
A uniform stick of mass $M$ is placed in a frictionless well as shown in the figure. The stick makes an angle $\theta$ with the horizontal. Then the force which the vertical wall exerts on right end of stick is:
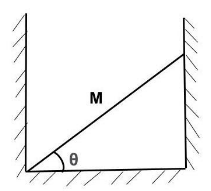
A. $\dfrac{{Mg}}{{2\cot \theta }}$
B. $\dfrac{{Mg}}{{2\tan \theta }}$
C. $\dfrac{{Mg}}{{2\cos \theta }}$
D. $\dfrac{{Mg}}{{2\sin \theta }}$

Answer
513k+ views
Hint: In physics, a force is any uncontested interaction that causes an object's velocity to change. As a result of a force, an item with mass can change its velocity, or accelerate. A push or a pull is an intuitive way to convey force.
Complete step by step answer:
An inclined plane, also known as a slope, is a flat supporting surface that is tilted at an angle to assist in the raising or lowering of a weight, with one end higher than the other. The inclined plane is one of Renaissance scientists' six ancient basic machines. A mechanical advantage is created by using an inclined plane to make labour easier. The inclined plane makes work easier by lowering the amount of effort required to lift or lower a load. This is done by extending the load's travel distance along the length of the slope.
Now, let us solve the given question;
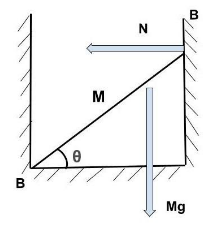
The vertical wall exerts a force of N on the stick, while the stick's weight of mg works downward as illustrated. Torque is the force that may rotate an object around an axis. In linear kinematics, force causes an object to accelerate. Torque is also what generates angular acceleration. As a result, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force.
When the torque is calculated around point A on the ground (as illustrated) for rotational equilibrium, the anti-clockwise torque by N is balanced by the clockwise torque by the stick's weight.
${\tau _{mg}} = {\tau _N} \\
\Rightarrow mg\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}\cos \theta } \right) = N\left( {1\sin \theta } \right)\, \\ $
The length of the stick is denoted by the letter ‘L.'
$\dfrac{{mg\cot \theta }}{2} = N \\
\therefore N = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2\tan \theta }} \\ $
As a result, the force exerted on the right end of the stick by the vertical wall is $\dfrac{{Mg}}{{2\tan \theta }}$.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:The route along which a force works on an item is referred to as the force line. The location where a force acts on an item is called the point of application of the force.Friction is a force that acts along the surfaces of two things in touch to oppose relative motion between them.
Complete step by step answer:
An inclined plane, also known as a slope, is a flat supporting surface that is tilted at an angle to assist in the raising or lowering of a weight, with one end higher than the other. The inclined plane is one of Renaissance scientists' six ancient basic machines. A mechanical advantage is created by using an inclined plane to make labour easier. The inclined plane makes work easier by lowering the amount of effort required to lift or lower a load. This is done by extending the load's travel distance along the length of the slope.
Now, let us solve the given question;

The vertical wall exerts a force of N on the stick, while the stick's weight of mg works downward as illustrated. Torque is the force that may rotate an object around an axis. In linear kinematics, force causes an object to accelerate. Torque is also what generates angular acceleration. As a result, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force.
When the torque is calculated around point A on the ground (as illustrated) for rotational equilibrium, the anti-clockwise torque by N is balanced by the clockwise torque by the stick's weight.
${\tau _{mg}} = {\tau _N} \\
\Rightarrow mg\left( {\dfrac{1}{2}\cos \theta } \right) = N\left( {1\sin \theta } \right)\, \\ $
The length of the stick is denoted by the letter ‘L.'
$\dfrac{{mg\cot \theta }}{2} = N \\
\therefore N = \dfrac{{mg}}{{2\tan \theta }} \\ $
As a result, the force exerted on the right end of the stick by the vertical wall is $\dfrac{{Mg}}{{2\tan \theta }}$.
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note:The route along which a force works on an item is referred to as the force line. The location where a force acts on an item is called the point of application of the force.Friction is a force that acts along the surfaces of two things in touch to oppose relative motion between them.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




