
A uniform cylinder of mass $M$ and radius $R$ rolls without slipping, down a slope of angle $\theta $. The cylinder is connected to a spring of spring constant $K$ while the other end is connected to a rigid support at $P$? The cylinder is released when the spring is unstretched. The maximum distance that the cylinder travels is?
Answer
489.3k+ views
Hint: In this question, we are given that the cylinder is rolling without slipping down on an inclined plane. So, this problem can be solved by applying the conservation of energy according to which when the body reaches the bottom of the inclined plane, then its total potential energy is converted into kinetic energy.
Complete step by step solution:
The free body diagram for this question will be:
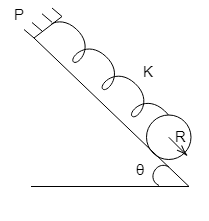
Let us consider that the uniform cylinder, which has mass $M$ and radius $R$, starts from a state of rest and gradually moves down the inclined plane which is inclined with an angle $\theta $ with the horizontal.
Also, let the acceleration due to gravity be represented by the symbol $g$.
The mechanical energy of the given stretched string $ = \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2}$.
Also, the loss in the gravitational potential energy $ = Mgh = Mg(x\sin \theta )$
Since there is no loss of any kind of energy due to the force of friction,
So, on applying the law of conservation of energy, we get
$\dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2} = Mgx\sin \theta $
$\dfrac{1}{2}Kx = Mg\sin \theta $
On keeping $x$ on the LHS and taking all other terms on the LHS, we get,
$x = \dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{K}$
So, the maximum distance travelled by the cylinder is $x = \dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{K}$.
Note:
Rolling without slipping is basically a combination of translation as well as rotation motion, where the point of contact is instantaneously at rest. When a body experiences a pure translational motion, then its every point moves with the same velocity as the centre of mass. This means that it moves in the same direction and with the same speed.
Complete step by step solution:
The free body diagram for this question will be:

Let us consider that the uniform cylinder, which has mass $M$ and radius $R$, starts from a state of rest and gradually moves down the inclined plane which is inclined with an angle $\theta $ with the horizontal.
Also, let the acceleration due to gravity be represented by the symbol $g$.
The mechanical energy of the given stretched string $ = \dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2}$.
Also, the loss in the gravitational potential energy $ = Mgh = Mg(x\sin \theta )$
Since there is no loss of any kind of energy due to the force of friction,
So, on applying the law of conservation of energy, we get
$\dfrac{1}{2}K{x^2} = Mgx\sin \theta $
$\dfrac{1}{2}Kx = Mg\sin \theta $
On keeping $x$ on the LHS and taking all other terms on the LHS, we get,
$x = \dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{K}$
So, the maximum distance travelled by the cylinder is $x = \dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{K}$.
Note:
Rolling without slipping is basically a combination of translation as well as rotation motion, where the point of contact is instantaneously at rest. When a body experiences a pure translational motion, then its every point moves with the same velocity as the centre of mass. This means that it moves in the same direction and with the same speed.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




