
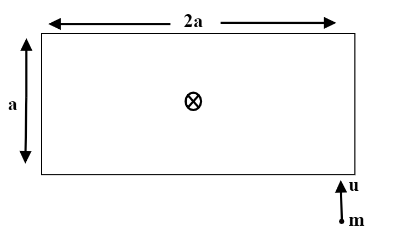
A uniform rectangular plate of mass m which is free to rotate about the smooth vertical hinge passing through the center and perpendicular to the plate is lying on a smooth horizontal surface. A particle of mass m moving with speed 'u' collides with the plate and sticks to it as shown in the figure. The angular velocity of the plate after the collision will be?
A). $ \dfrac{{12u}}{{5a}} $
B). $ \dfrac{{12u}}{{19a}} $
C). $ \dfrac{{3u}}{{2a}} $
D). $ \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $

Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: The particle of mass m moving with velocity u hits the rectangular plate. The plate will start to rotate in an anticlockwise direction due to the angular momentum which the impact of the particle imparts. This problem can be solved by using the concept of conservation of angular momentum.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let $ {L_m} $ be the momentum of the particle of mass m before collision.
$ {L_m} = a.mu $
Let $ \omega $ be the angular velocity of the rotating system after the collision.
Moment of inertia about a perpendicular axis passing through hinge is given by,
I= moment of inertia of particle of mass m about hinge + moment of inertia of the plate about hinge.
$ m.\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt {5a} }}{2}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{{12}}m({a^2} + {(2a)^2}) $
$ = \dfrac{5}{4}m{a^2} + \dfrac{5}{{12}}m{a^2} $
$ = \dfrac{{20}}{{12}}m{a^2} $
$ = \dfrac{5}{3}m{a^2} $
Angular momentum is conserved, therefore
$ {I_\omega } = {I_p} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{3}m{a^2}.\omega = mua $
$ \Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $
Therefore the angular velocity will be $ \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $ .
The correct answer is option D, $ \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $ .
Note:
Angular velocity, also known as rotational velocity or angular frequency vector, is a vector measure of rotation rate that describes how fast an object spins or revolves in respect to another point, i.e. how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes over time. During a collision of objects in a closed system, momentum is always conserved.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let $ {L_m} $ be the momentum of the particle of mass m before collision.
$ {L_m} = a.mu $
Let $ \omega $ be the angular velocity of the rotating system after the collision.
Moment of inertia about a perpendicular axis passing through hinge is given by,
I= moment of inertia of particle of mass m about hinge + moment of inertia of the plate about hinge.
$ m.\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt {5a} }}{2}} \right) + \dfrac{1}{{12}}m({a^2} + {(2a)^2}) $
$ = \dfrac{5}{4}m{a^2} + \dfrac{5}{{12}}m{a^2} $
$ = \dfrac{{20}}{{12}}m{a^2} $
$ = \dfrac{5}{3}m{a^2} $
Angular momentum is conserved, therefore
$ {I_\omega } = {I_p} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{5}{3}m{a^2}.\omega = mua $
$ \Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $
Therefore the angular velocity will be $ \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $ .
The correct answer is option D, $ \dfrac{{3u}}{{5a}} $ .
Note:
Angular velocity, also known as rotational velocity or angular frequency vector, is a vector measure of rotation rate that describes how fast an object spins or revolves in respect to another point, i.e. how fast the angular position or orientation of an object changes over time. During a collision of objects in a closed system, momentum is always conserved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




