
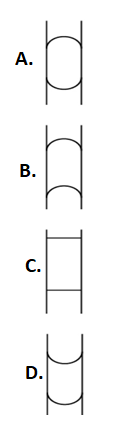
A vertical glass capillary tube, open at both ends, contains some water. Which of the following shapes may not be taken by the water in the tube?

Answer
523.9k+ views
Hint: The shape of water in a capillary tube is decided by the external pressure on the water. Since the tube is open at both ends, the weight of water will also play an important role. The surface tension of water tries to keep all other forces in equilibrium. This determines the shape of water.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Surface tension of any liquid is defined by the force per unit length of the line imagined along the surface of the liquid. To have a better idea, imagine that a rubber sheet is being expanded. That is the exact condition of the surface of a liquid like water.
For the upper shape:
In the upper part, the pressure of air and the pressure inside water are not the same. The atmospheric pressure is greater. As a result, water gets a concave shape and tries to anticipate the downward force due to excess pressure. The components of the surface tension along the upward direction is equal to the force due to atmospheric pressure. (Excess pressure is the difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure inside the water.) So, the upper side of water is concave.
For the lower shape:
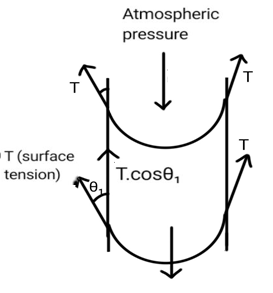
In the lower side, both the weight of the water and the atmospheric pressure applies a force in the downward direction. In order to anticipate this large force, the water surface is convex (when looked from the outside). In this way, the components of the surface tension along the upward direction is equal to the net downward force. Hence, this end is convex from the outside.
So, the only correct shape is the one shown in option D. And all the other shapes can not be taken by the water. So, the answer to this question is option A, B and C.
Note: Surface tension in any liquid arises due to attraction between the molecules. It makes the surface like a stretched rubber sheet that tries to apply force in the outward direction. The angles between the surface of water and the glass may not be the same at the upper and the lower surface.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Surface tension of any liquid is defined by the force per unit length of the line imagined along the surface of the liquid. To have a better idea, imagine that a rubber sheet is being expanded. That is the exact condition of the surface of a liquid like water.
For the upper shape:
In the upper part, the pressure of air and the pressure inside water are not the same. The atmospheric pressure is greater. As a result, water gets a concave shape and tries to anticipate the downward force due to excess pressure. The components of the surface tension along the upward direction is equal to the force due to atmospheric pressure. (Excess pressure is the difference between atmospheric pressure and the pressure inside the water.) So, the upper side of water is concave.
For the lower shape:

In the lower side, both the weight of the water and the atmospheric pressure applies a force in the downward direction. In order to anticipate this large force, the water surface is convex (when looked from the outside). In this way, the components of the surface tension along the upward direction is equal to the net downward force. Hence, this end is convex from the outside.
So, the only correct shape is the one shown in option D. And all the other shapes can not be taken by the water. So, the answer to this question is option A, B and C.
Note: Surface tension in any liquid arises due to attraction between the molecules. It makes the surface like a stretched rubber sheet that tries to apply force in the outward direction. The angles between the surface of water and the glass may not be the same at the upper and the lower surface.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




