
A viscous liquid flows through a horizontal pipe of varying cross-sectional area. Identify the option which correctly represents the variation of height of rise of liquid in each vertical tube.
A.
B.
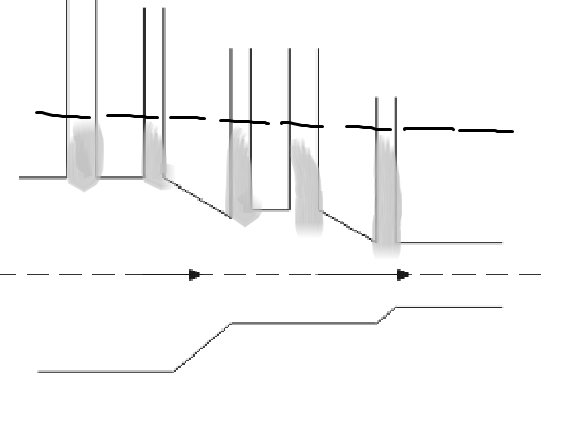
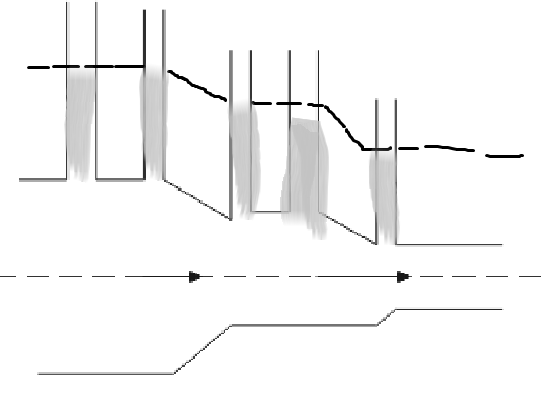
C.
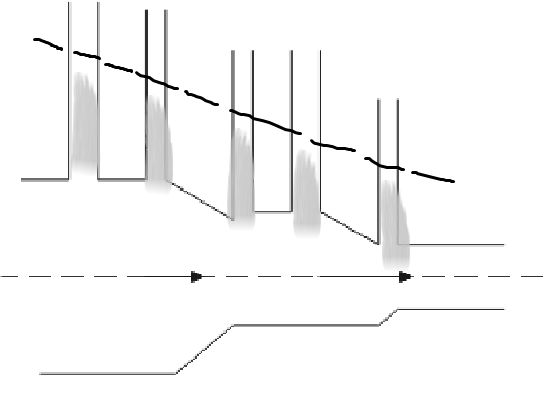
D. None of these



Answer
495k+ views
Hint: As the question is on varying cross-sectional areas, we can guess it’s on Bernoulli’s theorem. We know that the pressure of fluid decreases along the direction of the flow of the fluid, even in the case of a uniform cross-sectional area. See that given question is about varying areas.
Complete step by step solution:
We understood that if the cross-sectional area was uniform, the pressure would decrease and so would the height of liquid reduce, but given here we see that the cross-sectional area reduces as the water flows, hence by the theory of continuity $Av = $ constant, we can say that velocity increases as the water flows.
Now by Bernoulli’s principle we know for a fixed height (as the height of the flow of water is the same), the pressure decreases with increase in pressure, thus it can now be clearly understood, height of water would decrease with the direction of velocity.
Thus, the answer will be option C.
Additional information:
Some of the formulas you need to remember for solving these types of questions are:
Equation of continuity: $Av = $ constant.
Bernoulli’s equation: \[p + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2} + \rho gy = \] constant, where \[p\] = pressure
\[\rho \] = density of fluid, \[{v^2}\] = square of velocity of fluid, \[g\] = acceleration due to gravity
\[y\] = depth of fluid.
Note:
For solving these questions, always remember the formulas and apply them conceptually to get the answer. Always look for terms linking to pressure and area as these can be substituted by using the formula directly.
Complete step by step solution:
We understood that if the cross-sectional area was uniform, the pressure would decrease and so would the height of liquid reduce, but given here we see that the cross-sectional area reduces as the water flows, hence by the theory of continuity $Av = $ constant, we can say that velocity increases as the water flows.
Now by Bernoulli’s principle we know for a fixed height (as the height of the flow of water is the same), the pressure decreases with increase in pressure, thus it can now be clearly understood, height of water would decrease with the direction of velocity.
Thus, the answer will be option C.
Additional information:
Some of the formulas you need to remember for solving these types of questions are:
Equation of continuity: $Av = $ constant.
Bernoulli’s equation: \[p + \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2} + \rho gy = \] constant, where \[p\] = pressure
\[\rho \] = density of fluid, \[{v^2}\] = square of velocity of fluid, \[g\] = acceleration due to gravity
\[y\] = depth of fluid.
Note:
For solving these questions, always remember the formulas and apply them conceptually to get the answer. Always look for terms linking to pressure and area as these can be substituted by using the formula directly.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




