
A vertical pole stands at a point O on a horizontal ground. A and B are points on the ground $ 10m $ apart. The pole subtends an angle $ {30^0} $ and $ {60^0} $ at A and B respectively. Then the height of the tower equals.
(A) $ 10\sqrt 3\;m $
(B) $ 5\sqrt 3\;m $
(C) $ 15\sqrt 3\;m $
(D) None of these
Answer
571.8k+ views
Hint: Use the triangle property of $ \tan \theta $ to calculate the unknown variables using the given conditions. To solve this question, we will assume that the pole stands vertically upward on the ground making angle $ {90^0} $ with the ground.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe that diagram
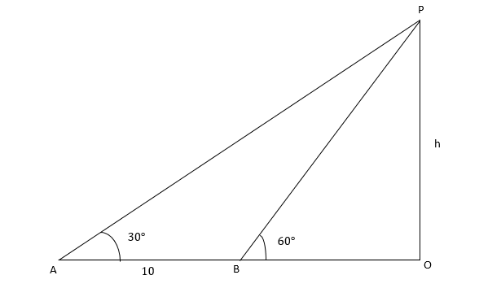
It is given in the question that,
$ \angle PAO = {30^0} $
$ \angle PBO = {60^0} $
$ AB = 10 m $
We have to find the height of the tower.
Let us assume that the height of the tower be $ h $
Let us consider the $ \Delta PAO $
In $ \Delta PAO $
Using the triangle properties of trigonometric function, we can write
$ \tan \angle PAO = \dfrac{h}{{OA}} $
$ \Rightarrow \tan {30^0} = \dfrac{h}{{OA}} $
From the figure, we can observe that
$ OA = AB + BO $
$ \Rightarrow OA = 10 + BO $
Therefore, we get
$ \tan {30^0} = \dfrac{h}{{10 + BO}} $
By substituting the value of $ \tan {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $ in above equation, we can write
$ \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{10 + BO}} $
By cross multiplying the above equation, we get
$ 10 + BO = h\sqrt 3 $
$ \Rightarrow BO = h\sqrt 3 - 10 $
Now let us consider the triangle \[\Delta PBO\]
In \[\Delta PBO\]
Using the triangle properties of trigonometric function, we can write
$ \tan \angle PBO = \dfrac{h}{{OB}} $
$ \Rightarrow \tan {60^0} = \dfrac{h}{{OB}} $
By substituting the value of $ \tan {60^0} = \sqrt 3 $ and the value of $ OB = h\sqrt 3 - 10 $ calculated above, we can write
$ \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{h}{{h\sqrt 3 - 10}} $
By cross multiplying, we get
$ \sqrt 3 (h\sqrt 3 - 10) = h $
By simplifying it, we get
$ 3h - 10\sqrt 3 = h $
$ \Rightarrow 2h = 10\sqrt 3 $
Dividing both the sides by $ 2 $ we get
$ h = 5\sqrt 3 $
So, the height of the tower is $ 5\sqrt 3\; m $
Therefore, form the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (B) $ 5\sqrt 3\;m $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: To use the triangle properties of a trigonometric function, we need to have a right angled triangle. Therefore, we cannot question the above if we do not consider the pole to be perpendicular to the ground. We have given two conditions to solve. In such a case, we use one condition to find one variable and the substitute that variable into the second condition to get the final answer. Just like we did in the above question by finding the value of BO using the first condition and the substituting that value into the second condition to find the height of the tower.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Observe that diagram

It is given in the question that,
$ \angle PAO = {30^0} $
$ \angle PBO = {60^0} $
$ AB = 10 m $
We have to find the height of the tower.
Let us assume that the height of the tower be $ h $
Let us consider the $ \Delta PAO $
In $ \Delta PAO $
Using the triangle properties of trigonometric function, we can write
$ \tan \angle PAO = \dfrac{h}{{OA}} $
$ \Rightarrow \tan {30^0} = \dfrac{h}{{OA}} $
From the figure, we can observe that
$ OA = AB + BO $
$ \Rightarrow OA = 10 + BO $
Therefore, we get
$ \tan {30^0} = \dfrac{h}{{10 + BO}} $
By substituting the value of $ \tan {30^0} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $ in above equation, we can write
$ \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{h}{{10 + BO}} $
By cross multiplying the above equation, we get
$ 10 + BO = h\sqrt 3 $
$ \Rightarrow BO = h\sqrt 3 - 10 $
Now let us consider the triangle \[\Delta PBO\]
In \[\Delta PBO\]
Using the triangle properties of trigonometric function, we can write
$ \tan \angle PBO = \dfrac{h}{{OB}} $
$ \Rightarrow \tan {60^0} = \dfrac{h}{{OB}} $
By substituting the value of $ \tan {60^0} = \sqrt 3 $ and the value of $ OB = h\sqrt 3 - 10 $ calculated above, we can write
$ \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{h}{{h\sqrt 3 - 10}} $
By cross multiplying, we get
$ \sqrt 3 (h\sqrt 3 - 10) = h $
By simplifying it, we get
$ 3h - 10\sqrt 3 = h $
$ \Rightarrow 2h = 10\sqrt 3 $
Dividing both the sides by $ 2 $ we get
$ h = 5\sqrt 3 $
So, the height of the tower is $ 5\sqrt 3\; m $
Therefore, form the above explanation, the correct answer is, option (B) $ 5\sqrt 3\;m $
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: To use the triangle properties of a trigonometric function, we need to have a right angled triangle. Therefore, we cannot question the above if we do not consider the pole to be perpendicular to the ground. We have given two conditions to solve. In such a case, we use one condition to find one variable and the substitute that variable into the second condition to get the final answer. Just like we did in the above question by finding the value of BO using the first condition and the substituting that value into the second condition to find the height of the tower.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




