
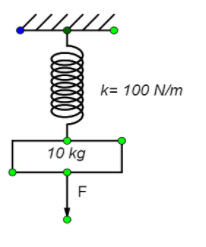
A vertical spring of force constant \[100N/m\] is attached with a hanging mass of \[10kg\]. Now an external force is applied on mass so that the spring is stretched (maximum) by additional \[2m\] The work force \[F\] is\[\left( {g = 10m/{s^2}} \right)\].
A \[200J\]
B \[400J\]
C\[450J\]
D \[600J\]

Answer
496.8k+ views
Hint: When the spring is extended to a length from its initial length, it implies that some force is applied to it which depends on the spring constant and the stretched distance. The force does some work due to the extension of the length. The formula of the work done due to the stretching of the spring has to be used here. The work done is directly proportional to the square of the extended length of the spring after being stretched.
Formula used:
The force applied on the spring during the stretching, \[F = kx\]
where $x$ is the extended length of the spring and, $k$ is the force-constant.
The work by the force,
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
Complete answer:
When the force is applied to a spring it is stretched and extended by some length.
The force on the spring is presented as \[F = kx\]. Where \[k\]is constant and $x$ is the extended (additional) length of the spring after being stretched.
And, The work done by the force,
$W = F.x$
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
Given, constant force\[k = 100\], additional length\[x = 2\],
\[\therefore W = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {2^2}J\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 200J\]
Hence, the answer is option A.
Note:
Potential energy is stored as a result of the stretching of a spring. Potential energy is equal to the work done to stretch the spring.
According to Hooke’s Law, the force required to stretch the spring is directly proportional to the amount of stretch.
The force required to stretch a spring changes with the distance so the calculation of work involves an integral.
Formula used:
The force applied on the spring during the stretching, \[F = kx\]
where $x$ is the extended length of the spring and, $k$ is the force-constant.
The work by the force,
\[W = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
Complete answer:
When the force is applied to a spring it is stretched and extended by some length.
The force on the spring is presented as \[F = kx\]. Where \[k\]is constant and $x$ is the extended (additional) length of the spring after being stretched.
And, The work done by the force,
$W = F.x$
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
Given, constant force\[k = 100\], additional length\[x = 2\],
\[\therefore W = \dfrac{1}{2}k{x^2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{1}{2} \times 100 \times {2^2}J\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = 200J\]
Hence, the answer is option A.
Note:
Potential energy is stored as a result of the stretching of a spring. Potential energy is equal to the work done to stretch the spring.
According to Hooke’s Law, the force required to stretch the spring is directly proportional to the amount of stretch.
The force required to stretch a spring changes with the distance so the calculation of work involves an integral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




