
A variable plane is at a constant distance p from the origin and meets the axes in A, B and C. The locus of the centroid of the triangle ABC is
(a) \[{{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}={{p}^{-2}}\]
(b) \[{{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=4{{p}^{-2}}\]
(c) \[{{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=16{{p}^{-2}}\]
(d) \[{{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=9{{p}^{-2}}\]
Answer
551.7k+ views
Hint: We can assume the coordinates of the points A, B and C as $\left( a,0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,b,0 \right)$ and $\left( 0,0,c \right)$. From these coordinates, we can determine the coordinates of the centroid of the triangle ABC as $x=\dfrac{a}{3},y=\dfrac{b}{3},z=\dfrac{c}{3}$. Also, the equation of the plane, from the intercept form can be determine as $\dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}+\dfrac{z}{c}=1$. From this equation, we can determine the distance of the plane from the origin, which is given to be equal to p, in terms of a, b and c. The values of a, b and c can be substituted in terms of the coordinates of the centroid given as $x=\dfrac{a}{3},y=\dfrac{b}{3},z=\dfrac{c}{3}$ to get the final equation of the locus of the centroid.
Complete step by step solution:
Let the coordinates of the points A, B and C be $\left( a,0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,b,0 \right)$ and $\left( 0,0,c \right)$, so that the plane will look like
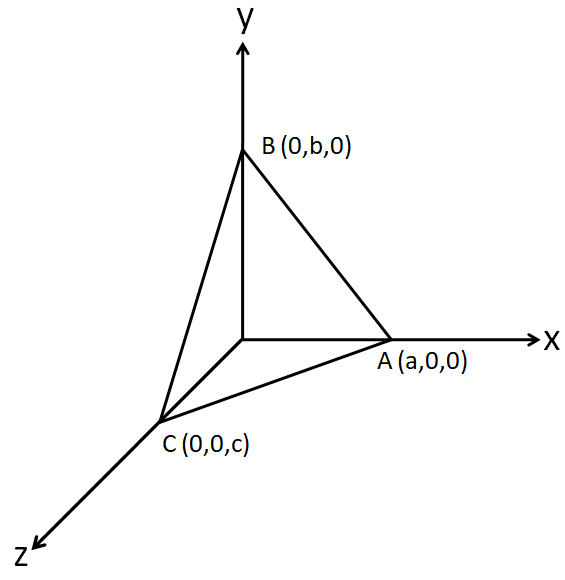
Therefore, the x coordinate of the triangle ABC becomes
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{a+0+0}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{a}{3}......\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, the y and the z coordinates can be given by
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{b}{3}......\left( ii \right) \\
& \Rightarrow z=\dfrac{c}{3}......\left( iii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Multiplying the equation (i) by $3$ we get
$\Rightarrow a=3x......\left( iv \right)$
Similarly, from the equations (ii) and (iii) we obtain
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow b=3y.......\left( v \right) \\
& \Rightarrow c=3z.......\left( vi \right) \\
\end{align}$
From the intercept form of the equation of a plane, we can write the equation of the given plane as
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}+\dfrac{z}{c}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}+\dfrac{z}{c}-1=0 \\
\end{align}$
According to the question, the distance of the plane from the origin is equal to p. Thereofr, we can write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{\left| \dfrac{0}{a}+\dfrac{0}{b}+\dfrac{0}{c}-1 \right|}{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking the reciprocals of both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{p}=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}}}$
Now, taking the squares of both the sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{1}{p} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{c}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the equations (iv), (v) and (vi) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{\left( 3x \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\left( 3y \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\left( 3z \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{9{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{9{{y}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{9{{z}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Multiplying both sides by \[9\] we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{y}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{z}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 9{{p}^{-2}}={{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=9{{p}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the locus of the triangle ABC is found out to be ${{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=9{{p}^{-2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option d”.
Note: For solving these kinds of questions, we need to remember the different forms of the equation of a plane. Also, we need to remember the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle, which are equal to the average of the coordinates of its vertices. Do not forget the square root sign in the distance formula.
Complete step by step solution:
Let the coordinates of the points A, B and C be $\left( a,0,0 \right)$, $\left( 0,b,0 \right)$ and $\left( 0,0,c \right)$, so that the plane will look like

Therefore, the x coordinate of the triangle ABC becomes
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{a+0+0}{3} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{a}{3}......\left( i \right) \\
\end{align}$
Similarly, the y and the z coordinates can be given by
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=\dfrac{b}{3}......\left( ii \right) \\
& \Rightarrow z=\dfrac{c}{3}......\left( iii \right) \\
\end{align}$
Multiplying the equation (i) by $3$ we get
$\Rightarrow a=3x......\left( iv \right)$
Similarly, from the equations (ii) and (iii) we obtain
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow b=3y.......\left( v \right) \\
& \Rightarrow c=3z.......\left( vi \right) \\
\end{align}$
From the intercept form of the equation of a plane, we can write the equation of the given plane as
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}+\dfrac{z}{c}=1 \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{x}{a}+\dfrac{y}{b}+\dfrac{z}{c}-1=0 \\
\end{align}$
According to the question, the distance of the plane from the origin is equal to p. Thereofr, we can write
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{\left| \dfrac{0}{a}+\dfrac{0}{b}+\dfrac{0}{c}-1 \right|}{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}}}} \\
\end{align}$
Taking the reciprocals of both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{p}=\sqrt{{{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}}}$
Now, taking the squares of both the sides, we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow {{\left( \dfrac{1}{p} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \dfrac{1}{a} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{b} \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \dfrac{1}{c} \right)}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{a}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{b}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{c}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}$
Substituting the equations (iv), (v) and (vi) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{\left( 3x \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\left( 3y \right)}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{\left( 3z \right)}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{9{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{9{{y}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{9{{z}^{2}}} \\
\end{align}\]
Multiplying both sides by \[9\] we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{9}{{{p}^{2}}}=\dfrac{1}{{{x}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{y}^{2}}}+\dfrac{1}{{{z}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow 9{{p}^{-2}}={{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}} \\
& \Rightarrow {{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=9{{p}^{-2}} \\
\end{align}$
Thus, the locus of the triangle ABC is found out to be ${{x}^{-2}}+{{y}^{-2}}+{{z}^{-2}}=9{{p}^{-2}}$.
So, the correct answer is “Option d”.
Note: For solving these kinds of questions, we need to remember the different forms of the equation of a plane. Also, we need to remember the coordinates of the centroid of a triangle, which are equal to the average of the coordinates of its vertices. Do not forget the square root sign in the distance formula.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




