
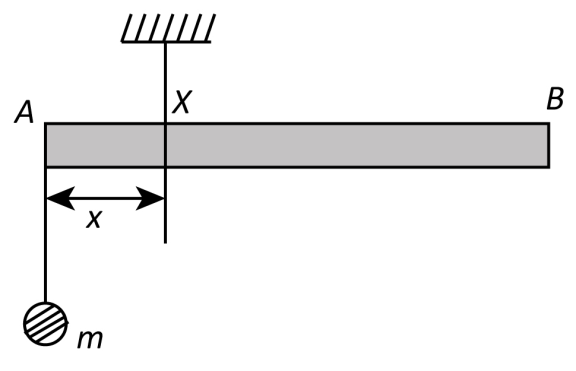
A uniform rod $ AB $ is suspended from a point X, at a variable distance $ x $ from A, as shown. To make the rod horizontal, a mass $ m $ is suspended from its end $ A $ . A set of ( $ m,x $ ) values is recorded. The appropriate variables that give a straight line, when plotted, are:
(A) $ m,\;\dfrac{1}{x} $
(B) $ m,\;\dfrac{1}{{{x^2}}} $
(C) $ m,\;x $
(D) $ m,\;{x^2} $

Answer
538.2k+ views
Hint :Assume mass and length of the rod and take a moment about point X and compare the equation with the equation of line, $ y = mx + c $ .
Complete Step By Step Answer:
From the given question, we know that the A uniform rod $ AB $ is suspended from a point X, at a variable distance $ x $ from A and mass $ m $ is suspended from the end $ A $ .
Let us consider the mass of the rod $ AB $ be $ M $ and length of the rod be $ L $ .
The figure below represents the free body diagram of the rod.
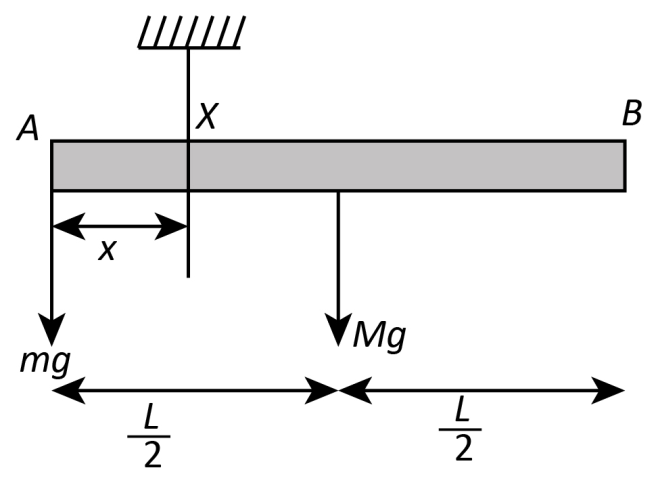
Now for the rod to be in equilibrium (horizontal), we take the moment about its end $ A $ ,
We are taking the anti- clockwise direction of the moment as positive.
$
\sum {{M_A} = 0} \\
mg\left( x \right) - Mg\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} - x} \right) = 0
$
Rewrite the above equation.
$ mg\left( x \right) = Mg\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} - x} \right) $
$ mx = \left( {\dfrac{{ML}}{2}} \right)\dfrac{1}{x} - M $ ... (I)
We know that the equation of a line is represented by $ {y_1} = m{y_2} + c $ where $ {y_1} $ and $ {y_2} $ are the variables of two axis’, $ m $ is slope and $ c $ is the intercept.
Compare the equation of line with equation (I), we get,
$ {y_1} = m $ and $ {y_2} = \dfrac{1}{x} $
Thus, the appropriate variables that give a straight line, when plotted, are $ m $ and $ \dfrac{1}{x} $ and option (A) is correct.
Note :
While taking the moment, you can assume a counter- clockwise direction as positive and clockwise wise direction is negative, but use assume also assume the opposite. And always the perpendicular distance from the force to the point about which you want to take a moment.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
From the given question, we know that the A uniform rod $ AB $ is suspended from a point X, at a variable distance $ x $ from A and mass $ m $ is suspended from the end $ A $ .
Let us consider the mass of the rod $ AB $ be $ M $ and length of the rod be $ L $ .
The figure below represents the free body diagram of the rod.

Now for the rod to be in equilibrium (horizontal), we take the moment about its end $ A $ ,
We are taking the anti- clockwise direction of the moment as positive.
$
\sum {{M_A} = 0} \\
mg\left( x \right) - Mg\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} - x} \right) = 0
$
Rewrite the above equation.
$ mg\left( x \right) = Mg\left( {\dfrac{L}{2} - x} \right) $
$ mx = \left( {\dfrac{{ML}}{2}} \right)\dfrac{1}{x} - M $ ... (I)
We know that the equation of a line is represented by $ {y_1} = m{y_2} + c $ where $ {y_1} $ and $ {y_2} $ are the variables of two axis’, $ m $ is slope and $ c $ is the intercept.
Compare the equation of line with equation (I), we get,
$ {y_1} = m $ and $ {y_2} = \dfrac{1}{x} $
Thus, the appropriate variables that give a straight line, when plotted, are $ m $ and $ \dfrac{1}{x} $ and option (A) is correct.
Note :
While taking the moment, you can assume a counter- clockwise direction as positive and clockwise wise direction is negative, but use assume also assume the opposite. And always the perpendicular distance from the force to the point about which you want to take a moment.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




