
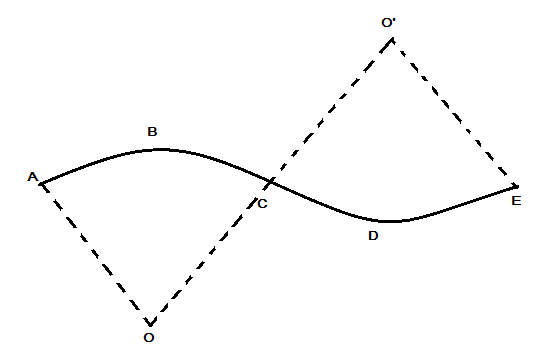
A track consists of two circular paths ABC and CDE of equal radius $ 100m $ and joined smoothly, as shown in figure. Each part subtends a right angle at its center. A cycle weighing $ 100kg $ together with the rider travels at a constant speed of $ 18km{h^{ - 1}} $ on the track.
A) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at B and at D.
B) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at B, C and D.
C) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C.
D) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with the constant speed? (take $ g = 10m{s^{ - 2}} $ )

Answer
533.4k+ views
Hint :Here, the two circular tracks are given and the cyclist is riding a cycle over this track that means the cycle is in contact with the surface of the circular track. Hence, we have to resolve the forces acting on the cycle and find the required answers. Resolution of all the forces must show in the figure.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider the figure given in the question and also resolve the forces acting on the cycle following the track given in figure from A to E.
The forces acting on the cycle are Normal $ N $ acting from the center of the circle in upward direction, centrifugal force $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $ , $ mg $ weight of the cycle.
Given data: Radius of curves $ = R = 100m $
Weight of the cycle $ = 100kg $
Velocity of the cycle $ = 18km{h^{ - 1}} $
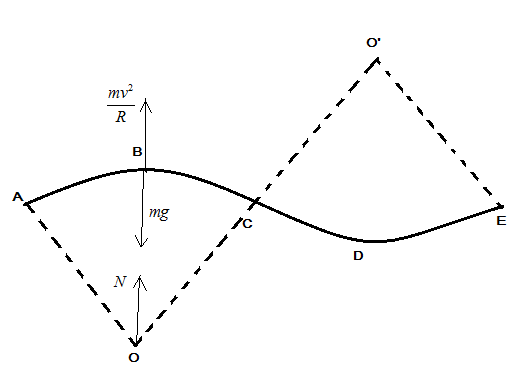
At point B
Net force is given by
$ N = mg - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = 100 \times 10 - \dfrac{{100 \times 25}}{{100}} $ …. (putting all the values from given data)
$ \Rightarrow N = 975N $
Now at point D, net force acting on cycle is given by
$ \Rightarrow N = mg + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = 1025N $
Here, we have to find the frictional force acting at point B, C and D
But, at B and D the cycle possesses no tendency to slide thus the friction here is zero.
So, at point C, frictional force is given by
$ mg\sin \theta = F $
$ \Rightarrow F = 1000 \times \sin 45 = 1000 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = 707.2N $ …… ( $ \sqrt 2 = 1.414 $ )
Here, the question asks about the normal force before point C and after point C is:
Before C, net force is given by
$ mg\cos \theta - N = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = mg\cos \theta - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} = 707.2 - 25 = 683.2N $
After C, net force is given by
$ N - mg\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} + mg\cos \theta = 25 + 707.2 = 732.2N $
To calculate the minimum desired coefficient of friction, we have to consider a point just before C, where N is minimum.
Therefore, $ \mu N = mg\sin \theta $ ……( $ \mu $ is friction coefficient )
$ \Rightarrow \mu \times 683.2 = 100 \times 10 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} $
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{707.2}}{{683.2}} = 1.037 $
Hence, we have calculated all the terms and find out all the answers as above.
Note :
Here, we have to carefully understand the question and look out for the forces that we have resolved their correct addition and subtraction is to be looked out, the forces are acting in same direction are always added and those which are in opposite direction are always subtracted ,but sometimes it can be equated depending on the question asked.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Let us consider the figure given in the question and also resolve the forces acting on the cycle following the track given in figure from A to E.
The forces acting on the cycle are Normal $ N $ acting from the center of the circle in upward direction, centrifugal force $ \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $ , $ mg $ weight of the cycle.
Given data: Radius of curves $ = R = 100m $
Weight of the cycle $ = 100kg $
Velocity of the cycle $ = 18km{h^{ - 1}} $

At point B
Net force is given by
$ N = mg - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = 100 \times 10 - \dfrac{{100 \times 25}}{{100}} $ …. (putting all the values from given data)
$ \Rightarrow N = 975N $
Now at point D, net force acting on cycle is given by
$ \Rightarrow N = mg + \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = 1025N $
Here, we have to find the frictional force acting at point B, C and D
But, at B and D the cycle possesses no tendency to slide thus the friction here is zero.
So, at point C, frictional force is given by
$ mg\sin \theta = F $
$ \Rightarrow F = 1000 \times \sin 45 = 1000 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} = 707.2N $ …… ( $ \sqrt 2 = 1.414 $ )
Here, the question asks about the normal force before point C and after point C is:
Before C, net force is given by
$ mg\cos \theta - N = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = mg\cos \theta - \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} = 707.2 - 25 = 683.2N $
After C, net force is given by
$ N - mg\cos \theta = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} $
$ \Rightarrow N = \dfrac{{m{v^2}}}{R} + mg\cos \theta = 25 + 707.2 = 732.2N $
To calculate the minimum desired coefficient of friction, we have to consider a point just before C, where N is minimum.
Therefore, $ \mu N = mg\sin \theta $ ……( $ \mu $ is friction coefficient )
$ \Rightarrow \mu \times 683.2 = 100 \times 10 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} $
$ \Rightarrow \mu = \dfrac{{707.2}}{{683.2}} = 1.037 $
Hence, we have calculated all the terms and find out all the answers as above.
Note :
Here, we have to carefully understand the question and look out for the forces that we have resolved their correct addition and subtraction is to be looked out, the forces are acting in same direction are always added and those which are in opposite direction are always subtracted ,but sometimes it can be equated depending on the question asked.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




