
A triangle has three vertices A (2,1,6), B (4,7,9), and C (8,5,-6). Determine the area of the triangle. Prove that the triangle is a right angle triangle?
Answer
481.2k+ views
Hint: In a 3d space area of triangles or parallelograms can be found by using the cross product of any two adjacent sides. If two vectors are perpendicular they don’t have any kind of projection on each other so their dot product comes to be zero.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Area triangle in a 3d space can be calculated by taking the half of the magnitude of the cross product of any two sides. And to check whether the triangle is a right-angle triangle or not we need to take the dot product of sides, if any one of the dot products becomes zero then those sides are at right angles to each other and the triangle is a right-angle triangle.
So, here we have a triangle with coordinates as A (2,1,6), B (4,7,9), and C (8,5,-6).
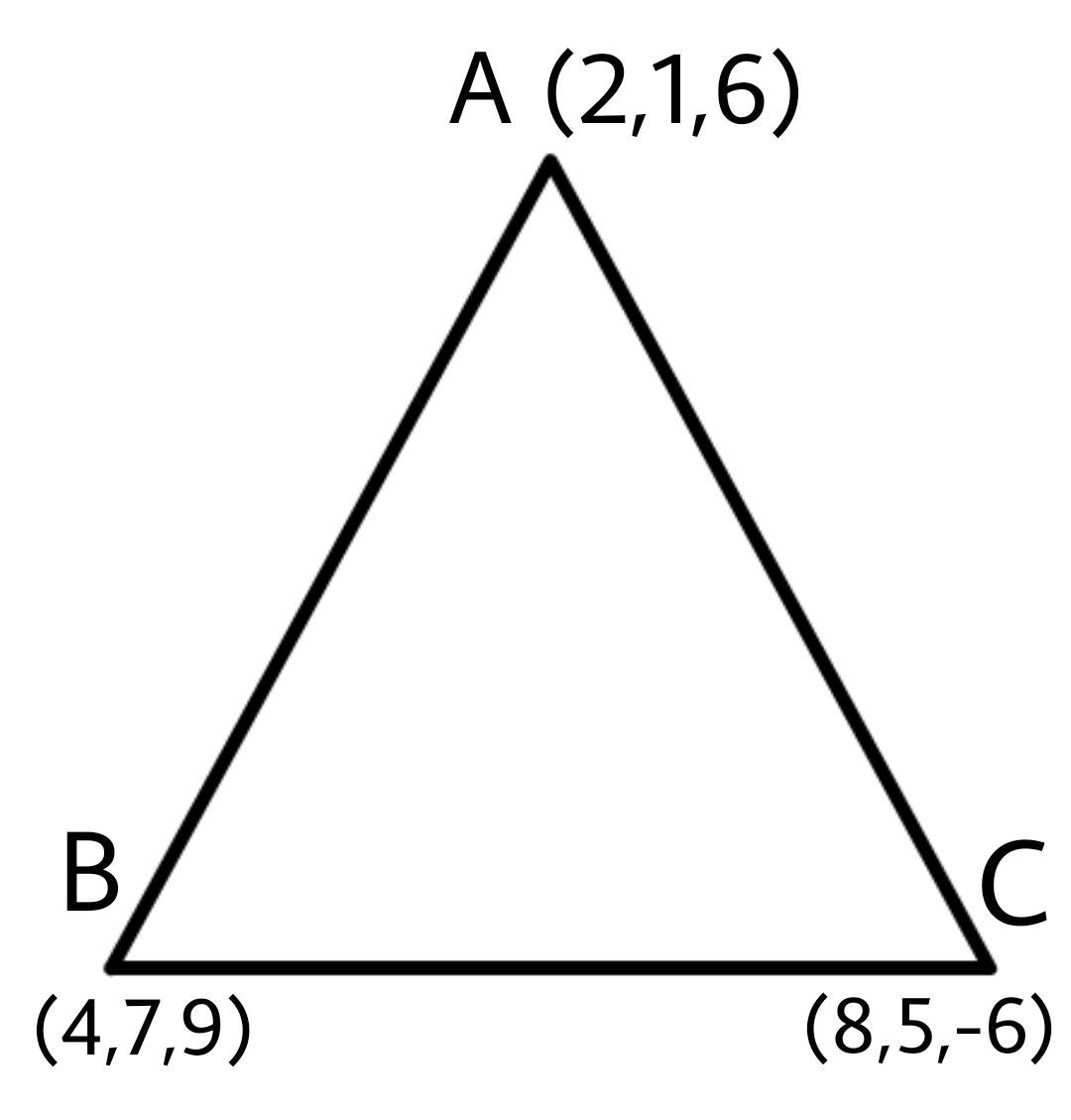
Let’s find the sides this is done by subtracting the coordinates:
For $\overrightarrow {AB} $ we will subtract the coordinates of A from the coordinates of B.
$\overrightarrow {AB} = \left( {4 - 2} \right)\widehat i + \left( {7 - 1} \right)\widehat j + \left( {9 - 6} \right)\widehat k$
$\overrightarrow {AB} = 2\widehat i + 6\widehat j + 3\widehat k$
For $\overrightarrow {BC} $ we will subtract the coordinates of B from the coordinates of C.
$\overrightarrow {BC} = \left( {8 - 4} \right)\widehat i + \left( {5 - 7} \right)\widehat j + \left( { - 6 - 9} \right)\widehat k$
\[\overrightarrow {BC} = 4\widehat i - 2\widehat j - 15\widehat k\]
For $\overrightarrow {AC} $ we will subtract the coordinates of A from the coordinates of C.
$\overrightarrow {AC} = \left( {8 - 2} \right)\widehat i + \left( {5 - 1} \right)\widehat j + \left( { - 6 - 6} \right)\widehat k$
\[\overrightarrow {AC} = 6\widehat i + 4\widehat j - 12\widehat k\]
Finding the area:
For area we will take the cross product of any two sides, let’s take $\overrightarrow {AB} $ and $\overrightarrow {AC} $
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\widehat i}&{\widehat j}&{\widehat k} \\
2&6&3 \\
6&4&{ - 12}
\end{array}} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = \widehat i\left( {6 \times \left( { - 12} \right) - 3 \times 4} \right) - \widehat j\left( {2 \times \left( { - 12} \right) - 3 \times 6} \right) + \widehat k\left( {2 \times 4 - 6 \times 6} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = \widehat i\left( { - 72 - 12} \right) - \widehat j\left( { - 24 - 18} \right) + \widehat k\left( {8 - 36} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = - 84\widehat i + 42\widehat j - 28\widehat k\]
Now let’s find the magnitude of \[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} \]:
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 84} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {42} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 28} \right)}^2}} $
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = \sqrt {7056 + 1764 + 784} $
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = \sqrt {9604} $
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = 98$
So the area is the half of the magnitude of the cross product of any two sides, that is half of $\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right|$
Area $ = \frac{1}{2}\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right|$
Area $ = \frac{1}{2} \times 98 = 49$
So the area of the triangle is 49 ${\left( {unit} \right)^2}$
Now let’s check whether the triangle is a right angle triangle or not by taking dot products of two sides. If the dot product comes to be zero, then the sides are perpendicular to each other
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = \left( {2 \times 4} \right)\widehat i.\widehat i + \left( {6 \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)\widehat j.\widehat j + \left( {3 \times \left( { - 15} \right)} \right)\widehat k.\widehat k$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = 8 - 12 - 45$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = - 49 \ne 0$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = \left( {2 \times 6} \right)\widehat i.\widehat i + \left( {6 \times 4} \right)\widehat j.\widehat j + \left( {3 \times \left( { - 12} \right)} \right)\widehat k.\widehat k$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 12 - 24 + 36$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 0$
Now $\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 0$ so sides $\overrightarrow {AC} $and $\overrightarrow {AB} $ are perpendicular to each other thus the triangle is a right angle triangle.
So the area of the triangle ABC is 49 ${\left( {unit} \right)^2}$and the sides AC and AB are perpendicular to each other.
Note: When calculating the cross product of two vectors be very careful as the major error in that specific region only. Especially with the signs as we have to multiply with a negative sign for every alternate product.
Another method to determine whether the triangle is a right-angled triangle is by calculating the length of all sides and checking whether the three fit into a Pythagoras triplet or not.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Area triangle in a 3d space can be calculated by taking the half of the magnitude of the cross product of any two sides. And to check whether the triangle is a right-angle triangle or not we need to take the dot product of sides, if any one of the dot products becomes zero then those sides are at right angles to each other and the triangle is a right-angle triangle.
So, here we have a triangle with coordinates as A (2,1,6), B (4,7,9), and C (8,5,-6).

Let’s find the sides this is done by subtracting the coordinates:
For $\overrightarrow {AB} $ we will subtract the coordinates of A from the coordinates of B.
$\overrightarrow {AB} = \left( {4 - 2} \right)\widehat i + \left( {7 - 1} \right)\widehat j + \left( {9 - 6} \right)\widehat k$
$\overrightarrow {AB} = 2\widehat i + 6\widehat j + 3\widehat k$
For $\overrightarrow {BC} $ we will subtract the coordinates of B from the coordinates of C.
$\overrightarrow {BC} = \left( {8 - 4} \right)\widehat i + \left( {5 - 7} \right)\widehat j + \left( { - 6 - 9} \right)\widehat k$
\[\overrightarrow {BC} = 4\widehat i - 2\widehat j - 15\widehat k\]
For $\overrightarrow {AC} $ we will subtract the coordinates of A from the coordinates of C.
$\overrightarrow {AC} = \left( {8 - 2} \right)\widehat i + \left( {5 - 1} \right)\widehat j + \left( { - 6 - 6} \right)\widehat k$
\[\overrightarrow {AC} = 6\widehat i + 4\widehat j - 12\widehat k\]
Finding the area:
For area we will take the cross product of any two sides, let’s take $\overrightarrow {AB} $ and $\overrightarrow {AC} $
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = \left( {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}}
{\widehat i}&{\widehat j}&{\widehat k} \\
2&6&3 \\
6&4&{ - 12}
\end{array}} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = \widehat i\left( {6 \times \left( { - 12} \right) - 3 \times 4} \right) - \widehat j\left( {2 \times \left( { - 12} \right) - 3 \times 6} \right) + \widehat k\left( {2 \times 4 - 6 \times 6} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = \widehat i\left( { - 72 - 12} \right) - \widehat j\left( { - 24 - 18} \right) + \widehat k\left( {8 - 36} \right)\]
\[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} = - 84\widehat i + 42\widehat j - 28\widehat k\]
Now let’s find the magnitude of \[\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} \]:
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = \sqrt {{{\left( { - 84} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {42} \right)}^2} + {{\left( { - 28} \right)}^2}} $
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = \sqrt {7056 + 1764 + 784} $
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = \sqrt {9604} $
$\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right| = 98$
So the area is the half of the magnitude of the cross product of any two sides, that is half of $\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right|$
Area $ = \frac{1}{2}\left| {\overrightarrow {AB} \times \overrightarrow {AC} } \right|$
Area $ = \frac{1}{2} \times 98 = 49$
So the area of the triangle is 49 ${\left( {unit} \right)^2}$
Now let’s check whether the triangle is a right angle triangle or not by taking dot products of two sides. If the dot product comes to be zero, then the sides are perpendicular to each other
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = \left( {2 \times 4} \right)\widehat i.\widehat i + \left( {6 \times \left( { - 2} \right)} \right)\widehat j.\widehat j + \left( {3 \times \left( { - 15} \right)} \right)\widehat k.\widehat k$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = 8 - 12 - 45$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {BC} = - 49 \ne 0$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = \left( {2 \times 6} \right)\widehat i.\widehat i + \left( {6 \times 4} \right)\widehat j.\widehat j + \left( {3 \times \left( { - 12} \right)} \right)\widehat k.\widehat k$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 12 - 24 + 36$
$\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 0$
Now $\overrightarrow {AB} .\overrightarrow {AC} = 0$ so sides $\overrightarrow {AC} $and $\overrightarrow {AB} $ are perpendicular to each other thus the triangle is a right angle triangle.
So the area of the triangle ABC is 49 ${\left( {unit} \right)^2}$and the sides AC and AB are perpendicular to each other.
Note: When calculating the cross product of two vectors be very careful as the major error in that specific region only. Especially with the signs as we have to multiply with a negative sign for every alternate product.
Another method to determine whether the triangle is a right-angled triangle is by calculating the length of all sides and checking whether the three fit into a Pythagoras triplet or not.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

RNA and DNA are chiral molecules their chirality is class 12 chemistry CBSE




