
A vertical lamp post of height 9 meters stands at the corner of a rectangular field. The angle of evolution of its top from the farthest corner is \[{30^ \circ }\], which from another corner it is \[{45^ \circ }\], the area of the field is
\[\begin{array}{l}A.9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ mete}}{{\rm{r}}^{\rm{2}}}\\B.81\sqrt 3 {\rm{ mete}}{{\rm{r}}^{\rm{2}}}\\C.81\sqrt 2 {\rm{ mete}}{{\rm{r}}^{\rm{2}}}\\D.9\sqrt 3 {\rm{ mete}}{{\rm{r}}^{\rm{2}}}\end{array}\]
Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: First of all, we will draw the diagram and then, by using the trigonometric ratios, we will find the side of a rectangle, we will be using the tangent ratio which is the ratio of perpendicular to base. Value of \[\tan \theta \]at standard angles such as \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}{\rm{ and }}\,{\rm{tan4}}{{\rm{5}}^ \circ }{\rm{ = 1}}\] must be known and used in the solution and we will use the formula of area of rectangle, which is equal to the product of length and breadth of a rectangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that, a lamp post of height 9 meters stands at the corner of a rectangular field. Also, the angle of elevation of its top from farthest corner is \[{30^ \circ }\] while from another corner is \[{45^ \circ }\]
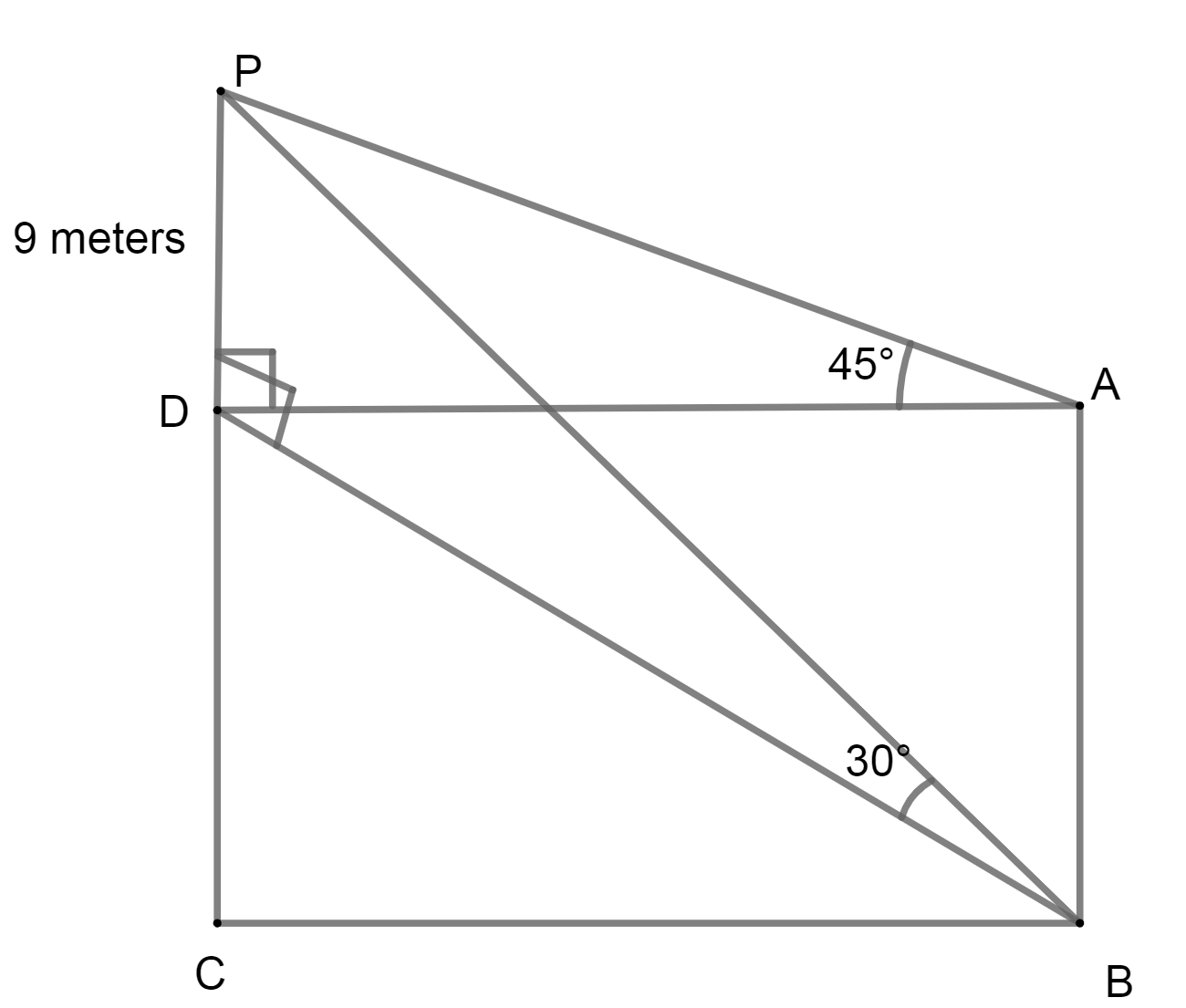
We have PD= 9 meters
Now, in \[\Delta AOP\],
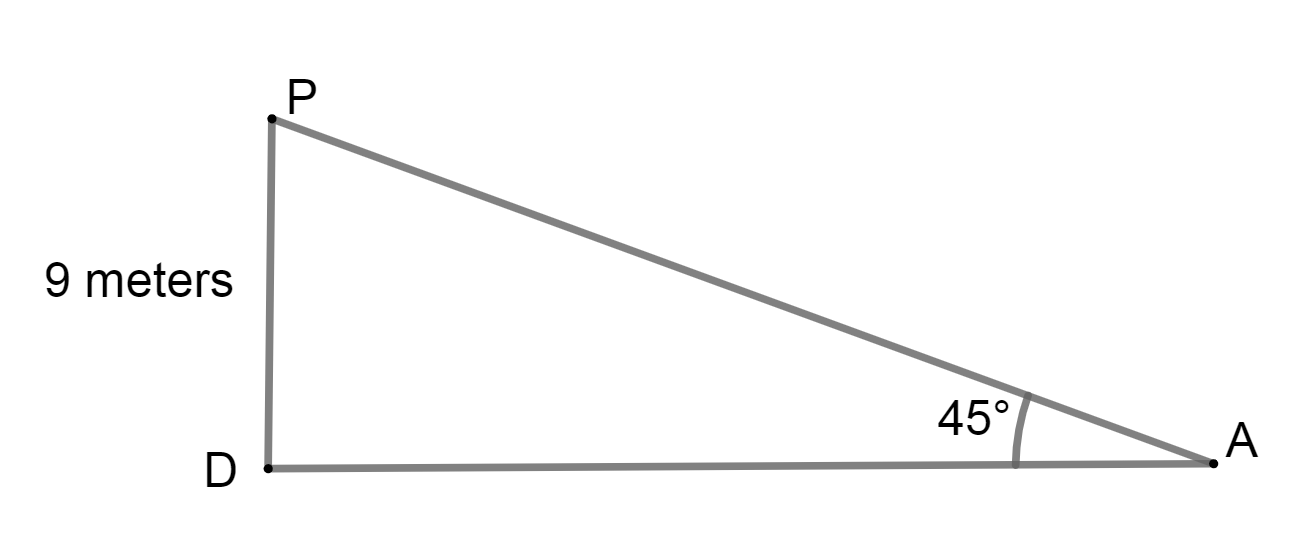
\[\begin{array}{l}\tan A = \dfrac{{PD}}{{AD}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{9}{{AD}}\end{array}\]
We know that, \[\tan {45^ \circ } = 1\]
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{9}{{AD}}\\ \Rightarrow AD = 9{\rm{ meter}}\end{array}\]
Again, in\[\Delta PDB\],
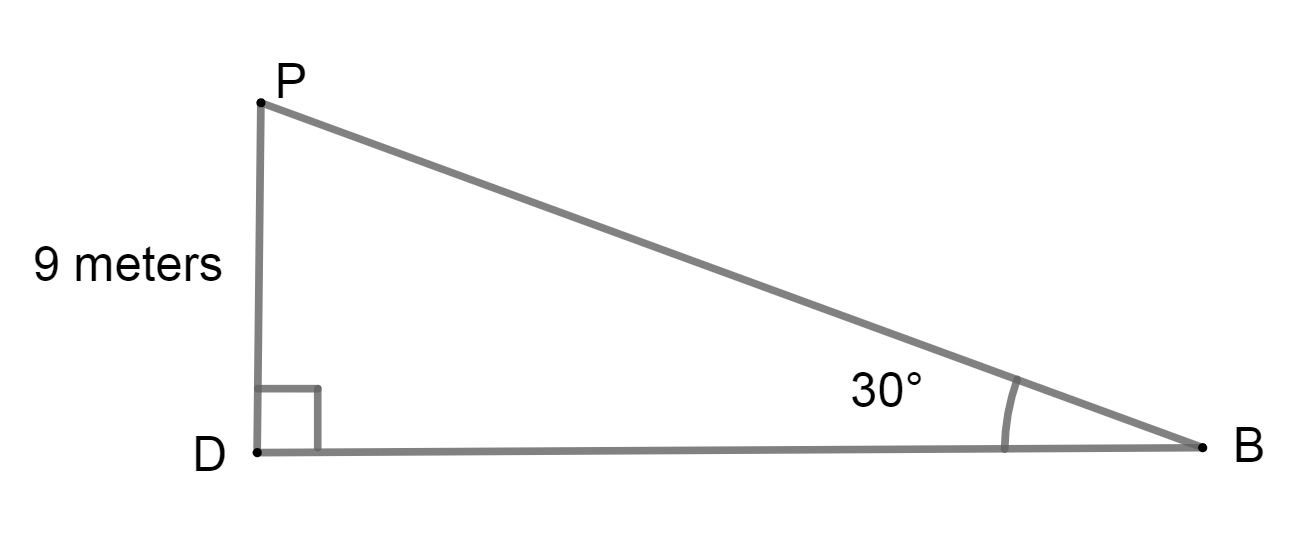
\[\begin{array}{l}\tan B = \dfrac{{PD}}{{BD}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{9}{{BD}}\end{array}\]
We know that, \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{9}{{BD}}\\ \Rightarrow BD = 9\sqrt 3 {\rm{ meter}}\end{array}\]
Now, 2n right angled triangle i.e. \[\Delta DAB\] by using Pythagoras theorem, we get
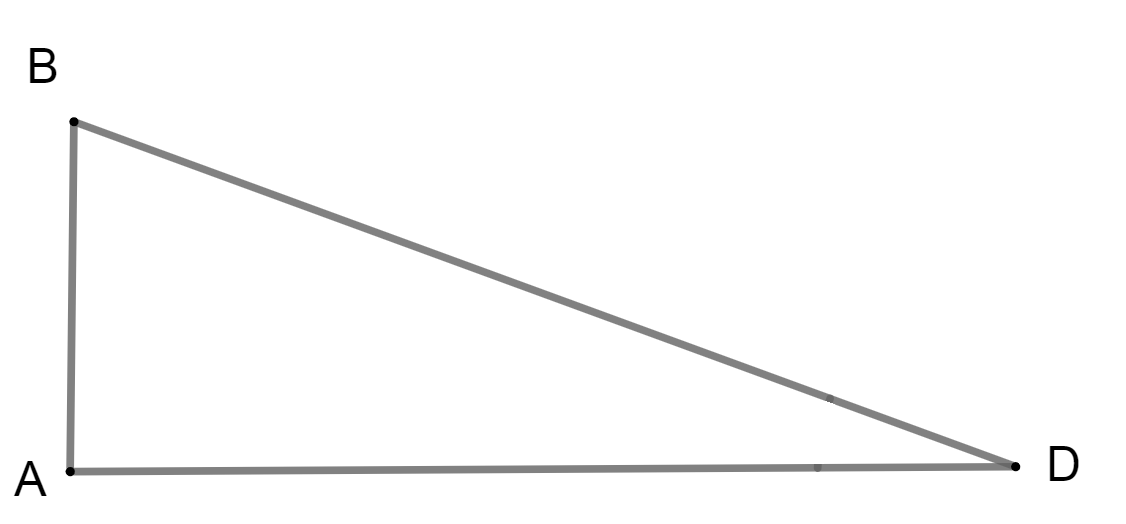
\[\begin{array}{l}A{B^2} + A{D^2} = B{D^2}\\A{B^2} + {9^2} = {\left( {9\sqrt 3 } \right)^2}\\A{B^2} + 81 = 243\\A{B^2} = 243 - 81\\A{B^2} = 162\\AB = \sqrt {162} \\AB = 9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ meter}}\end{array}\]
We know that, area of a rectangle is equal to the product of its length and breadth.
We have length = AD = 9 meter and
Breadth = AB = \[9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ meter}}\]
So,
\[\begin{array}{l}Area = AD \times AB\\ \Rightarrow 9 \times 9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ }}{{\rm{m}}^2}\\ \Rightarrow 81\sqrt 2 {\rm{ }}{{\rm{m}}^2}\end{array}\]
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note: It is very important to draw the diagram in height and distance problem as it becomes easy to visualize the things, which helps us to proceed further in the question. In this question, we might take \[{\rm{tan3}}{0^ \circ }\] as \[\sqrt 3 \] and get different answers. We have to find the sides of the rectangle, so we can use any technique to obtain the length. We must try to figure out how to proceed and then start calculating, this saves time and efforts too.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have been given that, a lamp post of height 9 meters stands at the corner of a rectangular field. Also, the angle of elevation of its top from farthest corner is \[{30^ \circ }\] while from another corner is \[{45^ \circ }\]

We have PD= 9 meters
Now, in \[\Delta AOP\],

\[\begin{array}{l}\tan A = \dfrac{{PD}}{{AD}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan {45^ \circ } = \dfrac{9}{{AD}}\end{array}\]
We know that, \[\tan {45^ \circ } = 1\]
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{9}{{AD}}\\ \Rightarrow AD = 9{\rm{ meter}}\end{array}\]
Again, in\[\Delta PDB\],

\[\begin{array}{l}\tan B = \dfrac{{PD}}{{BD}}\\ \Rightarrow \tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{9}{{BD}}\end{array}\]
We know that, \[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }}\]
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{9}{{BD}}\\ \Rightarrow BD = 9\sqrt 3 {\rm{ meter}}\end{array}\]
Now, 2n right angled triangle i.e. \[\Delta DAB\] by using Pythagoras theorem, we get

\[\begin{array}{l}A{B^2} + A{D^2} = B{D^2}\\A{B^2} + {9^2} = {\left( {9\sqrt 3 } \right)^2}\\A{B^2} + 81 = 243\\A{B^2} = 243 - 81\\A{B^2} = 162\\AB = \sqrt {162} \\AB = 9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ meter}}\end{array}\]
We know that, area of a rectangle is equal to the product of its length and breadth.
We have length = AD = 9 meter and
Breadth = AB = \[9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ meter}}\]
So,
\[\begin{array}{l}Area = AD \times AB\\ \Rightarrow 9 \times 9\sqrt 2 {\rm{ }}{{\rm{m}}^2}\\ \Rightarrow 81\sqrt 2 {\rm{ }}{{\rm{m}}^2}\end{array}\]
Therefore, the correct option is C.
Note: It is very important to draw the diagram in height and distance problem as it becomes easy to visualize the things, which helps us to proceed further in the question. In this question, we might take \[{\rm{tan3}}{0^ \circ }\] as \[\sqrt 3 \] and get different answers. We have to find the sides of the rectangle, so we can use any technique to obtain the length. We must try to figure out how to proceed and then start calculating, this saves time and efforts too.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




