
A transverse sinusoidal wave moves along a string in the positive $x$ - direction at a speed of \[10cm/s\] . The wavelength of the wave is \[0.5m\] and its amplitude is \[10cm\]. At a particular time \[t\] , the snapshot of the wave is shown in figure. The velocity of point $P$ when its displacement is \[5cm\] is:
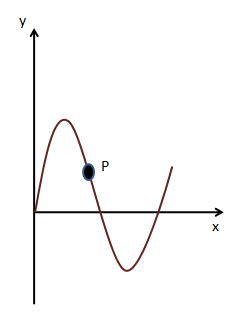
(A) $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}\widehat jm/s$
(B) $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}\widehat jm/s$
(C) $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}\widehat im/s$
(D) $\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}\widehat im/s$

Answer
568.5k+ views
Hint: The point $P$ is moving with a sinusoidal wave that is along a string in the positive $x$ - direction. Use the formula of velocity of particles in a wave.
Write the angular frequency in terms of the wave velocity and wavelength.
Find the velocity of the point using the given wavelength, the wave velocity, the amplitude, and the displacement.
Formula used:
The velocity of the point $P$ , ${v_p} = \omega \sqrt {{A^2} - {x^2}} $
$A = $ Amplitude and $x = $ the displacement
The angular frequency, $\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi v}}{\lambda }$
$v = $ The wave velocity and $\lambda = $ wavelength.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure shown below describes the motion of sinusoidal waves along a string. We have to find the velocity and direction of the point on the string.
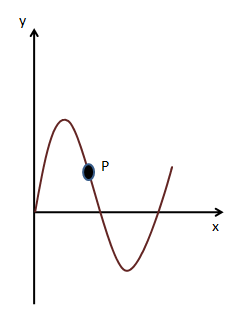
The sinusoidal wave is moving with a speed $v$ along a string in the positive $x$ - direction.
Let, the point $P$ moves with a speed ${v_P}$ which can be written as,
${v_p} = \omega \sqrt {{A^2} - {x^2}} $
Amplitude $A = 10cm = 0.1m$
The displacement $x = 5cm = 0.05m$
The angular frequency, $\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi v}}{\lambda }$
Hence, ${v_p} = \dfrac{{2\pi v}}{\lambda }\sqrt {{A^2} - {x^2}} $
The wave velocity $v = 10cm/s = 0.1m/s$
Wavelength $\lambda = 0.5m$
$\therefore {v_p} = \dfrac{{2\pi \times 0.1}}{{0.5}}\sqrt {{{(0.1)}^2} - {{(0.05)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{2}{5}\pi \sqrt {(0.01) - (0.0025)} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{2}{5}\pi \sqrt {0.0075} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}$
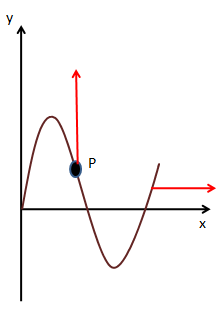
Since the direction of the point $P$ is towards the positive $y$- axis, the velocity can be written as a vector form i.e
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}\widehat j$
The unit vector $\widehat j$ is along the $y$- axis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: If we fix a string in two rigid supports it will stay in equilibrium position along the straight line. Now if the string is plucked and left, it vibrates towards the two sides of the equilibrium. No if we consider a point on the string, it will vibrate towards up and down directions periodically.
For the above problem the string is vibrated towards the two sides of the equilibrium position i.e. towards positive x-direction. And so the point $P$ on it vibrates onwards the upward direction.
Write the angular frequency in terms of the wave velocity and wavelength.
Find the velocity of the point using the given wavelength, the wave velocity, the amplitude, and the displacement.
Formula used:
The velocity of the point $P$ , ${v_p} = \omega \sqrt {{A^2} - {x^2}} $
$A = $ Amplitude and $x = $ the displacement
The angular frequency, $\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi v}}{\lambda }$
$v = $ The wave velocity and $\lambda = $ wavelength.
Complete step by step answer:
The figure shown below describes the motion of sinusoidal waves along a string. We have to find the velocity and direction of the point on the string.

The sinusoidal wave is moving with a speed $v$ along a string in the positive $x$ - direction.
Let, the point $P$ moves with a speed ${v_P}$ which can be written as,
${v_p} = \omega \sqrt {{A^2} - {x^2}} $
Amplitude $A = 10cm = 0.1m$
The displacement $x = 5cm = 0.05m$
The angular frequency, $\omega = \dfrac{{2\pi v}}{\lambda }$
Hence, ${v_p} = \dfrac{{2\pi v}}{\lambda }\sqrt {{A^2} - {x^2}} $
The wave velocity $v = 10cm/s = 0.1m/s$
Wavelength $\lambda = 0.5m$
$\therefore {v_p} = \dfrac{{2\pi \times 0.1}}{{0.5}}\sqrt {{{(0.1)}^2} - {{(0.05)}^2}} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{2}{5}\pi \sqrt {(0.01) - (0.0025)} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{2}{5}\pi \sqrt {0.0075} $
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}$
Since the direction of the point $P$ is towards the positive $y$- axis, the velocity can be written as a vector form i.e
$ \Rightarrow {v_p} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 \pi }}{{50}}\widehat j$
The unit vector $\widehat j$ is along the $y$- axis.
Hence, the correct answer is option (A).
Note: If we fix a string in two rigid supports it will stay in equilibrium position along the straight line. Now if the string is plucked and left, it vibrates towards the two sides of the equilibrium. No if we consider a point on the string, it will vibrate towards up and down directions periodically.
For the above problem the string is vibrated towards the two sides of the equilibrium position i.e. towards positive x-direction. And so the point $P$ on it vibrates onwards the upward direction.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




