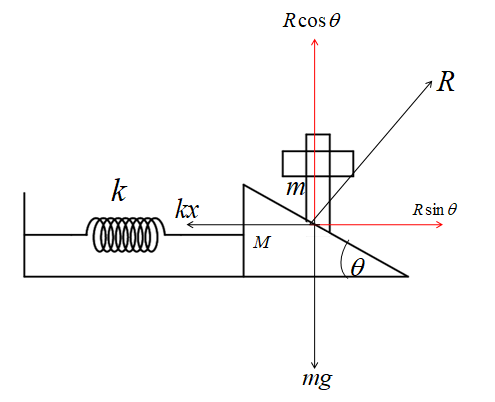
Now the system is in equilibrium it means, all the forces balance each other. From the figure, we can write these balancing forces.
$mg = R\cos \theta $ …………..(1)
$kx = R\sin \theta $……………. (2)
Let us divide equation (2) by (1) and get the value of $x$.
$\dfrac{{kx}}{{mg}} = \tan \theta $
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{mg\tan \theta }}{k}$ …………………. (3)
The formula to calculate the potential energy stored in the spring is given below.
$PE = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$
Let us now put the value of $x$from equation (3).
$PE = \dfrac{1}{2}k{\left( {\dfrac{{mg\tan \theta }}{k}} \right)^2}$
Let us further simplify it.
$PE = \dfrac{{{m^2}{g^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$
This is the potential energy stored in the spring when the system is in equilibrium.
Hence, the correct option is (C) $\dfrac{{{m^2}{g^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$.
Note:
An equilibrium condition for this type of system is when all the forces cancel or balance each other. To know which force is balanced by which, we have to draw the free body diagram.
To draw a free body diagram, we have to resolve all the forces in their horizontal and vertical components
Complete step by step solution:
Let us first draw a free body diagram to show all the forces acting on the rod as shown in the figure.

Now the system is in equilibrium it means, all the forces balance each other. From the figure, we can write these balancing forces.
$mg = R\cos \theta $ …………..(1)
$kx = R\sin \theta $……………. (2)
Let us divide equation (2) by (1) and get the value of $x$.
$\dfrac{{kx}}{{mg}} = \tan \theta $
$ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{mg\tan \theta }}{k}$ …………………. (3)
The formula to calculate the potential energy stored in the spring is given below.
$PE = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}$
Let us now put the value of $x$from equation (3).
$PE = \dfrac{1}{2}k{\left( {\dfrac{{mg\tan \theta }}{k}} \right)^2}$
Let us further simplify it.
$PE = \dfrac{{{m^2}{g^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$
This is the potential energy stored in the spring when the system is in equilibrium.
Hence, the correct option is (C) $\dfrac{{{m^2}{g^2}{{\tan }^2}\theta }}{{2k}}$.
Note:
An equilibrium condition for this type of system is when all the forces cancel or balance each other. To know which force is balanced by which, we have to draw the free body diagram.
To draw a free body diagram, we have to resolve all the forces in their horizontal and vertical components
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




