
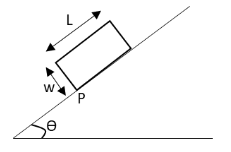
A uniform rectangular solid box of side length \[L\] and width \[w\] is placed on a frictionless incline of variable angle \[\theta \]. Assume that there is a very tiny peg preventing the box from sliding down the incline at the point labelled P. At what angle of incline will the box begin to tip over?
A. \[\theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\]
B. \[\theta = {\cos ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\]
C. \[\theta = {\tan ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\]
D. \[\theta = {\cot ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\]

Answer
560.7k+ views
Hint:Use the formula for torque acting on an object due to a force acting on the object. The condition for an object to be in equilibrium is the net torque due to all forces on the system is zero. Draw the free body diagram of the rectangular block and determine the net torque acting on the box about an axis passing through the point P. Solve the obtained equation and determine the angle for which the box will begin to tip over.
Formula used:
The torque \[\tau \] acting on an object due to the force \[F\] is given by
\[\tau = Fr\] …… (1)
Here, \[r\] is the perpendicular distance between the point of action of the force and centre of torque.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the length and width of the rectangular box placed on a frictionless inclined plane are \[L\] and \[w\] respectively. The angle made by the inclined plane with the horizontal is \[\theta \]. The peg placed at point P is preventing the rectangular block from sliding down. We have asked to determine the angle for which the block slides down the inclined plane. Let \[m\] be the mass of the rectangular block. Let us first draw the free body diagram of the rectangular block.
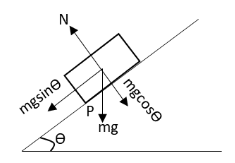
In the above free body diagram, \[mg\] is the weight of the rectangular block and \[N\] is the normal force exerted by the inclined plane on the block. The components of the weight of the rectangular block are shown in the free body diagram.
The rectangular block will be in equilibrium at point P if the net torque acting on this block about the point P is zero. The torque due to the forces \[N\] and \[mg\cos \theta \] will cancel each other. The net torque on the rectangular box about an axis passing through point P is only due to the forces \[mg\] and \[mg\sin \theta \]. The torque due to weight \[mg\] of the rectangular box is given by
\[{\tau _{mg}} = mg\dfrac{L}{2}\]
The torque due to the component of weight \[mg\sin \theta \] of the rectangular box is given by
\[{\tau _{mg\sin \theta }} = - mg\sin \theta \dfrac{w}{2}\]
Let us now determine the net torque acting on the rectangular block in equilibrium.
\[{\tau _{net}} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\tau _{mg}} + {\tau _{mg\sin \theta }} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow mg\dfrac{L}{2} - mg\sin \theta \dfrac{w}{2} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow mg\dfrac{L}{2} = mg\sin \theta \dfrac{w}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L = w\sin \theta \]
\[ \therefore \theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\]
Therefore, the angle of incline for which the box begins to tip over is \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\].
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: The students should not forget to use the correct sign for the torque due to different forces acting on the rectangular box as the sign for clockwise torque is negative and sign for counterclockwise torque is positive. Also the torque due to the equal force is zero. Hence, one should not consider the torque due to the equal forces as they will cancel each other.
Formula used:
The torque \[\tau \] acting on an object due to the force \[F\] is given by
\[\tau = Fr\] …… (1)
Here, \[r\] is the perpendicular distance between the point of action of the force and centre of torque.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the length and width of the rectangular box placed on a frictionless inclined plane are \[L\] and \[w\] respectively. The angle made by the inclined plane with the horizontal is \[\theta \]. The peg placed at point P is preventing the rectangular block from sliding down. We have asked to determine the angle for which the block slides down the inclined plane. Let \[m\] be the mass of the rectangular block. Let us first draw the free body diagram of the rectangular block.

In the above free body diagram, \[mg\] is the weight of the rectangular block and \[N\] is the normal force exerted by the inclined plane on the block. The components of the weight of the rectangular block are shown in the free body diagram.
The rectangular block will be in equilibrium at point P if the net torque acting on this block about the point P is zero. The torque due to the forces \[N\] and \[mg\cos \theta \] will cancel each other. The net torque on the rectangular box about an axis passing through point P is only due to the forces \[mg\] and \[mg\sin \theta \]. The torque due to weight \[mg\] of the rectangular box is given by
\[{\tau _{mg}} = mg\dfrac{L}{2}\]
The torque due to the component of weight \[mg\sin \theta \] of the rectangular box is given by
\[{\tau _{mg\sin \theta }} = - mg\sin \theta \dfrac{w}{2}\]
Let us now determine the net torque acting on the rectangular block in equilibrium.
\[{\tau _{net}} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\tau _{mg}} + {\tau _{mg\sin \theta }} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow mg\dfrac{L}{2} - mg\sin \theta \dfrac{w}{2} = 0\]
\[ \Rightarrow mg\dfrac{L}{2} = mg\sin \theta \dfrac{w}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L = w\sin \theta \]
\[ \therefore \theta = {\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\]
Therefore, the angle of incline for which the box begins to tip over is \[{\sin ^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{L}{w}} \right)\].
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: The students should not forget to use the correct sign for the torque due to different forces acting on the rectangular box as the sign for clockwise torque is negative and sign for counterclockwise torque is positive. Also the torque due to the equal force is zero. Hence, one should not consider the torque due to the equal forces as they will cancel each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




