
A uniform long tube is bent into a circle of radius R and it lies in a vertical plane. Two liquids of same volume but densities $\rho $ and $\delta $ fill half the tube. The angle $\theta $ is
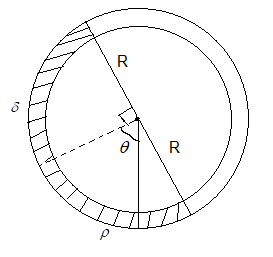
$\text{A}\text{. }{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\rho -\delta }{\rho +\delta } \right)$
$\text{B}\text{. }{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\rho }{\delta } \right)$
$\text{C}\text{. }{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\delta }{\rho } \right)$
$\text{D}\text{. }{{\tan }^{-1}}\left( \dfrac{\rho +\delta }{\rho -\delta } \right)$

Answer
596.1k+ views
Hint: Pressure only depends on the vertical height and not the horizontal distance. Pressure at every point at a given horizontal axis is the same. If we jump from an axis to an axis that at a distance of h below then the pressure increases by $\rho gh$.
Complete step by step answer:
To solve this the given question we have to do certain things.
Suppose a cylindrical container is filled with a liquid of density $\rho $. Then the pressure at a point inside the liquid that is at depth of h from the surface (in contact with air outside) of the liquid is given as $P=\rho gh$, where P is the pressure at that given point and g is acceleration due to gravity.
Pressure only depends on the vertical height and not the horizontal distance. Pressure at every point at a given horizontal axis is the same. This means that if we take two points A and such that both the points pass through the same horizontal axis, then the pressure is the same as both the points. Not only just two points, the pressure is the same at all the points on this axis.
In addition, the pressure inside a liquid does not depend on the shape of the container.
If we jump from an axis to an axis that at a distance of h below then the pressure increases by $\rho gh$.
With this information we will be able to solve the given problem.
Redraw the given figure and label it as given below.
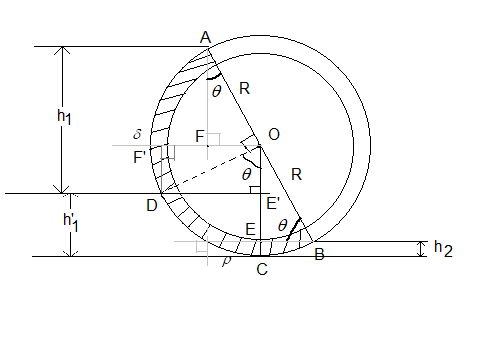
We will find the pressure at point C.
We can find the pressure at point C in two ways. One is by coming from point A and other is by coming from point B.
Consider the pressure at points A and B equal to zero.
From point B, the pressure at C is:
${{P}_{c}}=\rho g{{h}_{2}}$ ……………(i).
From point A, the pressure at D will be,
${{P}_{D}}=\delta g{{h}_{1}}$
From point D the pressure at C is:
${{P}_{c}}={{P}_{D}}+\rho gh{{'}_{1}}=\delta g{{h}_{1}}+\rho gh{{'}_{1}}$ ……………(ii).
If we use trigonometry ratios, we get that
$OE=R\sin \theta $ .
OC=R.
Therefore, ${{h}_{2}}=OC-OE=R-R\sin \theta $.
Substitute the value of ${{h}_{2}}$ in equation (i).
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{c}}=\rho g(R-R\sin \theta )$. …….(1).
We also get that,
$AF=R\sin \theta $
$F'D=R\cos \theta $
Therefore, ${{h}_{1}}=AF+F'D=R\cos \theta +R\sin \theta $.
And,
$OE'=R\cos \theta $
$OC=R$
$\Rightarrow E'C=OC-OE'=R-R\cos \theta $
$h{{'}_{1}}=E'C=R-R\cos \theta $.
Substitute the value of ${{h}_{1}}$and $h{{'}_{1}}$ in equation (ii).
${{P}_{c}}=\delta g\left( R\cos \theta +R\sin \theta \right)+\rho g\left( R-R\cos \theta \right)$. ………..(2).
Equate equations (1) and (2).
Therefore, $\rho g(R-R\sin \theta )=\delta g\left( R\cos \theta +R\sin \theta \right)+\rho g\left( R-R\cos \theta \right)$
$\Rightarrow \rho R-\rho R\sin \theta =\delta R\cos \theta +\delta R\sin \theta +\rho R-\rho R\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow \delta R\sin \theta +\rho R\sin \theta =\rho R\cos \theta -\delta R\cos \theta \rho R\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow (\delta +\rho )\sin \theta =(\rho -\delta )\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\dfrac{(\rho -\delta )}{(\rho +\delta )}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{(\rho -\delta )}{(\rho +\delta )}$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In the question, it is not mentioned that the two liquids are immiscible. It is to be noted that the two given liquids must be immiscible. Otherwise, the liquids will mix with each other.
Complete step by step answer:
To solve this the given question we have to do certain things.
Suppose a cylindrical container is filled with a liquid of density $\rho $. Then the pressure at a point inside the liquid that is at depth of h from the surface (in contact with air outside) of the liquid is given as $P=\rho gh$, where P is the pressure at that given point and g is acceleration due to gravity.
Pressure only depends on the vertical height and not the horizontal distance. Pressure at every point at a given horizontal axis is the same. This means that if we take two points A and such that both the points pass through the same horizontal axis, then the pressure is the same as both the points. Not only just two points, the pressure is the same at all the points on this axis.
In addition, the pressure inside a liquid does not depend on the shape of the container.
If we jump from an axis to an axis that at a distance of h below then the pressure increases by $\rho gh$.
With this information we will be able to solve the given problem.
Redraw the given figure and label it as given below.

We will find the pressure at point C.
We can find the pressure at point C in two ways. One is by coming from point A and other is by coming from point B.
Consider the pressure at points A and B equal to zero.
From point B, the pressure at C is:
${{P}_{c}}=\rho g{{h}_{2}}$ ……………(i).
From point A, the pressure at D will be,
${{P}_{D}}=\delta g{{h}_{1}}$
From point D the pressure at C is:
${{P}_{c}}={{P}_{D}}+\rho gh{{'}_{1}}=\delta g{{h}_{1}}+\rho gh{{'}_{1}}$ ……………(ii).
If we use trigonometry ratios, we get that
$OE=R\sin \theta $ .
OC=R.
Therefore, ${{h}_{2}}=OC-OE=R-R\sin \theta $.
Substitute the value of ${{h}_{2}}$ in equation (i).
$\Rightarrow {{P}_{c}}=\rho g(R-R\sin \theta )$. …….(1).
We also get that,
$AF=R\sin \theta $
$F'D=R\cos \theta $
Therefore, ${{h}_{1}}=AF+F'D=R\cos \theta +R\sin \theta $.
And,
$OE'=R\cos \theta $
$OC=R$
$\Rightarrow E'C=OC-OE'=R-R\cos \theta $
$h{{'}_{1}}=E'C=R-R\cos \theta $.
Substitute the value of ${{h}_{1}}$and $h{{'}_{1}}$ in equation (ii).
${{P}_{c}}=\delta g\left( R\cos \theta +R\sin \theta \right)+\rho g\left( R-R\cos \theta \right)$. ………..(2).
Equate equations (1) and (2).
Therefore, $\rho g(R-R\sin \theta )=\delta g\left( R\cos \theta +R\sin \theta \right)+\rho g\left( R-R\cos \theta \right)$
$\Rightarrow \rho R-\rho R\sin \theta =\delta R\cos \theta +\delta R\sin \theta +\rho R-\rho R\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow \delta R\sin \theta +\rho R\sin \theta =\rho R\cos \theta -\delta R\cos \theta \rho R\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow (\delta +\rho )\sin \theta =(\rho -\delta )\cos \theta $
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }=\dfrac{(\rho -\delta )}{(\rho +\delta )}$
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{(\rho -\delta )}{(\rho +\delta )}$
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note: In the question, it is not mentioned that the two liquids are immiscible. It is to be noted that the two given liquids must be immiscible. Otherwise, the liquids will mix with each other.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




