
A uniform chain of mass M and length L is held on a horizontal frictionless table with \[\dfrac{1}{\pi }th\] of its length hanging over the edge of the table. The work done in pulling the chain up on the table is
A. \[\dfrac{{MgL}}{\pi }\]
B. \[\dfrac{{MgL}}{{2\pi }}\]
C. \[\dfrac{{MgL}}{{{\pi ^2}}}\]
D. \[\dfrac{{MgL}}{{2{\pi ^2}}}\]
Answer
589.2k+ views
Hint: Consider the small element of length of the hanging portion of the chain. Derive the expression for the small work required to pull that element of the chain and integrate the equation to determine the work done to pull the whole hanging portion of the chain back on the table.
Formula used:
\[W = mgx\]
Here, m is the mass , g is the acceleration due gravity and x is the distance.
Complete step by step answer:
Let the small length \[dx\] of the hanging chain at a distance x from the table as shown in the figure below.
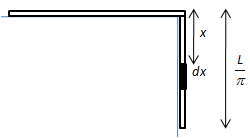
We can express the mass of the element \[dx\] as follows,
\[dm = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}} \right)dx\]
Now, we calculate the small work done by pulling the mass dm on the table as follows,
\[dW = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}dx} \right)gx\]
\[ \Rightarrow dW = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}gx} \right)dx\]
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, we have to calculate the total work done to pull \[\dfrac{L}{\pi }\] length of the chain back on the table as follows,
\[W = \int\limits_0^{\dfrac{L}{\pi }} {\left( {\dfrac{M}{L}gx} \right)dx} \]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{Mg}}{L}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{L}{\pi }} {x\,dx} \]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{Mg}}{L}\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \right)_0^{\dfrac{L}{\pi }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{Mg}}{L}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{L}{\pi }} \right)}^2}}}{2} - 0} \right)\]
\[ \therefore W = \dfrac{{MgL}}{{2{\pi ^2}}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
the work done by the gravitational force on the body of mass m to move a body at a distance x in the upward direction is can be expressed as,
\[W = mgx\]
The S.I. unit of work done is joule
Note:
The mass of the small element \[dx\] in the above figure is expressed as, \[dm = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}} \right)dx\]. Here, \[\dfrac{M}{L}\] is known as linear mass density of the chain. This expression is valid only for objects which have uniform density that is the mass of the chain should not be changed with distance.
Formula used:
\[W = mgx\]
Here, m is the mass , g is the acceleration due gravity and x is the distance.
Complete step by step answer:
Let the small length \[dx\] of the hanging chain at a distance x from the table as shown in the figure below.

We can express the mass of the element \[dx\] as follows,
\[dm = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}} \right)dx\]
Now, we calculate the small work done by pulling the mass dm on the table as follows,
\[dW = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}dx} \right)gx\]
\[ \Rightarrow dW = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}gx} \right)dx\]
Here, g is the acceleration due to gravity.
Now, we have to calculate the total work done to pull \[\dfrac{L}{\pi }\] length of the chain back on the table as follows,
\[W = \int\limits_0^{\dfrac{L}{\pi }} {\left( {\dfrac{M}{L}gx} \right)dx} \]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{Mg}}{L}\int\limits_0^{\dfrac{L}{\pi }} {x\,dx} \]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{Mg}}{L}\left( {\dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2}} \right)_0^{\dfrac{L}{\pi }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow W = \dfrac{{Mg}}{L}\left( {\dfrac{{{{\left( {\dfrac{L}{\pi }} \right)}^2}}}{2} - 0} \right)\]
\[ \therefore W = \dfrac{{MgL}}{{2{\pi ^2}}}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Additional Information:
the work done by the gravitational force on the body of mass m to move a body at a distance x in the upward direction is can be expressed as,
\[W = mgx\]
The S.I. unit of work done is joule
Note:
The mass of the small element \[dx\] in the above figure is expressed as, \[dm = \left( {\dfrac{M}{L}} \right)dx\]. Here, \[\dfrac{M}{L}\] is known as linear mass density of the chain. This expression is valid only for objects which have uniform density that is the mass of the chain should not be changed with distance.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




