
A uniform rod of mass m and length \[l\] is free to rotate about the fixed horizontal axis through its end and perpendicular to its length. Find the period of small oscillation of rod
Answer
493.8k+ views
Hint: The moment of inertia is dependent upon the axis of rotation.
The moment of inertia gets affected by two variables. Distance and mass are the two variables that affect the moment of inertia.
Complete step by step solution:
The ordinary object’s moment of inertia involves a continuous distribution of mass at a frequently varying distance from any rotation axis, the moments of inertia calculation involve calculus, the mathematics discipline it can handle continuous variables.
The resistance of a rigid body to rotational motion is called a moment of inertia. based on the distribution of mass over a rigid body the moment of inertia is altered. Consider the example: when the moment of Inertia increases the Torque of the object in rotational motion also increases.
Now,
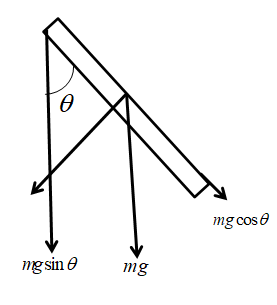
$z = mg\sin \theta \left( {\dfrac{l}{2}} \right)$
If $\theta $ is smaller than $\sin \theta \approx \theta $
Hence,
$z = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\theta = 1\alpha $
Now the equation becomes,
$\theta \dfrac{{mgl}}{2} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{3}\alpha $
After simplification,
$\alpha = \dfrac{{3g}}{{2l}}\theta = {\omega ^2}\theta $
Here,
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3g}}{{2l}}} $
And,
$T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
After substituting the values the above equation becomes,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{3g}}} $
Therefore the answer is, $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{3g}}} $
Note: The measure of the distribution of mass of an object is known as the mass moment of inertia. The geometrical property of an area that shows how points are distributed is known as the area moment of inertia. The polar moment of inertia is the function of shape which is referred to as shaft or beam resistance is distorted by the torsion.
The moment of inertia gets affected by two variables. Distance and mass are the two variables that affect the moment of inertia.
Complete step by step solution:
The ordinary object’s moment of inertia involves a continuous distribution of mass at a frequently varying distance from any rotation axis, the moments of inertia calculation involve calculus, the mathematics discipline it can handle continuous variables.
The resistance of a rigid body to rotational motion is called a moment of inertia. based on the distribution of mass over a rigid body the moment of inertia is altered. Consider the example: when the moment of Inertia increases the Torque of the object in rotational motion also increases.
Now,

$z = mg\sin \theta \left( {\dfrac{l}{2}} \right)$
If $\theta $ is smaller than $\sin \theta \approx \theta $
Hence,
$z = mg\dfrac{l}{2}\theta = 1\alpha $
Now the equation becomes,
$\theta \dfrac{{mgl}}{2} = \dfrac{{m{l^2}}}{3}\alpha $
After simplification,
$\alpha = \dfrac{{3g}}{{2l}}\theta = {\omega ^2}\theta $
Here,
$\omega = \sqrt {\dfrac{{3g}}{{2l}}} $
And,
$T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$
After substituting the values the above equation becomes,
$T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{3g}}} $
Therefore the answer is, $T = 2\pi \sqrt {\dfrac{{2l}}{{3g}}} $
Note: The measure of the distribution of mass of an object is known as the mass moment of inertia. The geometrical property of an area that shows how points are distributed is known as the area moment of inertia. The polar moment of inertia is the function of shape which is referred to as shaft or beam resistance is distorted by the torsion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




