
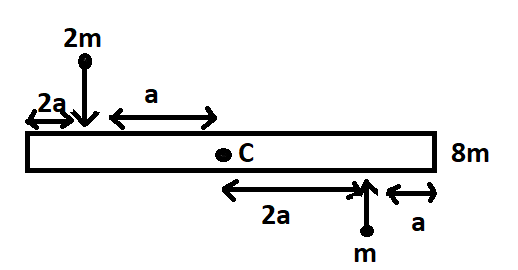
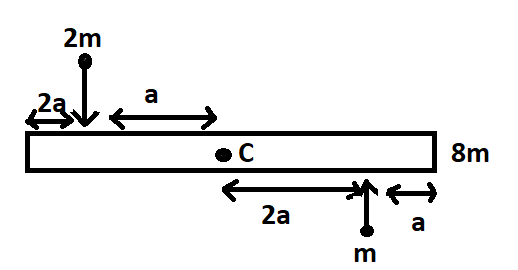
A uniform bar of length $6a$ and mass $8m$ lies on a smooth horizontal table. Two point masses $m$ and $2m$ moving in the same horizontal plane with speed $2v$ and $v$ respectively, strike the bar( as shown in figure) and stick to the bar after collision. C represents the centre of mass of the bar. Denoting angular velocity (about the centre of mass), total energy and velocity of centre of mass by $\omega, E$ and ${{\text{v}}_{c}}$ respectively, then after collision we have
$\begin{align}
& \text{A}\text{. }{{\text{v}}_{c}}=0 \\
& \text{B}\text{. }\omega =\dfrac{3\text{v}}{5a} \\
& \text{C}\text{. }\omega =\dfrac{\text{v}}{5a} \\
& \text{D}\text{. }E=\dfrac{3m{{\text{v}}^{2}}}{5} \\
\end{align}$

Answer
597k+ views
- Hint: We will have to calculate each physical quantity to find the correct answer for the given question. The two masses stick to the bar and hence there is no external force or torque on the bar and the conservation laws can be used.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We are given a uniform bar of length $6a$ and mass $8m$ which lies on a smooth horizontal table as shown in the figure. There are two masses $m$ and $2m$ striking the bar with velocities of $2v$ and $v$ respectively as shown in the figure.
Firstly, the body is experiencing no external force so
${{F}_{ext}}=0$
Therefore using law of conservation of linear momentum we can write the equation:
$({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}})V={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}{{v}_{3}}$
$(2m+m+8m){{v}_{c}}=-2mv+m\times 2v+0$
$11m{{v}_{c}}=0$
${{v}_{c}}=0$
Therefore, there is no translatory motion as velocity of centre of mass of the bar is zero
Now since the external torque on the system is also zero i.e.
${{\tau }_{ext}}=0$
Angular momentum of the system is also conserved. Thus, we will apply the law of conservation of angular momentum on the system
$({{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+{{I}_{3}})\omega ={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}{{r}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}{{r}_{2}}$
Here, we must use the formula of moment of inertia of a bar when the axis of rotation is perpendicular to bar and through its centre i.e,
$I\omega =\dfrac{M{{l}^{2}}}{12}$
$\begin{align}
& \left\{ 2m{{a}^{2}}+m{{(2a)}^{2}}+\dfrac{8m\times {{(6a)}^{2}}}{12} \right\}\omega =2mva+m(2v)(2a) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{72m{{a}^{2}}+288m{{a}^{2}}}{12} \right)\omega =6mva \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{360m{{a}^{2}}}{12}\omega =6mva \\
\end{align}$
$30m\omega {{a}^{2}}=6mva$
Cancelling the like terms, we get
$\Rightarrow \omega =\dfrac{v}{5a}$
This is the rotational velocity of the system.
Now,
$\text{Total energy=Rotational energy+Translational energy}$
(There is no translatory motion since ${{v}_{c}}=0$ )
$\text{E=}\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
$\text{E=}\dfrac{1}{2}(30m{{a}^{2}}){{\left( \dfrac{v}{5a} \right)}^{2}}$
$\text{E=}\dfrac{3}{5}m{{v}^{2}}$
The correct answers are A. ${{v}_{c}}=0$, C. $\omega =\dfrac{v}{5a}$, D. $E=\dfrac{3m{{v}^{2}}}{5}$
Note: Students must note that the centre of mass is nothing but a point where the whole mass of the body is concentrated. Also, certain formulas for moment of inertia for a rod, disc, cylinder, sphere should be memorised by the students to use directly in the numerical problems. The various formulas are given as
\[\begin{align}
& {{I}_{rod}}=\dfrac{1}{12}M{{r}^{2}} \\
& {{I}_{disc}}=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{r}^{2}} \\
& {{I}_{cylinder}}=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{r}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Complete step-by-step solution -
We are given a uniform bar of length $6a$ and mass $8m$ which lies on a smooth horizontal table as shown in the figure. There are two masses $m$ and $2m$ striking the bar with velocities of $2v$ and $v$ respectively as shown in the figure.

Firstly, the body is experiencing no external force so
${{F}_{ext}}=0$
Therefore using law of conservation of linear momentum we can write the equation:
$({{m}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}})V={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}+{{m}_{3}}{{v}_{3}}$
$(2m+m+8m){{v}_{c}}=-2mv+m\times 2v+0$
$11m{{v}_{c}}=0$
${{v}_{c}}=0$
Therefore, there is no translatory motion as velocity of centre of mass of the bar is zero
Now since the external torque on the system is also zero i.e.
${{\tau }_{ext}}=0$
Angular momentum of the system is also conserved. Thus, we will apply the law of conservation of angular momentum on the system
$({{I}_{1}}+{{I}_{2}}+{{I}_{3}})\omega ={{m}_{1}}{{v}_{1}}{{r}_{1}}+{{m}_{2}}{{v}_{2}}{{r}_{2}}$
Here, we must use the formula of moment of inertia of a bar when the axis of rotation is perpendicular to bar and through its centre i.e,
$I\omega =\dfrac{M{{l}^{2}}}{12}$
$\begin{align}
& \left\{ 2m{{a}^{2}}+m{{(2a)}^{2}}+\dfrac{8m\times {{(6a)}^{2}}}{12} \right\}\omega =2mva+m(2v)(2a) \\
& \Rightarrow \left( \dfrac{72m{{a}^{2}}+288m{{a}^{2}}}{12} \right)\omega =6mva \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{360m{{a}^{2}}}{12}\omega =6mva \\
\end{align}$
$30m\omega {{a}^{2}}=6mva$
Cancelling the like terms, we get
$\Rightarrow \omega =\dfrac{v}{5a}$
This is the rotational velocity of the system.
Now,
$\text{Total energy=Rotational energy+Translational energy}$
(There is no translatory motion since ${{v}_{c}}=0$ )
$\text{E=}\dfrac{1}{2}I{{\omega }^{2}}$
$\text{E=}\dfrac{1}{2}(30m{{a}^{2}}){{\left( \dfrac{v}{5a} \right)}^{2}}$
$\text{E=}\dfrac{3}{5}m{{v}^{2}}$
The correct answers are A. ${{v}_{c}}=0$, C. $\omega =\dfrac{v}{5a}$, D. $E=\dfrac{3m{{v}^{2}}}{5}$
Note: Students must note that the centre of mass is nothing but a point where the whole mass of the body is concentrated. Also, certain formulas for moment of inertia for a rod, disc, cylinder, sphere should be memorised by the students to use directly in the numerical problems. The various formulas are given as
\[\begin{align}
& {{I}_{rod}}=\dfrac{1}{12}M{{r}^{2}} \\
& {{I}_{disc}}=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{r}^{2}} \\
& {{I}_{cylinder}}=\dfrac{1}{2}M{{r}^{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




