
A vertical lamp post, 6 m high, stands at a distance of 2m from a wall, 4m high. A 1.5m tall man starts to walk away from the wall on the other side of the wall, in line with the lamp-post. The maximum distance to which the man can walk remaining in the shadow is
a.\[\dfrac{5}{2}m\]
b.\[\dfrac{3}{2}m\]
c.4m
d.None of these
Answer
603k+ views
Hint: First of all, draw the appropriate figure with the help of data provided in the question. PQ as the height of the vertical lamp, AB as the height of the wall, and CD as the height of the man. Now, join the points P, Q, and R. We have \[\Delta ABR\simeq \Delta CDR\] and \[\Delta PQR\simeq \Delta ABR\] . Using this, we can write \[\dfrac{BR}{DR}=\dfrac{AB}{CD}=\dfrac{4}{1.5}=\dfrac{8}{3}\] and \[\dfrac{PQ}{AB}=\dfrac{QR}{BR}\] . Now, solve these two equations and get the values of length BR and DR. The maximum distance to which the man can walk remaining in the shadow is BR-DR. Solve it further.
Complete step-by-step answer:
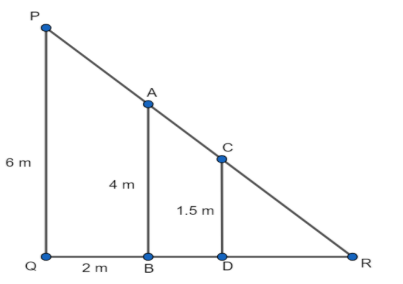
According to the figure we have, PQ as the height of the vertical lamp, AB as the height of the wall, and CD as the height of the man.
The distance between the wall and vertical lamp = QB = 2 m.
The height of the vertical lamp = PQ = 6 m.
The height of the wall = AB = 4 m.
The height of the man = CD = 1.5 m.
In the \[\Delta ABR\] and \[\Delta CDR\] , we have
\[\angle ABR=\angle CDR={{90}^{0}}\]
\[\angle ARB=\angle CRD\] (angles common in both triangles)
If any two triangles have two equal angles then the third angle of both triangles is also equal.
So, \[\angle BAR=\angle DCR\] .
So, \[\Delta ABR\simeq \Delta CDR\] .
We have, \[\Delta ABR\simeq \Delta CDR\] ,
\[\dfrac{BR}{DR}=\dfrac{AB}{CD}=\dfrac{4}{1.5}=\dfrac{8}{3}\] …………………..(1)
In the \[\Delta ABR\] and \[\Delta PQR\] , we have
\[\angle ABR=\angle PQR={{90}^{0}}\]
\[\angle ARB=\angle PRQ\] (angles common in both triangles)
If any two triangles have two equal angles then the third angle of both triangles is also equal.
So, \[\angle BAR=\angle QPR\] .
So, \[\Delta PQR\simeq \Delta ABR\]
We have, \[\Delta PQR\simeq \Delta ABR\] ,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{PQ}{AB}=\dfrac{QR}{BR} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{6}{4}=\dfrac{BQ+BR}{BR} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{2+BR}{BR} \\
& \Rightarrow 3BR=4+2BR \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow BR=4\] …………………..(2)
From equation (1) and equation (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{4}{DR}=\dfrac{8}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}=DR \\
\end{align}\]
From the figure, we can see that
BD = BR – DR = \[4-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{5}{2}\] .
So, the maximum distance to which the man can walk remaining in the shadow is \[\dfrac{5}{2}\] .
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In this question, one can think that the man walks between the wall and the vertical lamp post which is wrong. As in the question, it is given that the man walks away from the wall to the other side of the wall, so we can’t think that the man walks between the wall and the vertical lamp.
Complete step-by-step answer:

According to the figure we have, PQ as the height of the vertical lamp, AB as the height of the wall, and CD as the height of the man.
The distance between the wall and vertical lamp = QB = 2 m.
The height of the vertical lamp = PQ = 6 m.
The height of the wall = AB = 4 m.
The height of the man = CD = 1.5 m.
In the \[\Delta ABR\] and \[\Delta CDR\] , we have
\[\angle ABR=\angle CDR={{90}^{0}}\]
\[\angle ARB=\angle CRD\] (angles common in both triangles)
If any two triangles have two equal angles then the third angle of both triangles is also equal.
So, \[\angle BAR=\angle DCR\] .
So, \[\Delta ABR\simeq \Delta CDR\] .
We have, \[\Delta ABR\simeq \Delta CDR\] ,
\[\dfrac{BR}{DR}=\dfrac{AB}{CD}=\dfrac{4}{1.5}=\dfrac{8}{3}\] …………………..(1)
In the \[\Delta ABR\] and \[\Delta PQR\] , we have
\[\angle ABR=\angle PQR={{90}^{0}}\]
\[\angle ARB=\angle PRQ\] (angles common in both triangles)
If any two triangles have two equal angles then the third angle of both triangles is also equal.
So, \[\angle BAR=\angle QPR\] .
So, \[\Delta PQR\simeq \Delta ABR\]
We have, \[\Delta PQR\simeq \Delta ABR\] ,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{PQ}{AB}=\dfrac{QR}{BR} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{6}{4}=\dfrac{BQ+BR}{BR} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{2+BR}{BR} \\
& \Rightarrow 3BR=4+2BR \\
\end{align}\]
\[\Rightarrow BR=4\] …………………..(2)
From equation (1) and equation (2), we get
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{4}{DR}=\dfrac{8}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{3}{2}=DR \\
\end{align}\]
From the figure, we can see that
BD = BR – DR = \[4-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{5}{2}\] .
So, the maximum distance to which the man can walk remaining in the shadow is \[\dfrac{5}{2}\] .
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In this question, one can think that the man walks between the wall and the vertical lamp post which is wrong. As in the question, it is given that the man walks away from the wall to the other side of the wall, so we can’t think that the man walks between the wall and the vertical lamp.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




