
A uniform cylinder of mass M and radius \[R\] is released from rest on a rough inclined surface of inclination \[\theta \] with the horizontal as shown in figure. As the cylinder rolls down the inclined surface, the maximum elongation in the spring of stiffness \[k\] is ?
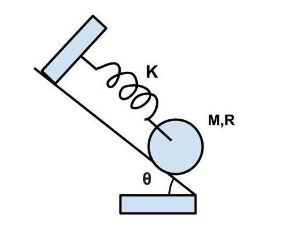
A. $\dfrac{3}{4}\dfrac{{Mg\sin \theta }}{k}$
B. $\dfrac{{2Mg\sin \theta }}{k}$
C. $\dfrac{{Mg\sin \theta }}{k}$
D. None of these

Answer
489.6k+ views
Hint: In order to answer the given question to know the maximum elongation in the spring of stiffness, we will use the concept of Conservation of energy, which states that Conservation of energy is a physical principle that states that the energy in a closed system remains constant.
Complete step by step answer:
Since the cylinder's stated motion, there is no energy loss owing to friction. Hence, based on the notion of energy conservation,
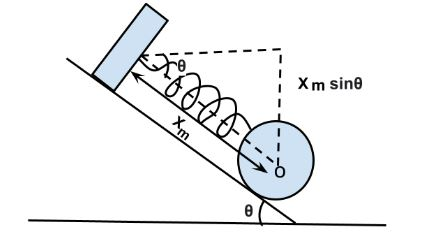
Maximum spring potential energy=maximum gravitational potential energy decrease
\[ \dfrac{1}{2}kx_m^2 = Mgh = Mg({x_m}sin\theta )\]
\[\therefore {x_m} = \dfrac{{2Mgsin\theta }}{k}\]
Therefore, the maximum elongation in the spring of stiffness \[k\] is \[\dfrac{{2Mgsin\theta }}{k}\].
So, the correct option is B.
Additional Information: The position of the object has no effect on a conservative force. If a force is conservative, it's possible to assign a numerical number to its potential at any time. When an object moves from one location to another, the force changes the potential energy of the object in a way that is independent of the path taken. Gravity and spring forces are examples of conservative forces.
Note: Non-conservative forces, like conservative forces, transfer energy from the moving item, but they do not transfer this energy back to the system's potential energy to retrieve it during reverse motion. Rather, they transfer energy from the system in an energy form that the force cannot employ to send it back to the moving object. Friction is an example of an anti-conservative force.
Complete step by step answer:
Since the cylinder's stated motion, there is no energy loss owing to friction. Hence, based on the notion of energy conservation,

Maximum spring potential energy=maximum gravitational potential energy decrease
\[ \dfrac{1}{2}kx_m^2 = Mgh = Mg({x_m}sin\theta )\]
\[\therefore {x_m} = \dfrac{{2Mgsin\theta }}{k}\]
Therefore, the maximum elongation in the spring of stiffness \[k\] is \[\dfrac{{2Mgsin\theta }}{k}\].
So, the correct option is B.
Additional Information: The position of the object has no effect on a conservative force. If a force is conservative, it's possible to assign a numerical number to its potential at any time. When an object moves from one location to another, the force changes the potential energy of the object in a way that is independent of the path taken. Gravity and spring forces are examples of conservative forces.
Note: Non-conservative forces, like conservative forces, transfer energy from the moving item, but they do not transfer this energy back to the system's potential energy to retrieve it during reverse motion. Rather, they transfer energy from the system in an energy form that the force cannot employ to send it back to the moving object. Friction is an example of an anti-conservative force.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




