
A uniform cylindrical rod of length $L$, cross-section $A$ and Young’s modulus $Y$ is acted upon by force as shown in figure. The Elongation of the rod is
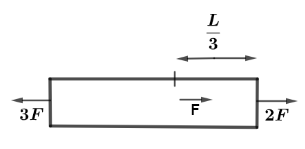
A. $\dfrac{2}{5}\dfrac{{FL}}{{AY}}$
B. $\dfrac{3}{8}\dfrac{{FL}}{{AY}}$
C. $\dfrac{3}{5}\dfrac{{FL}}{{AY}}$
D. $\dfrac{8}{3}\dfrac{{FL}}{{AY}}$

Answer
511.5k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, we need to understand the definition of Young’s modulus which states that it is a parameter to measure how easily we can bend or stretch matter. It is known as Elastic Modulus and is mathematically defined as the ratio of stress and strain. Stress is defined as force acting per unit area on the matter that changes the shape of material and stress is defined as fractional change in length of material.
Complete step by step answer:
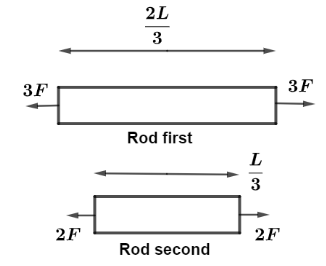
We will use the concept of superposition here. In this method we first have to know how much force is acting on each length. So we divide the rod into two parts of length $\dfrac{{2L}}{3}$ and $\dfrac{L}{3}$ as shown in figure below;
Now we will use formula of young’s modulus which is the ratio of stress and strain and calculated as $Y = \dfrac{f}{{A\left( {\dfrac{{\Delta l}}{l}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{fl}}{{A\Delta l}}$
Now for change in length $\Delta l = \dfrac{{fl}}{{AY}}$
So for first rod we have $f = 3F$ and $l = \dfrac{{2L}}{3}$
$\Delta {l_1} = \dfrac{{(3F \times \dfrac{{2L}}{3})}}{{AY}}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {l_1} = \dfrac{{2FL}}{{AY}}$
And for second rod we have $f = 2F$ and $l = \dfrac{L}{3}$
$\Delta {l_2} = \dfrac{{(2F \times \dfrac{L}{3})}}{{AY}}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {l_2} = \dfrac{{2FL}}{{3AY}}$
So total elongation in rod is $\Delta l = \Delta {l_1} + \Delta {l_2}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta l = \dfrac{{2FL}}{{AY}} + \dfrac{{2FL}}{{3AY}}$
$\Rightarrow \Delta l = \dfrac{{(6FL + 2FL)}}{{3AY}}$
$\therefore \Delta l = \dfrac{{8FL}}{{3AY}}$
So the correct option is D.
Note:It should be remembered that we have divided the rod into two parts so that net acting force could be identified and also net force should be equal and opposite to each other. It should be taken into consideration that force acting causing only stretching means only translation motion. At the atomic level on applying force atoms stretch so tension develops on each other so now atoms try to regain their original position and hence material regain its shape after stretching like rubber.
Complete step by step answer:
We will use the concept of superposition here. In this method we first have to know how much force is acting on each length. So we divide the rod into two parts of length $\dfrac{{2L}}{3}$ and $\dfrac{L}{3}$ as shown in figure below;

Now we will use formula of young’s modulus which is the ratio of stress and strain and calculated as $Y = \dfrac{f}{{A\left( {\dfrac{{\Delta l}}{l}} \right)}} = \dfrac{{fl}}{{A\Delta l}}$
Now for change in length $\Delta l = \dfrac{{fl}}{{AY}}$
So for first rod we have $f = 3F$ and $l = \dfrac{{2L}}{3}$
$\Delta {l_1} = \dfrac{{(3F \times \dfrac{{2L}}{3})}}{{AY}}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {l_1} = \dfrac{{2FL}}{{AY}}$
And for second rod we have $f = 2F$ and $l = \dfrac{L}{3}$
$\Delta {l_2} = \dfrac{{(2F \times \dfrac{L}{3})}}{{AY}}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta {l_2} = \dfrac{{2FL}}{{3AY}}$
So total elongation in rod is $\Delta l = \Delta {l_1} + \Delta {l_2}$
$ \Rightarrow \Delta l = \dfrac{{2FL}}{{AY}} + \dfrac{{2FL}}{{3AY}}$
$\Rightarrow \Delta l = \dfrac{{(6FL + 2FL)}}{{3AY}}$
$\therefore \Delta l = \dfrac{{8FL}}{{3AY}}$
So the correct option is D.
Note:It should be remembered that we have divided the rod into two parts so that net acting force could be identified and also net force should be equal and opposite to each other. It should be taken into consideration that force acting causing only stretching means only translation motion. At the atomic level on applying force atoms stretch so tension develops on each other so now atoms try to regain their original position and hence material regain its shape after stretching like rubber.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




