
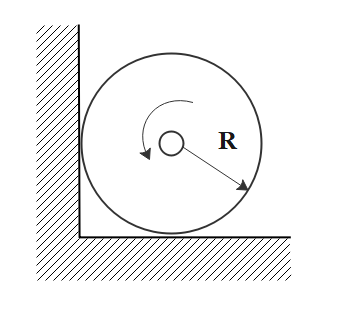
A uniform cylinder of radius $R$ is spinned about its axis to the angular velocity ${\omega _ \circ }$ and then placed into a corner (figure shown). The coefficient of friction between the corner walls and the cylinder is equal to $k$. The number of turns the cylinder accomplish before it stops is given by $\eta = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^{2)}}R}}{{x\pi k(1 + k)g}}$. Find the value of $x$.

Answer
574.2k+ views
Hint: Angular velocity of an object is defined as the rate of velocity at which an object or a particle is rotating around a center or a specific point in a given time period. We need to apply the concept of angular velocity and translational equilibrium in order to obtain the required answer.
Complete step by step solution:
An object is said to be in a translational equilibrium if the velocity of its translational motion is constant. An object which is not moving, or which is moving in a straight line with a constant velocity is considered in translational equilibrium. In the problem, the rigid body is in translational equilibrium but there is an angular retardation. We will first sketch the free body diagram of the cylinder. We know that the frictional forces acting on the cylinder are kinetic. From the condition of the translational equilibrium for the cylinder,
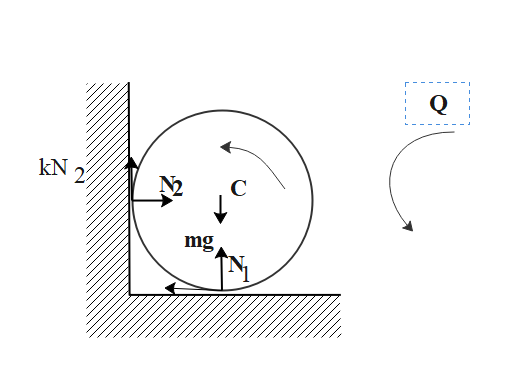
$mg = {N_1} = k{N_2}$ ; ${N_2} = k{N_1}$
Thus, ${N_1} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{1 + {k^2}}}$ ; ${N_2} = k\dfrac{{mg}}{{1 + {k^2}}}$
For pure rotation of the cylinder about its rotational axis, ${N_z} = I{\beta _z}$
$ \Rightarrow - k{N_1}R - k{N_2}R = \dfrac{{m{R^2}}}{2}{\beta _z}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - kmgR(1 + k)}}{{1 + {k^2}}} = \dfrac{{m{R^2}}}{2}{\beta _z}$
$ \Rightarrow {\beta _z} = \dfrac{{2k(1 + k)g}}{{(1 + {k^2})R}}$
Now, from kinematical equation,
${\omega ^2} = {\omega ^2}_ \circ + 2{\beta _z}\Delta \varphi $
We have, $\Delta \varphi = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^2})R}}{{4k(1 + k)g}}$ , because $\omega = 0$
Therefore, the number of turns,
$\eta = \dfrac{{\Delta \varphi }}{{2\pi }} = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^{2)}}R}}{{8\pi k(1 + k)g}}$
The number of turns the cylinder accomplish before it stops is given by $\eta = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^{2)}}R}}{{x\pi k(1 + k)g}}$
So, from comparing the given two quantities we get the value of $x = 8$.
Hence, the value of $x$ is $8$.
Note: Similarly, like translational equilibrium, the rotational equilibrium is defined as the body in which the net torque acting on it will be equal to zero. In rotational motion the concept remains the same as in the translational motion. For conversion of a translational equation into rotational just convert the variables of translational motion into their respective rotational equivalent.
Complete step by step solution:
An object is said to be in a translational equilibrium if the velocity of its translational motion is constant. An object which is not moving, or which is moving in a straight line with a constant velocity is considered in translational equilibrium. In the problem, the rigid body is in translational equilibrium but there is an angular retardation. We will first sketch the free body diagram of the cylinder. We know that the frictional forces acting on the cylinder are kinetic. From the condition of the translational equilibrium for the cylinder,

$mg = {N_1} = k{N_2}$ ; ${N_2} = k{N_1}$
Thus, ${N_1} = \dfrac{{mg}}{{1 + {k^2}}}$ ; ${N_2} = k\dfrac{{mg}}{{1 + {k^2}}}$
For pure rotation of the cylinder about its rotational axis, ${N_z} = I{\beta _z}$
$ \Rightarrow - k{N_1}R - k{N_2}R = \dfrac{{m{R^2}}}{2}{\beta _z}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{ - kmgR(1 + k)}}{{1 + {k^2}}} = \dfrac{{m{R^2}}}{2}{\beta _z}$
$ \Rightarrow {\beta _z} = \dfrac{{2k(1 + k)g}}{{(1 + {k^2})R}}$
Now, from kinematical equation,
${\omega ^2} = {\omega ^2}_ \circ + 2{\beta _z}\Delta \varphi $
We have, $\Delta \varphi = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^2})R}}{{4k(1 + k)g}}$ , because $\omega = 0$
Therefore, the number of turns,
$\eta = \dfrac{{\Delta \varphi }}{{2\pi }} = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^{2)}}R}}{{8\pi k(1 + k)g}}$
The number of turns the cylinder accomplish before it stops is given by $\eta = \dfrac{{{\omega _ \circ }^2(1 + {k^{2)}}R}}{{x\pi k(1 + k)g}}$
So, from comparing the given two quantities we get the value of $x = 8$.
Hence, the value of $x$ is $8$.
Note: Similarly, like translational equilibrium, the rotational equilibrium is defined as the body in which the net torque acting on it will be equal to zero. In rotational motion the concept remains the same as in the translational motion. For conversion of a translational equation into rotational just convert the variables of translational motion into their respective rotational equivalent.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




