
A uniform hollow cylinder of mass \[6.5\,{\text{kg}}\], inner radius \[0.13\,{\text{m}}\] and outer radius \[0.25\,{\text{m}}\] approaches a flat ramp and rolls up the ramp without slipping. The ramp is inclined at \[20^\circ \]. How far along the ramp does the cylinder roll before slipping, if its initial forward speed is \[12\,{\text{m/s}}\]?
(Given: \[\sin 20^\circ = 0.342\])
A. \[25\,{\text{m}}\]
B. \[15\,{\text{m}}\]
C. \[35\,{\text{m}}\]
D. \[70\,{\text{m}}\]

Answer
563.7k+ views
Hint:Use the formulae for linear kinetic energy, rotational kinetic energy, potential energy of an object. Use the formula for moment inertia of the hollow cylinder. Use the law of conservation of energy when the cylinder starts rolling on the ramp and the point where it stops. Calculate the vertical displacement of the cylinder at the point on the ramp where it stops. Then calculate the horizontal displacement of the cylinder.
Formulae used:
The translational kinetic energy \[{K_T}\] of an object is
\[{K_T} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] …… (1)
Here, \[m\] is the mass of the object and \[v\] is the velocity of the object.
The rotational kinetic energy \[{K_R}\] of an object is
\[{K_R} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}\] …… (2)
Here, \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the object and \[\omega \] is the angular speed of the object.
The potential energy \[U\] of an object is
\[U = mgh\] …… (3)
Here, \[m\] is the mass of the object, \[g\] is acceleration due to gravity and \[h\] is the height of the object from the ground.
The moment of inertia \[I\] of the hollow cylinder is
\[I = \dfrac{1}{2}M\left( {R_1^2 + R_2^2} \right)\] …… (4)
Here, \[M\] is the mass of the cylinder, \[{R_1}\] is inner radius of the cylinder and \[{R_2}\] is outer radius of the cylinder.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the mass of the hollow cylinder is \[6.5\,{\text{kg}}\]. The inner radius of the hollow cylinder is \[0.13\,{\text{m}}\] and the outer cylinder is \[0.25\,{\text{m}}\].
\[M = 6.5\,{\text{kg}}\]
\[\Rightarrow{R_1} = 0.13\,{\text{m}}\]
\[\Rightarrow{R_2} = 0.25\,{\text{m}}\]
The inclination of the ramp is \[20^\circ \].
\[\theta = 20^\circ \]
The initial forward speed of the hollow cylinder is \[12\,{\text{m/s}}\].
\[v = 12\,{\text{m/s}}\]
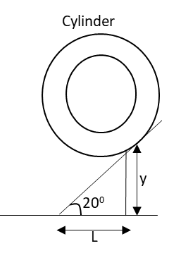
The diagram presenting the final position of the cylinder on the ramp is as follows:
According to the law of conservation of the energy, the initial total energy (translational kinetic energy and rotational kinetic energy) of the cylinder when it starts to move on the ramp is equal to the potential energy of the cylinder when it stops on the ramp.
\[{K_T} + {K_R} = U\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2} = Mgy\] …… (5)
The linear speed of the hollow cylinder is given by
\[v = {R_2}\omega \]
\[ \Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{v}{{{R_2}}}\]
Substitute \[\dfrac{v}{{{R_2}}}\] for \[\omega \] and \[\dfrac{1}{2}M\left( {R_1^2 + R_2^2} \right)\] for \[I\] in equation (5).
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2}M\left( {R_1^2 + R_2^2} \right)} \right]{\left( {\dfrac{v}{{{R_2}}}} \right)^2} = Mgy\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} + \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{R_1^2 + R_2^2}}{{R_2^2}}} \right) = gy\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} + \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{R_1^2 + R_2^2}}{{R_2^2}}} \right)}}{g}\]
Substitute \[12\,{\text{m/s}}\] for \[v\], \[0.13\,{\text{m}}\] for \[{R_1}\], \[0.25\,{\text{m}}\] for \[{R_2}\] and \[10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\] for \[g\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{{\left( {12\,{\text{m/s}}} \right)}^2} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {12\,{\text{m/s}}} \right)}^2}}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( {0.13\,{\text{m}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0.25\,{\text{m}}} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {0.25\,{\text{m}}} \right)}^2}}}} \right)}}{{10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{72 + 36\left( {\dfrac{{0.0794}}{{0.0625}}} \right)}}{{10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 11.77\,{\text{m}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \approx 12\,{\text{m}}\]
Hence, the vertical displacement of the hollow cylinder is \[12\,{\text{m}}\].
From the diagram, we can write
\[\sin 20^\circ = \dfrac{y}{L}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L = \dfrac{y}{{\sin 20^\circ }}\]
Substitute \[12\,{\text{m}}\] for \[y\] and \[0.342\] for \[\sin 20^\circ \] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow L = \dfrac{{12\,{\text{m}}}}{{0.342}}\]
\[ \therefore L = 35\,{\text{m}}\]
Therefore, the cylinder rolls a distance \[35\,{\text{m}}\] on the ramp.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The students should be careful while using the equation for initial angular velocity of the hollow cylinder in terms of linear velocity of the hollow cylinder before when it starts rolling on the ramp. The students should take the outer radius of the hollow cylinder and not the inner radius of the hollow cylinder.
Formulae used:
The translational kinetic energy \[{K_T}\] of an object is
\[{K_T} = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}\] …… (1)
Here, \[m\] is the mass of the object and \[v\] is the velocity of the object.
The rotational kinetic energy \[{K_R}\] of an object is
\[{K_R} = \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2}\] …… (2)
Here, \[I\] is the moment of inertia of the object and \[\omega \] is the angular speed of the object.
The potential energy \[U\] of an object is
\[U = mgh\] …… (3)
Here, \[m\] is the mass of the object, \[g\] is acceleration due to gravity and \[h\] is the height of the object from the ground.
The moment of inertia \[I\] of the hollow cylinder is
\[I = \dfrac{1}{2}M\left( {R_1^2 + R_2^2} \right)\] …… (4)
Here, \[M\] is the mass of the cylinder, \[{R_1}\] is inner radius of the cylinder and \[{R_2}\] is outer radius of the cylinder.
Complete step by step answer:
We have given that the mass of the hollow cylinder is \[6.5\,{\text{kg}}\]. The inner radius of the hollow cylinder is \[0.13\,{\text{m}}\] and the outer cylinder is \[0.25\,{\text{m}}\].
\[M = 6.5\,{\text{kg}}\]
\[\Rightarrow{R_1} = 0.13\,{\text{m}}\]
\[\Rightarrow{R_2} = 0.25\,{\text{m}}\]
The inclination of the ramp is \[20^\circ \].
\[\theta = 20^\circ \]
The initial forward speed of the hollow cylinder is \[12\,{\text{m/s}}\].
\[v = 12\,{\text{m/s}}\]
The diagram presenting the final position of the cylinder on the ramp is as follows:

According to the law of conservation of the energy, the initial total energy (translational kinetic energy and rotational kinetic energy) of the cylinder when it starts to move on the ramp is equal to the potential energy of the cylinder when it stops on the ramp.
\[{K_T} + {K_R} = U\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}I{\omega ^2} = Mgy\] …… (5)
The linear speed of the hollow cylinder is given by
\[v = {R_2}\omega \]
\[ \Rightarrow \omega = \dfrac{v}{{{R_2}}}\]
Substitute \[\dfrac{v}{{{R_2}}}\] for \[\omega \] and \[\dfrac{1}{2}M\left( {R_1^2 + R_2^2} \right)\] for \[I\] in equation (5).
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}M{v^2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{2}M\left( {R_1^2 + R_2^2} \right)} \right]{\left( {\dfrac{v}{{{R_2}}}} \right)^2} = Mgy\]
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} + \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{R_1^2 + R_2^2}}{{R_2^2}}} \right) = gy\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{v^2} + \dfrac{{{v^2}}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{R_1^2 + R_2^2}}{{R_2^2}}} \right)}}{g}\]
Substitute \[12\,{\text{m/s}}\] for \[v\], \[0.13\,{\text{m}}\] for \[{R_1}\], \[0.25\,{\text{m}}\] for \[{R_2}\] and \[10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}\] for \[g\] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{\dfrac{1}{2}{{\left( {12\,{\text{m/s}}} \right)}^2} + \dfrac{{{{\left( {12\,{\text{m/s}}} \right)}^2}}}{4}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( {0.13\,{\text{m}}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {0.25\,{\text{m}}} \right)}^2}}}{{{{\left( {0.25\,{\text{m}}} \right)}^2}}}} \right)}}{{10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = \dfrac{{72 + 36\left( {\dfrac{{0.0794}}{{0.0625}}} \right)}}{{10\,{\text{m/}}{{\text{s}}^2}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y = 11.77\,{\text{m}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow y \approx 12\,{\text{m}}\]
Hence, the vertical displacement of the hollow cylinder is \[12\,{\text{m}}\].
From the diagram, we can write
\[\sin 20^\circ = \dfrac{y}{L}\]
\[ \Rightarrow L = \dfrac{y}{{\sin 20^\circ }}\]
Substitute \[12\,{\text{m}}\] for \[y\] and \[0.342\] for \[\sin 20^\circ \] in the above equation.
\[ \Rightarrow L = \dfrac{{12\,{\text{m}}}}{{0.342}}\]
\[ \therefore L = 35\,{\text{m}}\]
Therefore, the cylinder rolls a distance \[35\,{\text{m}}\] on the ramp.
Hence, the correct option is C.
Note: The students should be careful while using the equation for initial angular velocity of the hollow cylinder in terms of linear velocity of the hollow cylinder before when it starts rolling on the ramp. The students should take the outer radius of the hollow cylinder and not the inner radius of the hollow cylinder.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




