
A tower of height 30 meters casts a shadow of length 40 meters at a certain instant. When the sun’s elevation increases by \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}\], the length of the shadow cast by the tower, in meters is:
(a) 20
(b) 25
(c) 30
(d) 45
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: Assume that the initial angle of inclination of the sun is $\theta $. Now, when the angle of the elevation of the sun is increased by \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}\] then the new angle of elevation becomes: $\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$. Assume the length of the shadow formed in this process as ‘x, here, ‘x’ will be smaller than 40 m. Draw the diagram of the given conditions and use the formula: $\tan \left( a+b \right)=\dfrac{\tan a+\tan b}{1-\tan a\tan b}$ to equate with $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$. By substituting all the given values, find the value of ‘x’.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume that the initial angle of inclination of the sun is $\theta $. When the angle of inclination of the sun increases by \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}\], the new angle of elevation becomes: $\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$. This will lead to a decrease in the length of shadow casted because, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$, so as $\theta $ increases, the value of base decreases. Assume that the length of shadow casted is ‘x’.
Let us draw that diagram of the given situations.
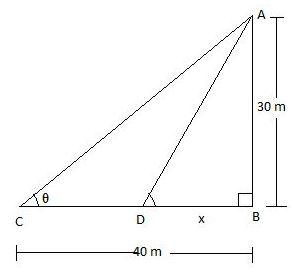
Clearly we can see that AB is the tower, $\angle ACB=\theta $ and BC is the length of the shadow when the angle of inclination is $\theta $. Also, $\angle ADB=\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$ and BD is the length of the shadow when the angle of inclination is $\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$.
Now, in right angle triangle ABC, we have,
$\angle ACB=\theta $, BC = 40 m and AB = 30 m. Therefore, using the relation: $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{30}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}.......................(i) \\
\end{align}$
Now, in right angle triangle ABD, we have,
$\angle ADB=\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$, BD = x and AB = 30 m. Therefore, using the relation: $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( \theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{BD} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \left( \theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
\end{align}$
Using the identity: $\tan \left( a+b \right)=\dfrac{\tan a+\tan b}{1-\tan a\tan b}$, we have,
$\tan \left( \theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)=\dfrac{\tan \theta +\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)}{1-\tan \theta \tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x}$
Therefore, substituting the value of $\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$ from equation (i) and using the identity: $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right)=x$, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{7} \right)}{\left( 1-\dfrac{3}{4}\times \dfrac{1}{7} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{21+4}{28} \right)}{\left( 1-\dfrac{3}{28} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{25}{28} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{28-3}{28} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{25}{28} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{25}{28} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow x=30 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the length of the shadow is 30 m. Hence, option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to draw a rough diagram of the given conditions because it will be helpful for us to solve the question. Now, the reason that the length of the shadow decreases when the angle of inclination increases is that: $\tan \theta $ is inversely proportional to the length of the base of the triangle, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$. Therefore, as $\theta $ increases, the value of $\tan \theta $ increases and hence, length of the base decreases.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume that the initial angle of inclination of the sun is $\theta $. When the angle of inclination of the sun increases by \[{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}\], the new angle of elevation becomes: $\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$. This will lead to a decrease in the length of shadow casted because, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$, so as $\theta $ increases, the value of base decreases. Assume that the length of shadow casted is ‘x’.
Let us draw that diagram of the given situations.

Clearly we can see that AB is the tower, $\angle ACB=\theta $ and BC is the length of the shadow when the angle of inclination is $\theta $. Also, $\angle ADB=\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$ and BD is the length of the shadow when the angle of inclination is $\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$.
Now, in right angle triangle ABC, we have,
$\angle ACB=\theta $, BC = 40 m and AB = 30 m. Therefore, using the relation: $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \theta =\dfrac{AB}{BC} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{30}{40} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}.......................(i) \\
\end{align}$
Now, in right angle triangle ABD, we have,
$\angle ADB=\theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7}$, BD = x and AB = 30 m. Therefore, using the relation: $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$, we get,
$\begin{align}
& \tan \left( \theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)=\dfrac{AB}{BD} \\
& \Rightarrow \tan \left( \theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
\end{align}$
Using the identity: $\tan \left( a+b \right)=\dfrac{\tan a+\tan b}{1-\tan a\tan b}$, we have,
$\tan \left( \theta +{{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)=\dfrac{\tan \theta +\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)}{1-\tan \theta \tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}\dfrac{1}{7} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x}$
Therefore, substituting the value of $\tan \theta =\dfrac{3}{4}$ from equation (i) and using the identity: $\tan \left( {{\tan }^{-1}}x \right)=x$, we have,
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{7} \right)}{\left( 1-\dfrac{3}{4}\times \dfrac{1}{7} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{21+4}{28} \right)}{\left( 1-\dfrac{3}{28} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{25}{28} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{28-3}{28} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{\left( \dfrac{25}{28} \right)}{\left( \dfrac{25}{28} \right)}=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow 1=\dfrac{30}{x} \\
& \Rightarrow x=30 \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the length of the shadow is 30 m. Hence, option (c) is the correct answer.
Note: It is important to draw a rough diagram of the given conditions because it will be helpful for us to solve the question. Now, the reason that the length of the shadow decreases when the angle of inclination increases is that: $\tan \theta $ is inversely proportional to the length of the base of the triangle, $\tan \theta =\dfrac{\text{Perpendicular}}{\text{Base}}$. Therefore, as $\theta $ increases, the value of $\tan \theta $ increases and hence, length of the base decreases.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




