
A tree is broken at a height of \[5\;m\] from the ground and its top touches the ground at a distance of \[12\;m\] from the base of the tree. Find the original height of the tree.
Answer
531.3k+ views
Hint: In this problem, we use the Pythagoras theorem to find the original height of the tree. By solving this problem by using Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A right triangle or right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle. The relation between the sides and angles of a right triangle is the basis for trigonometry. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
In the given problem,
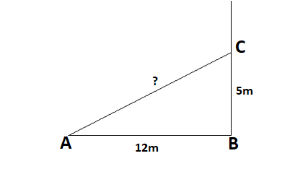
Let \[AB\] be the broken tree top that touches the ground at a distance of \[12\;m\] .
Let \[AC\] be a tree broken at a height of \[5\;m\] .
To find the original height of the tree, \[BC\]
By using Pythagoras theorem, we get
Pythagora's theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
From the diagram \[\Delta ABC\] are right angled triangles.
In \[\Delta ABC\] , we have
\[AC{\;^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
By substitute the values from the diagram, we get
\[
A{C^2} = {12^2} + {5^2} \\
A{C^2} = 25 + 144 \;
\]
To simplify, we get
\[
A{C^2} = 169 \\
A{C^2} = {13^2} \;
\]
Take square root on both sides, then we get
\[AC = 13\]
Therefore, the value of \[AC = 13\] .
The total height of the tree is \[BC + AC = 5 + 13 = 18\;m\]
Finally, the original height of tree is \[18\;m\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[18\;\;m\] ”.
Note: We have to convert the word problem into mathematical expression by the diagrammatic representation of right angled triangle has three sides are adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse sides. By solving this problem by using Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.

Complete step-by-step answer:
A right triangle or right-angled triangle is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle. The relation between the sides and angles of a right triangle is the basis for trigonometry. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
In the given problem,
Let \[AB\] be the broken tree top that touches the ground at a distance of \[12\;m\] .
Let \[AC\] be a tree broken at a height of \[5\;m\] .
To find the original height of the tree, \[BC\]
By using Pythagoras theorem, we get
Pythagora's theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
From the diagram \[\Delta ABC\] are right angled triangles.
In \[\Delta ABC\] , we have
\[AC{\;^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}\]
By substitute the values from the diagram, we get
\[
A{C^2} = {12^2} + {5^2} \\
A{C^2} = 25 + 144 \;
\]
To simplify, we get
\[
A{C^2} = 169 \\
A{C^2} = {13^2} \;
\]
Take square root on both sides, then we get
\[AC = 13\]
Therefore, the value of \[AC = 13\] .
The total height of the tree is \[BC + AC = 5 + 13 = 18\;m\]
Finally, the original height of tree is \[18\;m\]
So, the correct answer is “ \[18\;\;m\] ”.
Note: We have to convert the word problem into mathematical expression by the diagrammatic representation of right angled triangle has three sides are adjacent, opposite and hypotenuse sides. By solving this problem by using Pythagoras theorem states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse side is equal to the sum of squares of the other two sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE




