
A unit radian is approximately equal to
[a] $57{}^\circ 17'43''$
[b] $57{}^\circ 17'45''$
[c] $57{}^\circ 17'47''$
[d] $57{}^\circ 17'49''$
Answer
612k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that one complete angle in degrees is equal to $360{}^\circ $ and in radians is equal to $2\pi $radians. Hence find the measure of one radian in degrees.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Systems of measurement of an angle:
[i] Sexagesimal system or English system: In this system of measurement, an angle is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds. One complete rotation is equal to $360{}^\circ $ , and one degree consists of 60 minutes and one minute consists of 60 seconds.
[ii] Centesimal system or the French system: In this system of measurement, an angle is measured in grades, minutes and seconds. One right angle consists of 100 grads, and one grade consists of 100 minutes and one minute consists of 100 seconds.
[iii] Circular system: This is the standard system of measurement of an angle. In this system, an angle is measured in radians. The angle subtended by an arc of length equal to the radius of a circle at the centre of the circle is equal to 1 radian.
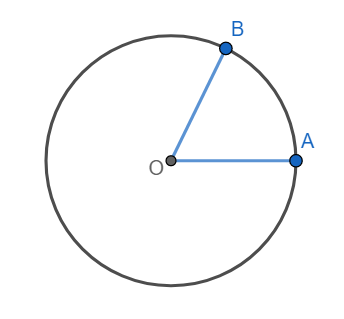
Consider angle AOB in which OA = 1unit and arc AB is of length 1 unit. Hence according to the definition $\angle AOB=1$ radians.
Since the complete length of the circular arc $=2\pi $, we have one complete rotation that is equal to $2\pi $ radians.
But one complete rotation is equal to $360{}^\circ $
Hence we have
$360{}^\circ =2\pi $ radians
Hence $1\text{ radian = }\dfrac{360{}^\circ }{2\pi }=57.296{}^\circ $
Now we have $0.296{}^\circ =0.296\times 60=17.76'$
Also, we have $0.76'=0.76\times 60=45.6''$
Hence $1\text{ radian }\approx \text{57}{}^\circ \text{17 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ 45}''$
Hence option [b] is correct.
Note: Alternatively, we can find the measure of one radian by calculating the area of the sector AOB in two different ways.
In the circulatory system area of the sector AOB $=\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\times \pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}$
In the sexagesimal system area of sector AOB $=\dfrac{\theta }{360{}^\circ }\times \pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}$, where $\theta $ is the measure of the angle in the sexagesimal system.
Hence we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\theta }{360{}^\circ }\times \pi =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\times \pi \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{360{}^\circ }{2\pi } \\
\end{align}$
which is the same as obtained above.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Systems of measurement of an angle:
[i] Sexagesimal system or English system: In this system of measurement, an angle is measured in degrees, minutes and seconds. One complete rotation is equal to $360{}^\circ $ , and one degree consists of 60 minutes and one minute consists of 60 seconds.
[ii] Centesimal system or the French system: In this system of measurement, an angle is measured in grades, minutes and seconds. One right angle consists of 100 grads, and one grade consists of 100 minutes and one minute consists of 100 seconds.
[iii] Circular system: This is the standard system of measurement of an angle. In this system, an angle is measured in radians. The angle subtended by an arc of length equal to the radius of a circle at the centre of the circle is equal to 1 radian.

Consider angle AOB in which OA = 1unit and arc AB is of length 1 unit. Hence according to the definition $\angle AOB=1$ radians.
Since the complete length of the circular arc $=2\pi $, we have one complete rotation that is equal to $2\pi $ radians.
But one complete rotation is equal to $360{}^\circ $
Hence we have
$360{}^\circ =2\pi $ radians
Hence $1\text{ radian = }\dfrac{360{}^\circ }{2\pi }=57.296{}^\circ $
Now we have $0.296{}^\circ =0.296\times 60=17.76'$
Also, we have $0.76'=0.76\times 60=45.6''$
Hence $1\text{ radian }\approx \text{57}{}^\circ \text{17 }\!\!'\!\!\text{ 45}''$
Hence option [b] is correct.
Note: Alternatively, we can find the measure of one radian by calculating the area of the sector AOB in two different ways.
In the circulatory system area of the sector AOB $=\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\times \pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}$
In the sexagesimal system area of sector AOB $=\dfrac{\theta }{360{}^\circ }\times \pi {{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}$, where $\theta $ is the measure of the angle in the sexagesimal system.
Hence we have
$\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\theta }{360{}^\circ }\times \pi =\dfrac{1}{2\pi }\times \pi \\
& \Rightarrow \theta =\dfrac{360{}^\circ }{2\pi } \\
\end{align}$
which is the same as obtained above.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




