
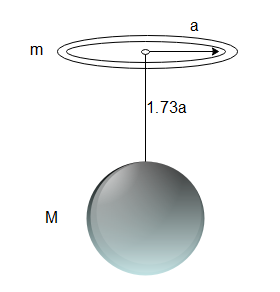
A uniform ring of mass m is lying at a distance $ 1.73a\; $ from the centre of a sphere of mass $ M $ just over the sphere where $ a $ is the small radius of the ring as well as that of the sphere. Then, the gravitational force exerted by one on the other is
(A) $ \dfrac{{GMm}}{{8{a^2}}} $
(B) $ \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{{\left( {1.73a} \right)}^2}}} $
(C) $ \sqrt 3 \dfrac{{GMm}}{{{a^2}}} $
(D) $ 1.73\dfrac{{GMm}}{{8{a^2}}} $

Answer
562.8k+ views
Hint: In this solution, we will calculate the gravitational force exerted by the ring on the sphere. The force exerted by one on the other will have the same magnitude but opposite directions.
Formula used:
In this solution, we will use the following formula:
- Gravitational acceleration due to a ring: $ F = GMm\dfrac{r}{{{{\left( {{r^2} + {R^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $ where $ R $ is the radius on the ring and $ r $ is the distance of the point from the ring.
Complete step by step answer:
In the configuration of the ring and the sphere given to us, we can calculate the force between the two objects by considering the mass of the sphere to be concentrated at a point that lies at the centre of the sphere.
Then the distance of the point that is at the centre of the sphere from the centre of the ring will be $ r = 1.73a $ . As the radius of the ring is $ R = a $ , the force between the ring and the sphere will be
$ F = GMm\dfrac{{1.73a}}{{{{\left( {{{\left( {1.73a} \right)}^2} + {a^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Simplifying the denominator, we can write
$ F = GMm\dfrac{{1.73a}}{{{a^3}{4^{3/2}}}} $
This can be simplified to
$ F = 1.73\dfrac{{GMm}}{{8{a^2}}} $
Hence the force between the sphere and the ring will be $ F = 1.73\dfrac{{GMm}}{{8{a^2}}} $ which corresponds to option (D).
Note:
In such solutions, we must realize to use the concepts of symmetry to break the problem down to calculating the gravitational force between a ring and a point mass. We cannot consider the ring as a point mass in this case since its mass distribution is not uniform in space. However, the mass distribution of the sphere is constant, which is why we can consider it a point mass lying at the center of the sphere which will simplify our calculations.
Formula used:
In this solution, we will use the following formula:
- Gravitational acceleration due to a ring: $ F = GMm\dfrac{r}{{{{\left( {{r^2} + {R^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $ where $ R $ is the radius on the ring and $ r $ is the distance of the point from the ring.
Complete step by step answer:
In the configuration of the ring and the sphere given to us, we can calculate the force between the two objects by considering the mass of the sphere to be concentrated at a point that lies at the centre of the sphere.
Then the distance of the point that is at the centre of the sphere from the centre of the ring will be $ r = 1.73a $ . As the radius of the ring is $ R = a $ , the force between the ring and the sphere will be
$ F = GMm\dfrac{{1.73a}}{{{{\left( {{{\left( {1.73a} \right)}^2} + {a^2}} \right)}^{3/2}}}} $
Simplifying the denominator, we can write
$ F = GMm\dfrac{{1.73a}}{{{a^3}{4^{3/2}}}} $
This can be simplified to
$ F = 1.73\dfrac{{GMm}}{{8{a^2}}} $
Hence the force between the sphere and the ring will be $ F = 1.73\dfrac{{GMm}}{{8{a^2}}} $ which corresponds to option (D).
Note:
In such solutions, we must realize to use the concepts of symmetry to break the problem down to calculating the gravitational force between a ring and a point mass. We cannot consider the ring as a point mass in this case since its mass distribution is not uniform in space. However, the mass distribution of the sphere is constant, which is why we can consider it a point mass lying at the center of the sphere which will simplify our calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




